Physics 8
advertisement

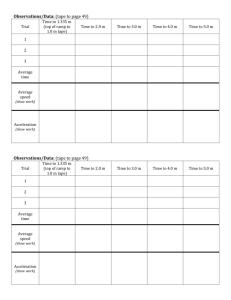
Physics 8 Name ________________________________ Chapter 11.2 Lab Start Date ________________ Period ______ Due Date _________________ Speed of Marble – Two Positions Introduction: This activity is designed to help with equation skills, graph development, graph interpretation, and applying learned information to future situations. You will be rolling a marble down an inclined plane (ramp). You will measure and record time (seconds) at the 50 cm mark and at the 100 cm mark. Speed can then be calculated because you know distance and time for each position. Use your own wording for the written answers. Equation: v= (df – di) / (tf – ti) v = d/t Equipment: one textbook marble Question: v df di ti tf = speed or velocity = distance final position : (50cm or 100cm for this lab) = distance initial : (0cm for this lab) = time initial : (0 seconds for this lab) = time final position stopwatch timer pencil or pen calculator inclined plane (with length marked) How will the speed of the marble at the 50cm mark compare to the speed of the marble at the 100cm mark? Hypothesis: _______________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________________________ Set-up Diagram: 0 cm mark 50 cm mark marble 100 cm mark textbook Inclined Plane stopwatch timer Procedure: 1. Locate a table, clear of obstructions (binders, purses, water bottles, etc.) 2. Review safety procedures with today’s materials. 3. Gather materials. 4. Setup the textbook and inclined plane as shown in the setup diagram. 5. Locate the 50cm mark on the inclined plane. Place a pen or pencil on the table at the 50cm mark so as the marble rolls, you can see when to stop the timer. 6. Place the marble at the top of the inclined plane at zero distance (0cm). Data Gathering: 7. Find the time necessary for the marble to roll from 0cm to the 50cm mark [to the nearest 1/100ths of a second (.01s)]. Record the time as Trial #1 on the data table titled “Marble Rolling Data Table.” 8. Repeat steps 6 and 7 for two other trials for a total of three trials at the 50cm mark. 9. Repeat steps 6 and 7 for a total of three trials for time at the 100cm mark. 10. Calculate the average of the three trials for the 50cm mark and the 100cm mark to the nearest .01 second. Show the 2(average time of 50cm, 100cm) “average time” ESA’s below. Record on the “Marble Rolling Data Table.” Marble Roll Data Table Final Distance (df) From Start (cm) Time Trial #1 (s) Time Trial #2 (s) Time Trial #3 (s) tf Average Time (s) Speed (cm/s) 0 0 0 0 0 0 50 100 Workspace to calculate average time: average time = Trial #1+ Trial #2+ Trial #3 3 Equation Skills: 11. Calculate the speed of the marble at the 50cm mark and 100cm mark to the nearest .01 cm/second. Write the ESA’s for each distance on the “Speed Calculations Table.” Be sure to have units for EVERY number! ( Ex. 2.10 sec) di = ocm Speed Calculations Table Equation Substitution (units) Answer (units) Speed at the 50cm mark Speed at the 100cm mark 12. Record the speed values for the 50cm mark and 100 cm mark into the “Marble Roll Data Table.” Graph Development: 13. The horizontal axis is called the “x” axis or the independent axis. Label the independent axis “time in seconds”. Set-up your time axis from 0s to 4s. 14. The vertical axis is called the “y” axis or the dependent axis. Label the dependent axis “distance in centimeters”. Set-up your distance axis from 0m to 100m. Notice that you spread out your values (make your highest value near the end of the axis). 15. Plot the 3 points of data on the graph. Start with 0cm, 0s. Look on your Marble Roll Data Table. 16. Connect the three points with a curved line. This line represents the graphical relationship of distance with time, for the rolling marble. In other words, the slope of the line represents speed of the marble. 17. Notice the curved line representing speed of the marble with time. 18. Return all materials to the appropriate area. Conclusion Questions: These questions will help you to see, interpret, and draw conclusions from your data measurements. 1. Was your hypothesis correct? Explain by using your speed ESA’s. _____________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________ Graph Interpretation: 2. Plot these values on your “Time-Distance Graph:” (0s, 0cm), (1s, 25cm), (3s, 75cm), (4s, 100cm). Label line “Steady Speed of 25cm/s.” 3. Describe how the graph displayed the change in speed of the marble for the first 3 seconds. Include data from the Speed Calculations Table. _____________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________ Title: Time – Distance Graph of a marble