View
advertisement
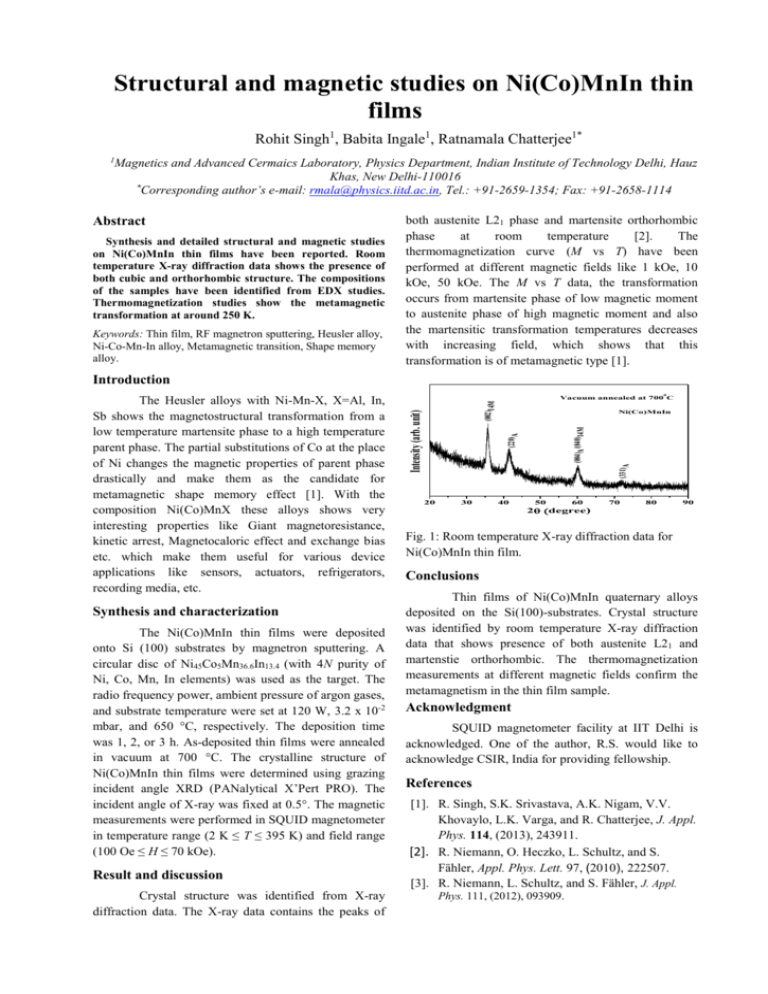
Structural and magnetic studies on Ni(Co)MnIn thin films Rohit Singh1, Babita Ingale1, Ratnamala Chatterjee1* 1 Magnetics and Advanced Cermaics Laboratory, Physics Department, Indian Institute of Technology Delhi, Hauz Khas, New Delhi-110016 * Corresponding author’s e-mail: rmala@physics.iitd.ac.in, Tel.: +91-2659-1354; Fax: +91-2658-1114 Abstract Synthesis and detailed structural and magnetic studies on Ni(Co)MnIn thin films have been reported. Room temperature X-ray diffraction data shows the presence of both cubic and orthorhombic structure. The compositions of the samples have been identified from EDX studies. Thermomagnetization studies show the metamagnetic transformation at around 250 K. Keywords: Thin film, RF magnetron sputtering, Heusler alloy, Ni-Co-Mn-In alloy, Metamagnetic transition, Shape memory alloy. both austenite L21 phase and martensite orthorhombic phase at room temperature [2]. The thermomagnetization curve (M vs T) have been performed at different magnetic fields like 1 kOe, 10 kOe, 50 kOe. The M vs T data, the transformation occurs from martensite phase of low magnetic moment to austenite phase of high magnetic moment and also the martensitic transformation temperatures decreases with increasing field, which shows that this transformation is of metamagnetic type [1]. Introduction Synthesis and characterization The Ni(Co)MnIn thin films were deposited onto Si (100) substrates by magnetron sputtering. A circular disc of Ni45Co5Mn36.6In13.4 (with 4N purity of Ni, Co, Mn, In elements) was used as the target. The radio frequency power, ambient pressure of argon gases, and substrate temperature were set at 120 W, 3.2 x 10-2 mbar, and 650 °C, respectively. The deposition time was 1, 2, or 3 h. As-deposited thin films were annealed in vacuum at 700 °C. The crystalline structure of Ni(Co)MnIn thin films were determined using grazing incident angle XRD (PANalytical X’Pert PRO). The incident angle of X-ray was fixed at 0.5°. The magnetic measurements were performed in SQUID magnetometer in temperature range (2 K ≤ T ≤ 395 K) and field range (100 Oe ≤ H ≤ 70 kOe). Result and discussion Crystal structure was identified from X-ray diffraction data. The X-ray data contains the peaks of 0 (002)14M Vacuum annealed at 700 C (004)A/(040)14M Ni(Co)MnIn (331)A (220)A Intensity (arb. unit) The Heusler alloys with Ni-Mn-X, X=Al, In, Sb shows the magnetostructural transformation from a low temperature martensite phase to a high temperature parent phase. The partial substitutions of Co at the place of Ni changes the magnetic properties of parent phase drastically and make them as the candidate for metamagnetic shape memory effect [1]. With the composition Ni(Co)MnX these alloys shows very interesting properties like Giant magnetoresistance, kinetic arrest, Magnetocaloric effect and exchange bias etc. which make them useful for various device applications like sensors, actuators, refrigerators, recording media, etc. 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 2degree) Fig. 1: Room temperature X-ray diffraction data for Ni(Co)MnIn thin film. Conclusions Thin films of Ni(Co)MnIn quaternary alloys deposited on the Si(100)-substrates. Crystal structure was identified by room temperature X-ray diffraction data that shows presence of both austenite L21 and martenstie orthorhombic. The thermomagnetization measurements at different magnetic fields confirm the metamagnetism in the thin film sample. Acknowledgment SQUID magnetometer facility at IIT Delhi is acknowledged. One of the author, R.S. would like to acknowledge CSIR, India for providing fellowship. References [1]. R. Singh, S.K. Srivastava, A.K. Nigam, V.V. Khovaylo, L.K. Varga, and R. Chatterjee, J. Appl. Phys. 114, (2013), 243911. [2]. R. Niemann, O. Heczko, L. Schultz, and S. Fähler, Appl. Phys. Lett. 97, (2010), 222507. [3]. R. Niemann, L. Schultz, and S. Fähler, J. Appl. Phys. 111, (2012), 093909.