Precalculus Name: Notes on the Binomial Theorem 10/4/13 I
advertisement
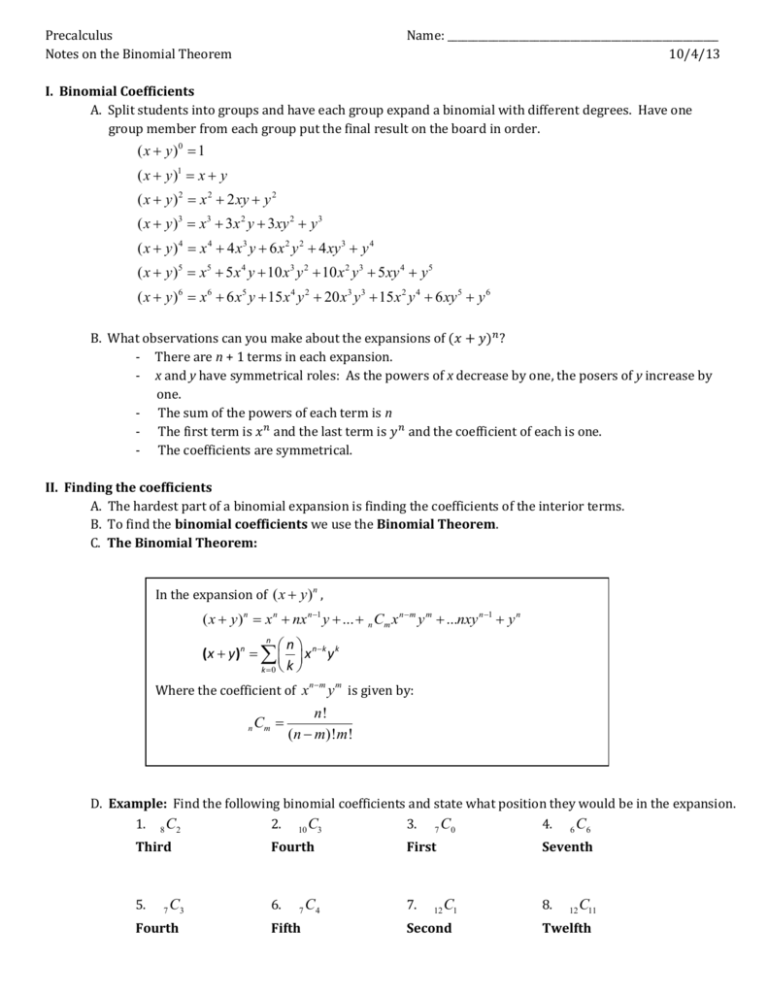
Precalculus Notes on the Binomial Theorem Name: _____________________________________________________ 10/4/13 I. Binomial Coefficients A. Split students into groups and have each group expand a binomial with different degrees. Have one group member from each group put the final result on the board in order. ( x y )0 1 ( x y )1 x y ( x y ) 2 x 2 2 xy y 2 ( x y )3 x 3 3 x 2 y 3xy 2 y 3 ( x y ) 4 x 4 4 x 3 y 6 x 2 y 2 4 xy 3 y 4 ( x y )5 x5 5 x 4 y 10 x3 y 2 10 x 2 y 3 5 xy 4 y 5 ( x y )6 x 6 6 x 5 y 15 x 4 y 2 20 x 3 y 3 15 x 2 y 4 6 xy 5 y 6 B. What observations can you make about the expansions of (𝑥 + 𝑦)𝑛 ? - There are n + 1 terms in each expansion. - x and y have symmetrical roles: As the powers of x decrease by one, the posers of y increase by one. - The sum of the powers of each term is n - The first term is 𝑥 𝑛 and the last term is 𝑦 𝑛 and the coefficient of each is one. - The coefficients are symmetrical. II. Finding the coefficients A. The hardest part of a binomial expansion is finding the coefficients of the interior terms. B. To find the binomial coefficients we use the Binomial Theorem. C. The Binomial Theorem: In the expansion of ( x y)n , ( x y ) n x n nx n 1 y ... n Cm x n m y m ...nxy n 1 y n n n ( x y )n x nk y k k 0 k Where the coefficient of x nm y m is given by: n Cm n! (n m)!m ! D. Example: Find the following binomial coefficients and state what position they would be in the expansion. 1. 8 C2 2. 10 C3 3. 7 C0 4. 6 C6 Third Fourth First 5. 6. 7. 7 C3 Fourth 7 Fifth C4 12 Seventh C1 Second 8. 12 C11 Twelfth III. Pascal’s Triangle A. Every row has the number 1 at the beginning and end. B. Each number is obtained by adding the two numbers immediately above it. C. These numbers are the coefficients of the binomial expansions. D. The nth row gives the coefficients of ( x y)n . E. Use Pascal’s Triangle to find the coefficients of ( x y )8 1, 8, 28, 56, 70, 56, 28, 8, 1 IV. Binomial Expansions A. Write the expansion of ( x 1)3 : ( x 1)3 x3 3x 2 (1) 3x(1)2 1(1)3 ( x 1)3 x3 3x 2 3x 1 B. Write the expansion of ( x 2) 4 : ( x 2)4 x 4 4 x3 (2) 6 x 2 (2) 2 4 x(2)3 (2) 4 ( x 2)4 x 4 8 x3 24 x 2 32 x 16 C. Write the expansion of (9 2 x)5 : (9 2 x)5 (9)5 5(9)4 (2 y) 10(9)3 (2 y) 2 10(9) 2 (2 y)3 5(9)(2 y) 4 (2 y)5 (9 2 y)5 59,049 65,610 y 29,160 y 2 6, 480 y 3 720 y 4 32 y 5 V. Finding a specific term in a Binomial Expansion A. Find the sixth term in the expansion of (3a 2b)12 : - Let 𝑥 = 3𝑎 𝑎𝑛𝑑 𝑦 = 2𝑏 and in the sixth term the exponents would be: 𝑥 7 𝑦 5 - To find the coefficient given by Pascal’s triangle, recall that we can use the Binomial Theorem: - n Cm 12 C5 12! 792 7!5! - Therefore, the sixth term of the expansion is: 12 C5 x 7 y 5 792(3a)7 (2b)5 55, 427,328a 7b5 B. Find the coefficient of the given term in the expansion of the binomial: Binomial: ( x 3)9 Term: ax 6 This is the fourth term of the expansion so, use: n Cm x n m y m 9 C3 x 6 (3)3 84 x 6 (27) 2268 x 6 Binomial: (2 x y)14 Term: ax9 y 5 This is the sixth term in the expansion, so use: n Cm x n m y m 14 C5 (2 x)9 y 5 2002(512) x 9 y 5 1, 025, 024 x 9 y 5