World Geography Study Guide/Notes
advertisement

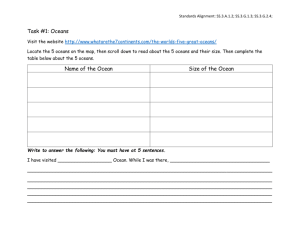
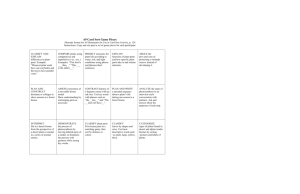
AVA Heading: Unit 1: World Geography Directions: Please fill out the following notes and warm-ups during class. At the end of the unit, during your test, your teacher will grade this packet. If you have any questions filling out this packet, please ask your teacher when appropriate. Thank you! Day 1: Warm-up 1. What is the procedure for going to the restroom? 2. What are the procedures for sharpening your pencil? 3. What are the procedures when you finish early? 4. What is the procedure when Mr. Yanaitis is gone? Lesson Objective: - Students will learn the 5 themes of geography. The Five Themes of Geography: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Location: Where are we? - Absolute _____________. A ______________ and longitude or a street address. 1 - Relative ______________. Described by landmarks, time, direction or ________________. From one place to another. Activity: On your own, please write the correct answer below (either absolute location or relative location). ________________1. 2131 Low Meadow Blvd. Castle Rock, CO 80109 ________________2. Turn left on to Praire Hawk then go straight through Meadows Parkway. Then turn right for the hospital. ________________3. 39.7439°N, 105.0200°W Place: What is it like there, what kind of place is it? Human Characteristics: What are the main _______________, customs, and beliefs. How many people _____________, work, and visit a place. Physical Characteristics: _________________ (mountains, rivers, etc.), climate, vegetation, wildlife, soil, etc. Human-Environmental Interaction: How do humans and the environment _______________ each other - We ____________ on it. We _______________ it. We _____________ to it. Movement: How are people, goods, ideas moved from place to place? -Human _______________. Trucks, Trains, Planes. - ______________ Movement: Phones, computer (email), mail - ______________ Movement: TV, Radio, Magazines 2 Regions: How are regions similar to and different from other places? Formal Regions: Regions defined by ________________ or administrative boundaries (States, Countries, Cities) Functional Regions: Regions defined by a ______________ (newspaper service area, cell phone coverage area). Vernacular Regions: ____________ defined by people’s perception (middle east, the south) Day 2: Warm-Up 1. How many types of maps are there? 2. List the type of maps that you have seen. 3. Why would you need to know how to read a map? 4. Do you know how to read a map? Lesson Objective: - Students will learn how to read various types of maps. - Students will demonstrate their ability to locate a position on the map based on its coordinates. IN PENCIL! Label the seven continents Label the five oceans Label the Equator Label the Prime Meridian 3 Symbols on a Map: The _____________________ tells us direction. The ______________________ is used to measure the distance. The _________ ___________ shows us what the symbol means. Political Map: - Shows boundaries that divide regions, _____________, states, _____________, ect. Climate Map: - Shows general information about precipitation like ____________ and ____________ of a region. - Does latitude, terrain, and altitude affect climate location? YES or NO (Circle one) 4 Distribution Map: - Shows the distribution of Gross Domestic Product or ____________. GDP measures the final __________ and ____________ produced in a country. Summary: - Name the seven continents. - Name the five oceans - What purpose does the equator serve? - What labels might you find on a map? 5 Day 3: Warm-up 1. List at least 2 different types of maps. 2. What does a political map tell us? 3. What is the largest continent in the world? 4. Name the 3 of the 5 oceans. Lesson Objectives: - Students will locate and label on a map the major oceans and continents. Continents and Oceans: - The surface of the ____________ is made up of land and water. The large bodies of land are called ________________. The continents are separated by _________________ Africa: Has the largest ________________, the Sahara. Contains the longest __________, the ____________, which flows north. Africa is the second largest ________________. Antarctica: Is the _________________ largest continent on Earth. The only people that live here are Scientists (Mrs. Bisbee’s husband!) the ____________________ Ocean surrounds all sides of the continent. Is covered mostly by _________. Has the _______________ and windiest climate on the planet. 6 Asia: Is the ________________ continent, about 30% of the land on Earth. Has the ________________ population of all the continents. Contains 44 countries. Borders Europe and Europe and Africa on the West. Borders the ______________ Ocean on the East and the _______________ Ocean on the South. Australia: -Is the ________ continent, about 5% of the land mass. Has the smallest population. Is made up of a ________ country, ____________. Europe: Is only bigger than __________________, takes up about 6% of the land mass. The ________________ Ocean is located to the West. The ____________________ Sea is located to the South. Do Now: Use your notes. 1. What are the largest and smallest continents? 2. Which continent has the most people living on it? 3. Which continents start with the letter A? 4. Which ocean is between China and the US? North America: - Is the ________ largest continent, about 16% of the land on earth. Contains 23 countries including _____________, Mexico & Central Mexico, & the United States of America. Both the __________ Ocean and ____________ Ocean border this continent. 7 South America: - Is the ___ largest continent, about 12% of the land mass. Contains _______ countries. Has some major natural landforms, the ______________ River, Andes Mountains, and the rainforest. Oceans: Cover __________ of the Earth’s surface. Contain ___________ of the Earth’s water supply. The ocean influence _____________ and _____________. _____________ distribute heat energy around the globe. Summary: Not using your notes, label the five oceans. Write a summary of what you learned today (3-5 complete sentences long) 8 Day 4: Warm-up 1. What % of the earth is covered by water? 2. Oceans are important because… (at least 2 reasons) 3. If I were an ocean current my job would be to… Lesson Objective: -Students will be able to label and draw imaginary lines Imaginary Lines: What are the 8 imaginary lines using the map? 1. 5. 2. 6. 3. 7. 4. 8. Equator: - _____________ degrees latitude. It divides the globe into ________________ and __________________ Hemispheres. Halfway between the _____________ and ___________ poles. Prime Meridian: - Prime Meridian _____________ the world into _______________ and ______________ Hemispheres. ____________ degrees longitude. The Earth’s time zones are measured from here. International Date Line is located along the _______________ line of longitude. Do now: How many time zones are there? 9 Hemispheres: - There are _______ hemispheres. List some countries located in each hemisphere. Northern Hemisphere: Southern Hemisphere: Eastern Hemisphere: Western Hemisphere: What is Latitude? - Like climbing a ______________. They run parallel with the _____________. Its reference point is the ______________. Lines are ______________to the Equator at regular intervals. Lines of Latitude are used to ______________. What is Longitude? - Runs parallel with the __________ _____________. Runs through _______________, England. Why are Latitude and Longitude important? - They help us ______________areas on the Earth through the use of __________________ and__________________. Please complete the worksheet on the following page. 10 11 Day 5: Warm-up 1. What are two imaginary lines that we learned other than latitude and longitude? 2. How many times zones are there in total? 3-4. Label the globe that has longitude lines and the globe that has latitude lines. 3.____________________ 4.___________________ 5. What makes a desert a desert? Lesson Objectives: - Students will be able to list the characteristics of a desert biome, rainforest biome, and an aquatic biome. What is a Biome? - A biome is a geographic area characterized by specific kinds of ___________ and _______________. Deserts, tropical rainforests, and aquatic are all types of ___________. What are the different types of biomes? (Write them below) 12 Desert Biome: Please answer the following questions below using the map in the power point. 1. What color is represented as desert? 2. What continents are mostly desert? Climate of a Desert Biome: - The desert is usually the ____________ biome on Earth. It has its extremes. It can be over ________ degrees during the day and below _______ degrees at night. Less than 25 cm of ________________ every year. Desert Characteristics: There can be hot, _________, dry, semi arid, and _____________ deserts. Plants in the deserts survive by conserving _________. Examples: Short shrubs, cacti. Animals tend to come out at dusk or at _________. Examples: Snakes, owls, lizards Oasis: - An oasis is where _____________ is almost always available. The water can ______________ people to settle and even grow crops in the desert. Rainforest: - Why is a rainforest called a rain forest? -An average of _______-_________ inches of rain falls yearly! - The average temperature is ______-_________ degrees Fahrenheit. Rainforests produce ______% of Earth’s oxygen!! Aquatic: -Two types: ____________ water and ___________ water. Fresh water includes __________, rivers, streams, ponds, wetlands. What are examples of salt water? (Answer below) 13 -Aquatic Biomes makes up of _________% of the Earth’s ________________. Aquatic Plants and Animals: Animals: Tuna, _____________, sea birds. Plants: Plankton, ____________ Aquatic Importance: Why do you think our waters are important? Summary: (Please answer on your own) - What are the three biomes we studied? - What makes a desert a desert? - What makes a rainforest a rainforest? 14