375 310 anal env che.. - Department of Environmental Sciences
advertisement

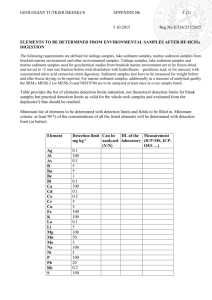
Syllabus ANALYTICAL ENVIRONMENTAL CHEMISTRY LABORATORY (11:375:310 2 credits) INSTRUCTORS: Wednesday: Lisa Rodenburg (formerly Totten) room 348, 848-932-5774 rodenburg@envsci.rutgers.edu Friday: Kelly Francisco room 265, kfrancisco@envsci.rutgers.edu TEACHING ASSISTANT: Jia Guo guojia@eden.rutgers.edu SECTION 1: Fridays 9:15 – 1:55; Room 205 ENRS Building SECTION 2: Wednesdays 10:55-3:35; Room 205 ENRS Building DESCRIPTION: A chemistry laboratory course covering basic chemical lab techniques for the analysis of environmental samples with emphasis on written presentation of analytical results. TEXT: NONE GRADING: 3 lab write-ups; 3 homework assignment Write ups (each is due 1 week after conclusion of lab or at final exam period) 1. A comparison of UV-vis spectroscopy and ion chromatography for measurement of anions 2. PCBs in sediment by GC/ECD 3. Trace metals in water 4. Sorption isotherms measured by HPLC (optional) IMPORTANT NOTICES: No cell phones and no texting in class You must wear shoes with closed toes, and bring your safety glasses. Most course business will be conducted through the sakai site. If you are registered for the class, you should be able to log on the course page on sakai TENTATIVE SCHEDULE: Week 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. Topic Check-in; write-ups and citations, weighing and pipetting Raritan sampling (meet at boat dock) pH; sulfate by UV-vis spectroscopy Anions in water by IC part I: sample prep Anions in water by IC part II: ion chromatography PCBs in sediment by GC/ECD part I: sample collection and extraction PCBs in sediment by GC/ECD part II: “clean up" PCBs in sediment by GC/ECD part III: GC/ECD analysis PCBs in sediment by GC/ECD part IV: data analysis Trace metals in water part I Trace metals in water part II Thanksgiving - NO CLASS Sorption isotherms HPLC I Sorption isotherms HPLC II LEARNING GOALS This class will contribute toward students’ ability to (numbers refer to ES learning goals at http://envsci.rutgers.edu/programs/envsci_ug_learning_goals.shtml): 1. apply knowledge from the sciences and mathematics to environmental problems and solutions; 2. use the skills and modern environmental science techniques and tools necessary for a successful career in the field; 3. design and conduct experiments, and analyze and interpret data; 4. function effectively on multidisciplinary teams; 5. communicate technical information effectively (orally, in writing, and through electronic media). 6. professional ethical responsibilities; 7. contemporary environmental science issues and the impact of environmental science in a global and societal context; ASSESSMENT ACTIVITIES 1. Ability to apply knowledge from the sciences and mathematics to environmental problems and solutions Instructional Activity: Contaminant concentrations will be measured in water and sediment in order to assess compliance with water quality standards and sediment quality guidelines. Assessment Activity: Compare measured concentrations to water quality standards and sediment quality guidelines in lab reports (100% of assessment) 2. use the skills and modern environmental science techniques and tools necessary for a successful career in the field; Instructional Activity: Ultraviolet-visible light absorption/scattering will be used to measure anions. Chromatography (ion chromatography, high-pressure liquid chromatography, gas chromatography) will be used to measure several environmental contaminants. Inductively coupled plasma optical emission spectroscopy (ICP-OES) will be used to measure trace metals in environmental samples. Assessment Activity: Report measured concentrations in lab reports (100% of assessment) 3. design and conduct experiments, and analyze and interpret data; Instructional Activity: Concepts of blank contamination (sources, corrections) will be discussed in class and applied to the measured concentrations. Sources of uncertainty will be identified and quantified. Linear regressions will be performed using Microsoft Excel software. Assessment Activity: Use linear calibration curves to calculate and report measured concentrations in lab reports (25% of assessment) Perform blank corrections on measure concentrations and report the results in lab reports (25% of assessment) Determine and report in the lab report the uncertainty in measured concentrations (25% of assessment) Name possible sources of blank contamination in lab reports (25% of assessment) 4. function effectively on multidisciplinary teams; Instructional Activity: Students will work in teams of four to conduct laboratory exercises. Assessment Activity: Data that was collected as a team is reported in all lab reports (50% of assessment) Team members give each other pass/fail evaluation (50% of assessment) 5. communicate technical information effectively (orally, in writing, and through electronic media). Instructional Activity: Students will write three lab reports that report and interpret the data gathered during the laboratory exercises. Reports will use the scientific structure (Abstract, Introduction, Methods, Results, Discussion, References). Proper format and grammar will be taught in lecture. Assessment Activity: Communication of data and interpretation via lab reports (100% of assessment) 6. professional ethical responsibilities Instructional Activity: Students will receive a lecture on ethics regarding proper production and use of scientific data and regarding plagiarism. Assessment Activity: Lab reports will be evaluated for proper citation of references without plagiarism. (100% of assessment) 7. contemporary environmental science issues and the impact of environmental science in a global and societal context Instructional Activity: By focusing on the Raritan River, students will explore the societal context of water quality and will consider the legal and regulatory context of their data (i.e. do the measured parameters exceed water quality standards?), as well as the social context (what are the sources of pollution? How are these sources being addressed through the TMDL process?) Assessment Activity: The final homework assignment will ask students to place their results in the regulatory and social context of the Raritan River. (100% of assessment) Performance Target Criteria Unsatisfactory (D or F) Satisfactory (C) Good (B) Outstanding (A) 1. Ability to apply knowledge from the sciences and mathematics to environmental problems and solutions Does not attempt to compare water quality standards or sediment quality guidelines with measured values. Attempts to compare water quality standards or sediment quality guidelines with measured values but used wrong criteria or inaccurate comparison Successfully compares water quality standards or sediment quality guidelines with measured values with only minor errors. Successfully compares water quality standards or sediment quality guidelines with measured values and discusses implications. 2. Ability to use the skills and modern environmental science techniques and tools necessary for a successful career in the field Is not able to report measured data due to a lack of understanding of methods. Reports measured concentrations, but makes significant math or methodology errors. Reports measured concentrations, with only minor math or methodology errors. Reports measured concentrations, with no errors, correct number of significant figures, and gives context about the meaning of the results. 3. Ability to design and conduct experiments, and analyze and interpret data Cannot perform a linear regression to obtain concentrations for lab reports, does not mention blank contamination or correct for it. Derives measured results using a linear calibration curve, mentions blank contamination and corrects for it if necessary, but may have significant errors in math or understanding. Derives measured results using a linear calibration curve, mentions blank contamination and corrects for it if necessary, and has only minor errors in math or understanding. Derives measured results using a linear calibration curve, mentions blank contamination and corrects for it if necessary, and has no significant errors in math or understanding. 4. Functions effectively on multidisciplinary Does not show up for class, does not participate Shows up for class, contributes to the Shows leadership in conducting lab exercises, Shows leadership inside and outside of class, in the lab exercise, all team members rate conduct as “not satisfactory”. laboratory exercises, most team members rate conduct as “satisfactory”. speaks on behalf of team during class, all team members rate conduct as “satisfactory”. speaks on behalf of team, helps team members outside of class, all team members rate conduct as “satisfactory”. 5. Communicate technical information effectively (orally, in writing, and through electronic media) Does not complete a lab report, or completes a lab report that has major flaws such as no cited references, missing data, or unreadable grammar and spelling. Completes a lab report that contains all relevant data, cites multiple references, and is readable, but has significant errors. Completes a lab report that contains all relevant data, cites multiple references, is readable, and has only minor errors. Completes a lab report that contains all relevant data, cites multiple references, is readable, and has virtually no errors. 6. professional ethical responsibilities Plagiarized multiple references in lab reports, copies other students’ work, uses web resources to generate a lab report that is not substantially independent work. Unintentionally plagiarizes references by not citing them properly in the lab reports Makes only small errors in citing other’s work. Cites the work of others correctly at all times. 7. contemporary environmental science issues and the impact of environmental science in a global and societal context Does not recognize that the measurements performed in class relate to the Raritan River, cannot relate them to applicable regulatory standards, cannot name possible sources of Articulates a link between the Raritan River and the measured parameters, but displays confusion about which standards apply to the Raritan River, or cannot name sources. Correctly relates the measured parameters to the applicable regulatory limits and can name sources, but does not describe what activities can be taken to reduce pollution. Correctly relates the measured parameters to the applicable regulatory limits, can name sources, and describes several activities that can be taken to reduce pollution. teams pollution