Images in Converging Lenses
advertisement

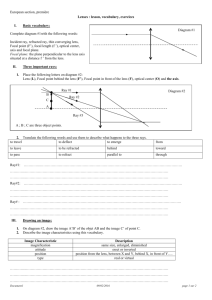
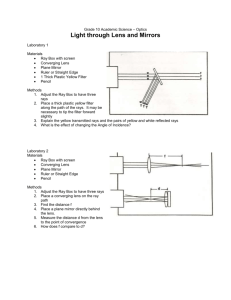
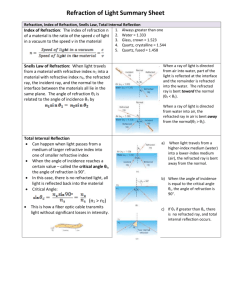
A lens is a transparent object that is used to refract light. A converging lens is a lens that is thicker in the middle and thinner at the edges. When parallel rays pass through a converging lens they converge or come together through the focal point (principal focus). FOCAL POINT Point where light rays (F) converge OPTICAL CENTRE (O) Point at the centre of the lens PRINCIPAL AXIS (PA) Line through the optical centre and focal point NORMAL Imaginary line perpendicular to principal axis REFRACTION RULES FOR IMAGES IN CONVERGING LENSES Incident Ray Refracted Ray Parallel to Principal Axis Through focal point (on opposite side of lens) 2F F F 2F Parallel to Principal Axis (on opposite side of lens) 2F F F 2F Through focal point Diagram Incident ray passes straight through optical centre (without being refracted) 2F F RAY DIAGRAM #1: Object beyond 2F S A L T RAY DIAGRAM 2: Object at 2F S A L T F 2F RAY DIAGRAM #3: Object between 2F and F RAY DIAGRAM #4: Object at F Do your refracted rays intersect at all? Is an image formed? S A L T S A L T RAY DIAGRAM #5: Object between F and lens S A L T When drawing a ray diagram when the object is between F and the lens, these are the steps: 1. Draw incident ray #1 from the top of the object toward the lens and parallel to the principal axis. 2. Draw refracted ray #1 through the focal point (on the other side of the lens) and extend it (on the same side as the object) using a dashed line. 3. Draw incident ray #2 from the top of the object and make sure to line up your ruler with the top of the object and the focal point (on the same side as the object). 4. Draw refracted ray #2 backward and parallel to the principal axis and extend it (on the same side as the object) using a dashed line. 5. Draw the image between the point where the dashed lines meet and the principal axis.