Conic Sections Foldable Notes
advertisement
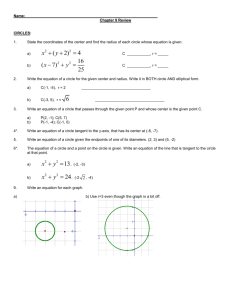
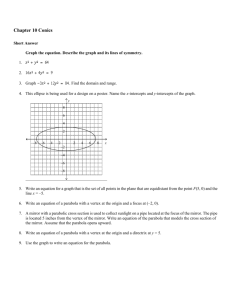
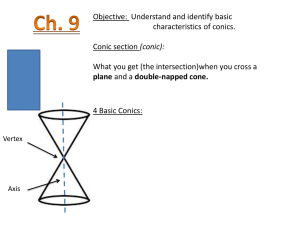
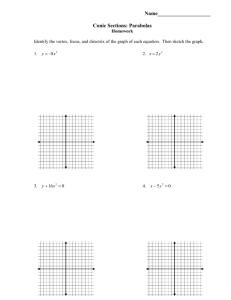
Unit 4 Conics Conic Sections are formed by the intersection of a double right cone and a plane. Circles ( x h)2 ( y k )2 r 2 Vocabulary: Parts of a Circle 1. Center: the point equidistant from all points on the edge 2. Radius: The segment from the center to the edge of a circle 3. Diameter: a chord that passes through the center of a circle 4. Chord: a segment whose endpoints are on the circle 5. Tangent: Intersects the circle at exactly one point 6. Secant: a line that intersects the circle at 2 points. Example: center: (4, 3) Radius: 2 Equation: Domain: Range: Example: center: Origin Radius: 5 Equation: Domain: Range: y -1 -2 -3 -4 -5 -6 -7 -8 -9 All points a set distance from a center point. Standard Form: ( x h)2 ( y k )2 r 2 Center: (h, k) Radius: r Graph: 1. Write the equation in standard form 2. Identify the center and the radius 3. Plot the center and use the radius to find all points “r” units from the center y 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 y 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 -9 -8 -7 -6 -5 -4 -3 -2 -1 Circles 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 x 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 -9 -8 -7 -6 -5 -4 -3 -2 -1 -1 -2 -3 -4 -5 -6 -7 -8 -9 x 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 -9 -8 -7 -6 -5 -4 -3 -2 -1 -1 -2 -3 -4 -5 -6 -7 -8 -9 x 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 ( x h) (y k ) 1 2 2 a b 2 Ellipse 2 Ellipse All points on a plane where the sum of the distance from each point to the foci is constant Vertical Major Axis Horizontal Major Axis ( x h) (y k ) 1 2 a b2 2 2 (y k ) ( x h) 1 2 a b2 2 Center: (h, k) Major axis is 2a. Each vertex is “a” units from center Minor axis is 2b. Each co-vertex is “b” units from center 2 2 2 Foci are located “c” units from center where c a b 2 Center: (h, k) Major axis is 2a. Each vertex is “a” units from center Minor axis is 2b. Each co-vertex is “b” units from center 2 2 2 Foci are located “c” units from center where c a b y 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 -9 -8 -7 -6 -5 -4 -3 -2 -1 -1 -2 -3 -4 -5 -6 -7 -8 -9 Graph: x 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 1. Put in standard form 2. Find “a” (in an ellipse, “a” is always bigger) 3. Find “b” (use one of the following methods) a. “b” is given b. Focus “c” is given use c 2 a 2 b 2 c. A point is given, substitute and solve for “b” 4. Determine orientation Eccentricity Ellipse is more circular If c is closer to 0: Then, Foci are closer to center. a Ellipse is very elongated If c is closer to 1: Then, Foci are closer to vertices. a ( x h) (y k ) 1 a2 b2 2 Hyperbola All points on a plane where the difference of the distance from each point to the foci is constant. 2 Hyperbola The Fundamental Rectangle: The diagonals of the fundamental rectangle extended in either direction are the asymptotes of the hyperbola. Vertical Transverse Axis How to graph hyperbolas: (y k ) ( x h) 1 2 a b2 2 2 Center: (h, k) 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Transverse Axis is 2a units. Vertices are “a” units from center Conjugate Axis is 2b units. Co-vertices are “b” units from center 6. 7. Write the equation in standard form Find Center Determine the Transverse Axis. (“a” always comes first) Find vertices Draw the Fundamental Rectangle a. Plot the vertices “a” units from center b. Plot points on conjugate axis “b” units from center c. Draw lines through each vertex (hor/ver) d. Draw lines through each point (hor/ver) Draw Asymptotes (diagonals) Sketch Graph Foci are “c” units from center where c 2 a2 b2 y ( x h) (y k ) 1 2 a b2 2 2 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 Horizontal Transverse Axis Center: (h, k) Transverse Axis is 2a units. Vertices are “a” units from center Conjugate Axis is 2b units. Co-vertices are “b” units from center Foci are “c” units from center where c 2 a2 b2 -9 -8 -7 -6 -5 -4 -3 -2 -1 -1 -2 -3 -4 -5 -6 -7 -8 -9 x 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 2 ( x h ) 4 p( y k ) Parabola Parabola All points the same distance from a fixed line (directrix) and a fixed point (focus). Equation with vertex (h, k,) Equation with vertex (h, k,) ( y k ) 4 p( x h) Direction parabola opens Right ( x h) 4 p( y k ) Direction parabola opens Up ( y k ) 4( p)( x h) Left ( x h)2 4( p)( y k ) Down 2 2 2 Vertex: (h, k) Vertex: (h, k) Focus: “p” units from vertex inside parabola Focus: “p” units from vertex inside parabola Directrix: a vertical line “p” units from vertex outside parabola Directrix: a horizontal line “p” units from vertex outside parabola y Graph 1. Plot the vertex of the parabola (h, k) 2. Find the direction the parabola opens by using the tables above 3. Sketch the axis of symmetry. a. Use the vertex and focus b. The focus is “p” units away from the vertex in the direction the parabola opens. c. The directrix is a vertical or horizontal line “p” units away from the vertex opposite from the focus 4. Find two reference points 2p units above/below or left/right of the focus based on its orientation. 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 -9 -8 -7 -6 -5 -4 -3 -2 -1 -1 -2 -3 -4 -5 -6 -7 -8 -9 x 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 Examples y Circles A circle is centered at (-3, 5) and has a circumference of 8 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 -9 -8 -7 -6 -5 -4 -3 -2 -1 Standard Form 2 x 2 2y 2 4 x 16 y 10 0 6 x 2 6 y 2 5 x 2y 7 0 x 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 -1 -2 -3 -4 -5 -6 -7 -8 -9 x 2 y 2 14 x 20 y 6 0 3 x 2 3 y 2 27 0 Parabolas y 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 -9 -8 -7 -6 -5 -4 -3 -2 -1 An ellipse centered at (-2, 3) with major axis length of 8 and parallel to the y-axis, minor axis length 2 9 x 2 6 x 4 y 2 0 4 x 2 6 x 2y 26 0 x 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 -1 -2 -3 -4 -5 -6 -7 -8 -9 y 2 3 x 6 y 9 0 y 2 x 2y 27 0 Ellipses 5 x 2 2y 2 10 x 8y 10 0 y 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 -9 -8 -7 -6 -5 -4 -3 -2 -1 A vertical hyperbola with conjugate axis length 10, center (2, -1) and one vertex at (2, 5) 8 y 2 x 2 14 x 6 y 6 0 15y 2 10 x 2 45 x 25y 8 0 x 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 -1 -2 -3 -4 -5 -6 -7 -8 -9 7 x 2 9 y 2 x 2y 4 0 Hyperbolas 10 x 2 14y 2 6 x 2y 100 0 x 2 4y 2 16y 32 0 y 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 -9 -8 -7 -6 -5 -4 -3 -2 -1 -1 -2 -3 -4 -5 -6 -7 -8 -9 A parabola with focus at (4, 0) and directrix x=-4 x 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 9 x 2 2y 2 27 x 16 y 54 0 1.5 x 2 4y 2 4.5 x 8 y 20 0 Complete the Square 1. Complete the square of x 2 y 2 - 6x 2y - 6 0 2. Complete the square of 4 x 2 25y 2 - 40 x 100y 100 0 3. Complete the square 3y 2 4 x 2 12y 24 x 36 4. Complete the square y 2 2y 2x 7 0