Webquest: Drugs, Alcohol, and the Teen Brain I. Type the following
advertisement
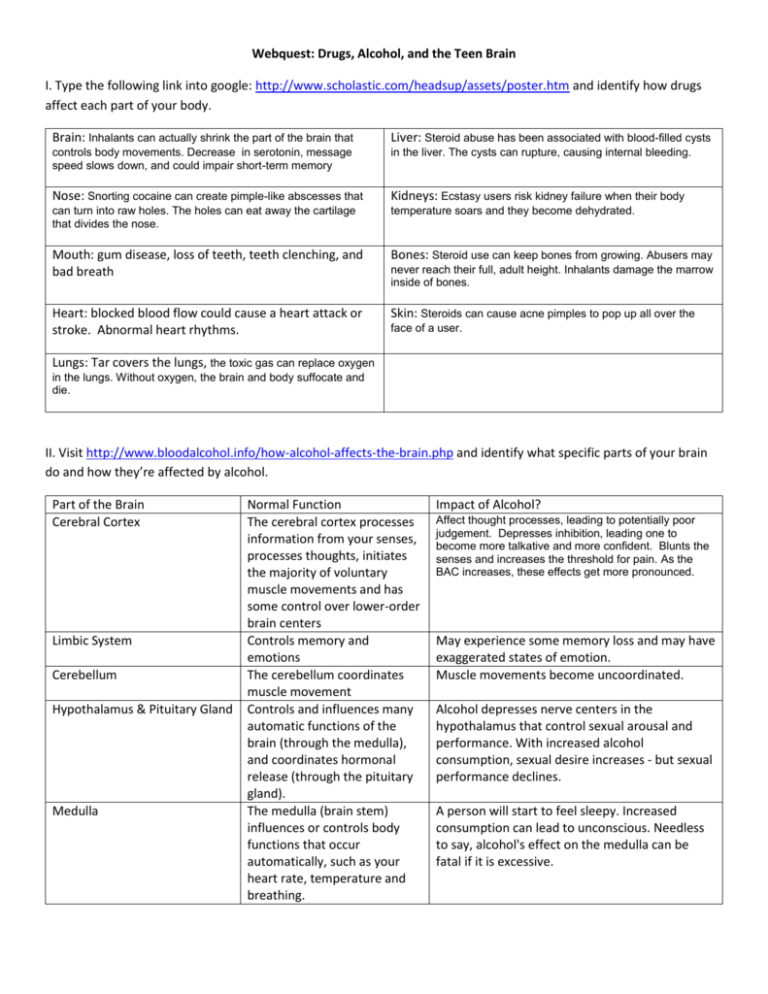
Webquest: Drugs, Alcohol, and the Teen Brain I. Type the following link into google: http://www.scholastic.com/headsup/assets/poster.htm and identify how drugs affect each part of your body. Brain: Inhalants can actually shrink the part of the brain that Liver: Steroid abuse has been associated with blood-filled cysts controls body movements. Decrease in serotonin, message speed slows down, and could impair short-term memory in the liver. The cysts can rupture, causing internal bleeding. Nose: Snorting cocaine can create pimple-like abscesses that Kidneys: Ecstasy users risk kidney failure when their body can turn into raw holes. The holes can eat away the cartilage that divides the nose. temperature soars and they become dehydrated. Mouth: gum disease, loss of teeth, teeth clenching, and bad breath Bones: Steroid use can keep bones from growing. Abusers may Heart: blocked blood flow could cause a heart attack or stroke. Abnormal heart rhythms. Skin: Steroids can cause acne pimples to pop up all over the never reach their full, adult height. Inhalants damage the marrow inside of bones. face of a user. Lungs: Tar covers the lungs, the toxic gas can replace oxygen in the lungs. Without oxygen, the brain and body suffocate and die. II. Visit http://www.bloodalcohol.info/how-alcohol-affects-the-brain.php and identify what specific parts of your brain do and how they’re affected by alcohol. Part of the Brain Cerebral Cortex Limbic System Cerebellum Hypothalamus & Pituitary Gland Medulla Normal Function The cerebral cortex processes information from your senses, processes thoughts, initiates the majority of voluntary muscle movements and has some control over lower-order brain centers Controls memory and emotions The cerebellum coordinates muscle movement Controls and influences many automatic functions of the brain (through the medulla), and coordinates hormonal release (through the pituitary gland). The medulla (brain stem) influences or controls body functions that occur automatically, such as your heart rate, temperature and breathing. Impact of Alcohol? Affect thought processes, leading to potentially poor judgement. Depresses inhibition, leading one to become more talkative and more confident. Blunts the senses and increases the threshold for pain. As the BAC increases, these effects get more pronounced. May experience some memory loss and may have exaggerated states of emotion. Muscle movements become uncoordinated. Alcohol depresses nerve centers in the hypothalamus that control sexual arousal and performance. With increased alcohol consumption, sexual desire increases - but sexual performance declines. A person will start to feel sleepy. Increased consumption can lead to unconscious. Needless to say, alcohol's effect on the medulla can be fatal if it is excessive. III. Type in the website: http://www.teenshealth.org/teen Click on Drugs and Alcohol and then click on Alcohol 1. What percentage of high school students have tried alcohol? 80% 2. Describe the process of fermentation. Fermentation is a process that uses yeast or bacteria to change the sugars in the food into alcohol. Fermentation is used to produce many necessary items — everything from cheese to medications. Alcohol has different forms and can be used as a cleaner, an antiseptic, or a sedative. 3. List some strategies to avoid drinking. Many different answers are possible here. Go back to the homepage of drugs and alcohol and click on drugs. Click on drugs what you should know. 4. How do drugs work? Drugs are chemicals or substances that change the way our bodies work. When you put them into your body (often by swallowing, inhaling, or injecting them), drugs find their way into your bloodstream and are transported to parts of your body, such as your brain. In the brain, drugs may either intensify or dull your senses, alter your sense of alertness, and sometimes decrease physical pain. 5. Describe the difference of a drug being helpful or harmful. A drug may be helpful or harmful. The effects of drugs can vary depending upon the kind of drug taken, how much is taken, how often it is used, how quickly it gets to the brain, and what other drugs, food, or substances are taken at the same time. Effects can also vary based on the differences in body size, shape, and chemistry. Although substances can feel good at first, they can ultimately do a lot of harm to the body and brain. Drinking alcohol, smoking tobacco, taking illegal drugs, and sniffing glue can all cause serious damage to the human body. Some drugs severely impair a person's ability to make healthy choices and decisions. IV. Alcohol affects teens differently than adults. Answer the following questions about the article “Alcohol a TwoEdged Sword for Teens.” Type the title of the article into google to get there. a. When compared to an adult brain, what two things hold true for adolescents and alcohol? The adolescent brain is more sensitive to the effects of alcohol on functions that serve memory and other mental activities. But it is less sensitive to the effects of alcohol on sedation - that is, alcohol makes adolescents less sleepy. b. What two problems can this cause for adolescents? First, since they're not as sleepy, they may consume more alcohol, resulting in greater mental impairment. Second, they may be more likely to engage in activities that put them at risk, such as driving a car. V. Visit http://pubs.niaaa.nih.gov/publications/arh27-2/186-196.htm to explore the effects of alcohol on memory by reading the report “What Happened? Alcohol, Memory Blackouts, and the Brain.” a. What is the difference between passing out and blacking out? Large amounts of alcohol, particularly if consumed rapidly, can produce partial (i.e., fragmentary) or complete (i.e., en bloc) blackouts, which are periods of memory loss for events that transpired while a person was drinking. b. Reflect on the potential consequences either activity could have for an adolescent your age. Many possible answers for this one as well. VI. Visit http://easyread.drugabuse.gov/drugs-of-abuse.php to explore factors relating to drug abuse and addiction. a. Click on What is Addiction? Why is drug addiction considered to be a brain disease? Addiction is a brain disease. Drugs change how the brain works. These brain changes can last for a long time. They can cause problems like mood swings, memory loss, even trouble thinking and making decisions. Addiction is a disease, just as diabetes and cancer are diseases. Addiction is not simply a weakness. People from all backgrounds, rich or poor, can get an addiction. Addiction can happen at any age, but it usually starts when a person is young . c. Click on Drugs that People Abuse. Why do people take drugs in the first place? People abuse drugs for many reasons: •They want to feel good. Taking a drug can feel really good for a short time. That's why people keep taking them—to have those good feelings again and again. But even though someone may take more and more of a drug, the good feelings don't last. Soon the person is taking the drug just to keep from feeling bad. •They want to stop feeling bad. Some people who feel very worried, afraid, or sad abuse drugs to try to stop feeling so awful. This doesn't really help their problems and can lead to addiction, which can make them feel much worse. •They want to do well in school or at work. Some people who want to get good grades, get a better job, or earn more money might think drugs will give them more energy, keep them awake, or make them think faster. But it usually doesn't work, may put their health at risk, and may lead to addiction. d. What are the 7 abused drugs? Marijuana, cocaine, heroin, painkillers, meth, alcohol, and cigarettes. e. Click on Prevent Drug Abuse. Scroll down and click on Help Children and Teens Stay Drug Free. Why is adolescence such a crucial time for preventing drug abuse? The teen years are the most likely time for someone to s tart taking drugs. And starting drug use as a teen can lead to drug problems when they grow up. VII. Type in the website: Truth. The Anti-Drug: Effects of Alcohol Intoxication:http://www.indiana.edu/~adic/effects.html Questions 1-3 will be under the “Specific Effects (related to the Blood Alcohol Concentration (BAC))” section of the page. 1. What are the effects of alcohol at the BAC level: 0.10-0.125? Significant impairment of motor coordination and loss of good judgement. Speech may be slurred; balance, vision, reaction time and hearing will be impaired. Euphoria. It is illegal to operate a motor vehicle at this level of intoxication. 2. What are the effects of alcohol at the BAC level: 0.25? Needs assistance in walking; total mental confusion. Dysphoria with nausea and some vomiting. 3. What are the effects of alcohol at the BAC level: 0.40 and up? Onset of coma, possible death due to respiratory arrest. Questions 4-5 will be under the “Effects of Alcohol Intoxication” at the top of the page. 4. What is the “general effect” of alcohol intoxication? Alcohol is a DOWNER that reduces activity in the central nervous system. The alcohol intoxicated person exhibits loose muscle tone, loss of fine motor coordination, and often has a staggering "drunken" gait. 5. What are the “visual signs” of alcohol intoxication? The eyes may appear somewhat "glossy" and pupils may be slow to respond to stimulus. At high doses pupils may become constricted VIII. Reflection – What is it that makes drug and alcohol use so appealing to teenagers? Is it the media, is it the fact that it’s illegal, is it boredom? Do you think drug and alcohol abuse is a problem in our school or local community? Why or why not? VIIII. Application- You are now a 30-40 year old parent of a teenager. How would you talk to your child about drugs and alcohol? What would you want to tell them to protect them or keep them safe or to help them make informed decisions about their behavior?











