35 - Cabrillo College
advertisement
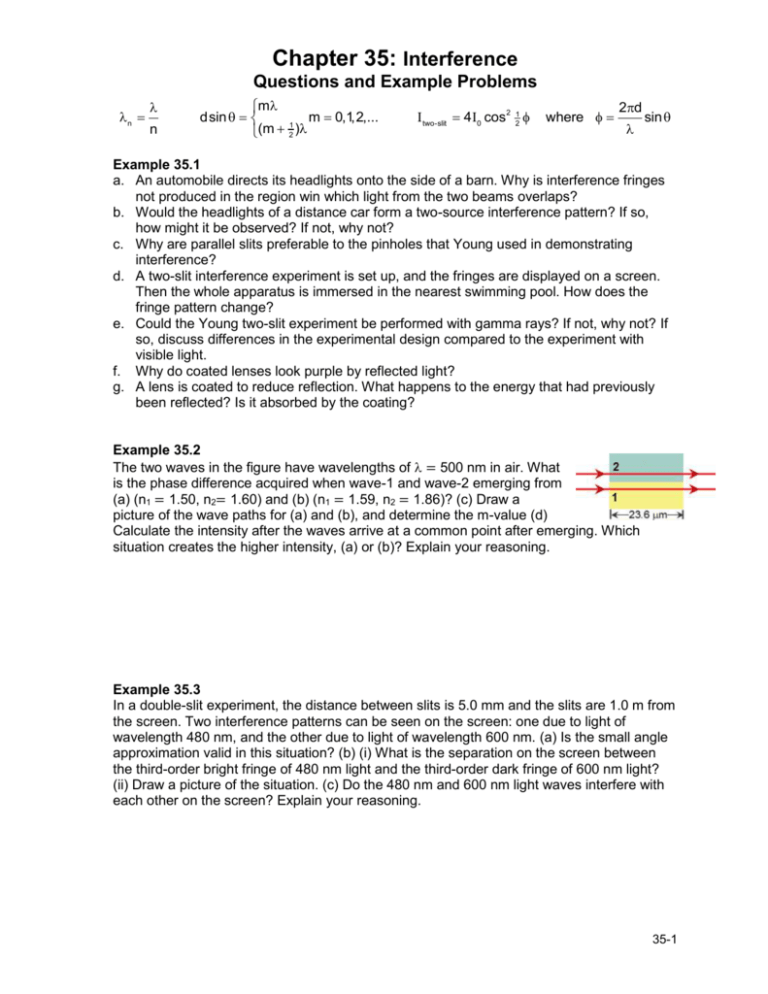
Chapter 35: Interference Questions and Example Problems n n m dsin m 0,1,2,... 1 (m 2 ) I two-slit 4 I0 cos2 21 where 2d sin Example 35.1 a. An automobile directs its headlights onto the side of a barn. Why is interference fringes not produced in the region win which light from the two beams overlaps? b. Would the headlights of a distance car form a two-source interference pattern? If so, how might it be observed? If not, why not? c. Why are parallel slits preferable to the pinholes that Young used in demonstrating interference? d. A two-slit interference experiment is set up, and the fringes are displayed on a screen. Then the whole apparatus is immersed in the nearest swimming pool. How does the fringe pattern change? e. Could the Young two-slit experiment be performed with gamma rays? If not, why not? If so, discuss differences in the experimental design compared to the experiment with visible light. f. Why do coated lenses look purple by reflected light? g. A lens is coated to reduce reflection. What happens to the energy that had previously been reflected? Is it absorbed by the coating? Example 35.2 The two waves in the figure have wavelengths of = 500 nm in air. What is the phase difference acquired when wave-1 and wave-2 emerging from (a) (n1 = 1.50, n2= 1.60) and (b) (n1 = 1.59, n2 = 1.86)? (c) Draw a picture of the wave paths for (a) and (b), and determine the m-value (d) Calculate the intensity after the waves arrive at a common point after emerging. Which situation creates the higher intensity, (a) or (b)? Explain your reasoning. Example 35.3 In a double-slit experiment, the distance between slits is 5.0 mm and the slits are 1.0 m from the screen. Two interference patterns can be seen on the screen: one due to light of wavelength 480 nm, and the other due to light of wavelength 600 nm. (a) Is the small angle approximation valid in this situation? (b) (i) What is the separation on the screen between the third-order bright fringe of 480 nm light and the third-order dark fringe of 600 nm light? (ii) Draw a picture of the situation. (c) Do the 480 nm and 600 nm light waves interfere with each other on the screen? Explain your reasoning. 35-1 Example 35.4 In the figure, two isotropic point sources S1 and S2 emit light in phase at wavelength and at the same amplitude. The sources are separated by distance d = 6.00 on an x axis. A viewing screen is at distance D = 20.0 from S1 and parallel to the y axis. The figure shows two rays reaching point P on the screen, at height yP. a. Conceptually explain each situation and draw a picture of the situation: i. At what value of yP do the rays have the minimum possible phase difference and what is this phase in terms of and ? ii. At what value of yP do the rays have the maximum possible phase difference and what is this phase in terms of and ? b. Calculate the phase difference when yP = d? Is the resulting intensity maximum, minimum, intermediate but closer to maximum, or intermediate but closer to minimum? Example 35.5 Suppose a radio station operating at a frequency of 60 MHz has two identical vertical dipole antennas spaced 10 m apart, oscillating in phase. The intensity at a distance of 700 m in the +x-direction (corresponding to = 0) is I0 = 0.080 W/m2. a. What is the mathematical expression for the intensity as a function of θ? b. What is the (i) intensity and (ii) relative intensity when θ = 4°? c. For what angle is the relative intensity one-half? d. What are the angular locations of all dark and bright fringes? How many dark and bright fringes are in the interference patterns? Draw a picture of the situation. Example 35.6 A disabled tanker leaks kerosene (n = 1.20) into the Persian Gulf, creating a large slick on top of the water (n =1.30). (a) If you are looking straight down from an airplane, while the Sun is overhead, at a region of the slick where its thickness is 460 nm, for which wavelength(s) of visible light is the reflection brightest because of constructive interference? Draw a picture of the situation. (b) If you are scuba diving directly under this same region of the slick, for which wavelength(s) of visible light is the transmitted intensity strongest? Draw a picture of the situation. 35-2