Sense note pack
advertisement

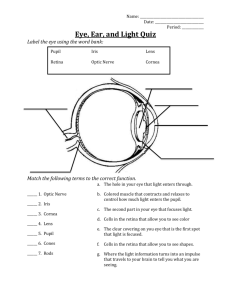
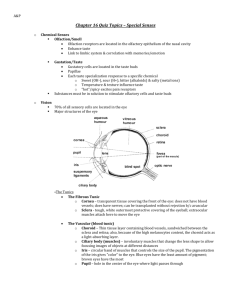
Notes on Ch. 14 - Senses Week 12 notes Unit Outcomes Explain other ways that humans sense their environment and their spatial orientation in it › olfactory receptors, proprioceptors, taste receptors, receptors in the skin Describe the structure and function of the parts of the human eye › cornea, lens, sclera, choroid, retina, rods and cones, fovea centralis, pupil, iris, and optic nerve Describe the structure and function of the parts of the human ear › pinna, auditory canal, tympanum, ossicles, cochlea, organ of Corti, auditory nerve, semicircular canals, and Eustachian tube Receptors Table 1 pg 446 Figure 2 pg 447 Taste Taste receptors are concentrated in _______________________ on our tongues Specific chemicals stimulate receptors › 5 types: ________, _______, _______, _________ and __________ each cell (each taste bud)can detect all tastes, but is particularly responsive to a certain type/chemical 1 Notes on Ch. 14 - Senses Eye Structure Has 3 separate layers › _______________ › _______________________________ › _______________ Sclera This is the white of your eye It is the ____________________ layer and its function is to ______________ and maintain the ___________ of the eye 2 Notes on Ch. 14 - Senses It includes the ___________ and _____________________________ Cornea Front portion of _______________ Clear Strongly curved Starts to __________________ light Aqueous Humour _____________ Supplies nutrients to cornea Fills _____________ (anterior) eye cavity Choroid Layer This is the _____________________ layer of your eye It contains the _____________________ for the retina It includes the __________, ___________, __________, ____________________, and ___________________________________ Iris and Pupil Iris is the ________________ part that makes up the front of choroid layer It contains muscles to change _________ diameter › Circular muscles close pupil › Radial muscles open pupil The ________ is just a hole in the iris that light comes through 3 Notes on Ch. 14 - Senses Ciliary Muscles (Body) Smooth muscle that changes _________________________ Attaches to ligaments which are connected to lens Muscle contraction changes shape of lens Secretes aqueous humour Lens _______________ light on retina Controlled by muscles of ciliary body Lens _________ for distant objects › Image is ______________ when light passes through Image is projected on retina upside-down. The changing __________ of the lens will focus the image on the retina Vitreous Humour __________, jelly-like material Maintains the ___________ of the eyeball Helps ___________ ___________ onto the retina 4 Notes on Ch. 14 - Senses Retina This is the __________________ layer of your eye It contains ___________________ and has 4 different layers of cells › Pigmented epithelium › Light-sensitive cells (__________________ ____________________) › Bipolar cells › Cell of the ___________________ _____________________ Light-sensitive cells (sensory receptors) › _________ which are cells for low-intensity light › _________ which are cells for high-intensity light and identify _________ › Cones are concentrated in the __________ ____________ located at the back of the eye › Rods are located around the ________________ of the fovea. › There are no receptors (rods and cones) where the optic nerve and retina join ___________ _________ Pathway of Light Light __________ the retina through the pigmented epithelium, which helps focus the light onto the _______ and ________. The signal is then sent through the ______________ cells to the cells of the ____________ __________ which transmit the message to the brain. 5 Notes on Ch. 14 - Senses Chemistry of Vision Rods contain _________________, a light senstive pigment › Light hits the rhodopsin and causes an _________ ___________ in the rod. › Neurotransmitters communicate this stimulus (AP) to the bipolar cells and then to the optic neurons › Rhodopsin is sensitive to light and breaks down in high light intensity, so it works best in _________ light intensity situations › Negatively affected by Vitamin A deficiency. Cones have a less sensitive pigment, so they work better in _________ intensity situations, allowing you to see __________. Each cone is sensitive to one of the three primary colours of source light › Red › Blue › Green Combinations of cones being stimulated by different wavelengths allows you to perceive different colours 6 Notes on Ch. 14 - Senses Colour Blindness This happens when one or more types of cones are _______________ The most common type is red-green colourblindness where the red sensitive cones are defective Afterimages __________ = you can see the shape of a camera’s flash after you close your eyes. › Image has been “burned” onto your retina ___________ = color reversal › caused by fatigue of cones responsible for particular colors, while others continue to fire Accommodation Normal focusing of light › __________ bends light to _________: light slows down as it travels through the cornea (dense material) = refraction of light inward toward lens. Lens is thicker in middle than edges, so light bends to a focal point (center of _____________) Viewing close up › ciliary muscle __________ and lens becomes ___________ = additional bending of light. Pupil constricts to focus the image (light is focused more onto the fovea centralis) Viewing farther away › ______________ of ciliary muscle causes lens to _________ out. Pupil dilates to let in more light As you age: layers of protein cover the lens, hardening it so it is less flexible; more difficulty accommodating for close up (reading). 7 Notes on Ch. 14 - Senses Vision Defects Near-Sightedness (________________) › Eyeball is __________ ____________ › Rays from distant objects focus in front of the ____________ › Myopia can be corrected using a concave lens. Far-Sightedness (_________________________________) › Eyeball is _________ ______________ › Rays from near objects focus ____________ the retina › Hypermetropia can be corrected with a convex lens Glaucoma › Buildup of ___________ humour › Increases _______________ in the eye which causes retinal ganglion cells (nerve cells) to die › Results in loss of vision Cataracts › __________ becomes opaque (can’t see through it) › Light can’t pass through › Can remove the lens and wear strong prescription glasses Astigmatism › Lens or cornea is irregularly ______________ › Light doesn’t ______________ on back center of retina (fovea centralis) 8 Notes on Ch. 14 - Senses Ear Structure The ear is made up of three main structures › _________ Ear ____________ sound waves Transfers sound waves to middle ear › _________ Ear ____________ sound waves Transfers sound waves to inner ear › _________ Ear Turns ________________ ____________ (from sound waves) into ______________ ____________ which are sent to the brain through the auditory nerve 9 Notes on Ch. 14 - Senses Outer Ear The outer ear consists of the __________ and the ___________ _________ __________ › External ear flap › Collects sound ___________ ___________ › Carries sound to the eardrum › Has sweat glands that produce ear wax Tympanic membrane (____ _______) › Thin tissue layer that receives sound vibrations › Sends the vibrations from the sound waves into the middle ear Middle Ear The middle ear consists of the ___________ and _________________ _______ Ossicles › Consists of three small bones that amplify and carry sound from tympanic membrane to the oval window of the cochlea _________ (hammer) _________ (anvil) _________ (stirrup) Sound vibrations transfer from the ________________ _____________ to the malleus, which then hits the incus which hits the stapes which vibrates against the membrane covering the ________ ___________ of the cochlea 10 Notes on Ch. 14 - Senses Sound is ________________ by concentrating the sound energy from the tympanic membrane to the smaller oval window ______________ tube › Does not help with hearing › It is an air-filled tube that equalizes _______________ between the external and internal ear › Where your ears “pop” Inner Ear The inner ear consists of the ______________, _________________ _______ and the cochlea Vestibule (for __________) › Involved in ___________ equilibrium/head positiion Semicircular canals (for ___________) › Involved in _______________ equilibrium/body movement Cochlea (_________________) › Coiled structure that turns sound waves into __________ ___________ › Contains the __________________________________ Has sound receptors where waves become impulses Hair cells attached to ________________ _________________ 11 Notes on Ch. 14 - Senses Cochlea Movement of __________ in the cochlea causes the basilar membrane to vibrate › Different pitches of notes make different areas of membrane vibrate Small hairs (______________) are attached to the basilar membrane The hairs rub and bend against the ________________ membrane The bending generates a sensory nerve impulse that is sent to the ___________ 12 Notes on Ch. 14 - Senses Hearing Summary Sound _________ push against _______________ membrane; these vibrations are passed onto the _____________ (malleus then incus and finally stapes). The ossicles concentrate and ____________ the _______________ (exerting greater force by concentrating the energy in a very small area). ________ _____________ receives vibrations from stapes which causes the oval window to move in and out. This results in the round window (below it) to also move in and out (in alternation with oval window). The two windows moving in and out cause fluid to move in the inner ear. The cochlea receives __________ ____________ and converts them into _______________ impulses. ___________ waves move the basilar membrane, the hairs on the membrane brush against tectorial membrane and bend. This stimulates _________________ __________ in the basilar membrane to send impulses to auditory nerve then to brain. Ear Safety Small muscles in your ears help protect your hearing When loud noises are around: › Muscles attached to the malleus (hammer) contract and restrict intense movements › A second muscle contracts, pulling the stapes (stirrup) away from the oval window, limiting inner ear damage This doesn’t work for sudden loud noises 13 Notes on Ch. 14 - Senses Hearing Loss ________________________ Hearing Loss › Sound waves can’t enter ___________ _______ › caused by wax buildup, middle ear infection, or punctured eardrum › Fixed by medical/surgical procedures ________________ Hearing Loss › ___________ _________ is severed or damaged or hair cells of the cochlea are damaged or dead. › caused by aging, loud noises, head trauma or genetic conditions Hearing Aids › pick up sound (microphone), amplify it and transmit it to eardrum › won’t work for Sensorineural hearing loss (vibrations can’t be transmitted to brain) Cochlear Implants › does not make sounds louder or clearer › bypasses damaged parts and converts sounds into electrical impulses that are sent to the brain. › has a microphone (picks up sounds), a speech processor (selects and arranges sounds), a transmitter and receiver/stimulator receive signals from the speech processor and convert into electrical impulses. Electrodes send them to the auditory nerves. * Doesn’t replicate exact sounds (like we hear them), provides sounds that allow person to interpret their environment. Over time, person learns to decipher impulses and can understand speech.* 14 Notes on Ch. 14 - Senses Equilibrium and Balance _____________ equilibrium (Am I upside down) › Movement along one plane (vertical or horizontal) › Detected by the _______________ › Involves two other structures ___________ ___________ › Fluid filled › Contains tiny ___________ (cilia) When the head is upright: calcium carbonate crystals in the fluid (___________) don’t move = fluid doesn’t move = cilia don’t move When the head is bent forward: the otoliths shift _____________, pulling on the fluid. This causes the _______ to bend which _______________ the nerve cell. Sends a nerve __________ to brain (cerebellum) informing of head position relative to gravity _____________ Equilibrium (Moving forwards or backwards, spinning, flipping around) Detected by the _______________________ ______________ › Has 3 different fluid filled rings Vertical Horizontal Diagonal 15 Notes on Ch. 14 - Senses Each canal has an ampulla (pocket) that holds a cupula When you move, __________ in the semicircular canals moves, bending ________ (that are on hair cells found in the cupula). › Results in nerve signals sent to __________. Rapid, continuous movement of the fluids causes motion sickness ****Table 1, pg 461**** Formative Week 12 Do the following questions for practice Pg 448 #1,3 Pg 455 #1,4 Pg 458 #2 Pg 466 #1-14, 20-23 Send me pg 448 #1,3; pg 466 #1,4,7,10 16