Quadratics Unit Plan | 49.7KB
advertisement

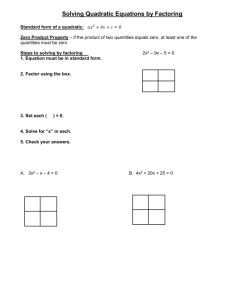
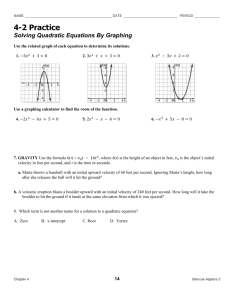
Progressive Mathematics Initiative www.njctl.org Mathematics Curriculum Unit Plan # 3 Title: Quadratics Subject: Algebra 2 Length of Time: 3 weeks Unit Summary: The unit covers quadratic equations. Students learn to graph quadratic functions and find the zeros of the function through graphing, factoring, square roots, completing the square, and the quadratic formula. The standard form of quadratics and graphing quadratic inequalities will also be discussed. Learning Targets Conceptual Category: Algebra Domain: Seeing Structure in Expressions Cluster: Interpret the structure of expressions Use the structure of an expression to identify ways to rewrite it. For example, see x4 – A-SSE.2 y4 as (x2)2 – (y2)2, thus recognizing it as a difference of squares that can be factored as (x2 – y2)(x2 + y2). Cluster: Write expressions in equivalent forms to solve problems A-SSE-3 Choose and produce an equivalent form of an expression to reveal and explain properties of the quantity represented by the expression. a. Factor a quadratic expression to reveal the zeros of the function it defines. b. Complete the square in a quadratic expression to reveal the maximum or minimum value of the function it defines. Conceptual Category: Algebra Domain: Arithmetic with Polynomials & Rational Expressions Cluster: Understand the relationship between zeros and factors of polynomials A-APR.3 Identify zeros of polynomials when suitable factorizations are available, and use the zeros to construct a rough graph of the function defined by the polynomial. Conceptual Category: Algebra Domain: Creating Equations Cluster: Create equations that describe numbers or relationships A-CED.1 Create equations and inequalities in one variable and use them to solve problems. Conceptual Category: Algebra Domain: Reasoning with Equations & Inequalities Cluster: Solve equations and inequalities in one variable A-REI.4 Solve quadratic equations in one variable. Cluster: Represent and solve equations and inequalities graphically A-REI.10 Understand that the graph of an equation in two variables is the set of all its solutions plotted in the coordinate plane, often forming a curve (which could be a line). Conceptual Category: Functions Domain: Interpreting Functions Cluster: Interpret functions that arise in applications in terms of the context F-IF.4 For a function that models a relationship between two quantities, interpret key features of graphs and tables in terms of the quantities, and sketch graphs showing key features given a verbal description of the relationship. F-IF.5 Relate the domain of a function to its graph and, where applicable, to the quantitative relationship it describes. Cluster: Analyze functions using different representations F-IF.7 Graph functions expressed symbolically and show key features of the graph, by hand in simple cases and using technology for more complicated cases. a. Graph linear and quadratic functions and show intercepts, maxima, and minima. Algebra II – Quadratics ~1~ NJCTL.org F-IF.8 Write a function defined by an expression in different but equivalent forms to reveal and explain different properties of the function. a. Use the process of factoring and completing the square in a quadratic function to show zeros, extreme values, and symmetry of the graph, and interpret these in terms of a context. F-IF.9 Compare properties of two functions each represented in a different way (algebraically, graphically, numerically in tables, or by verbal descriptions). For example, given a graph of one quadratic function and an algebraic expression for another, say which has the larger maximum. Conceptual Category: Functions Domain: Building Functions Cluster: Build new functions from existing functions Identify the effect on the graph of replacing f(x) by f(x) + k, k f(x),f(kx), and f(x + k) for F-BF.3 specific values of k (both positive and negative); find the value of k given the graphs. Experiment with cases and illustrate an explanation of the effects on the graph using technology. Include recognizing even and odd functions from their graphs and algebraic expressions for them. Conceptual Category: Geometry Domain: Expressing Geometric Properties with Equations Cluster: Translate between the geometric description and the equation for a conic sections G-GPE.2 Derive the equation of a parabola given a focus and directrix. Unit Essential Question: Unit Enduring Understandings: How can we find the position of an object at a The graph of a quadratic is U-shaped and given time, including when it hits the ground? called a parabola. A quadratic can have 0, 1, or 2 zeros. How are quadratic functions used to model, The x-intercepts of a quadratic can also be analyze and interpret mathematical relationships? called zeros or solutions. What are the advantages of a quadratic function in To find the zeros of a quadratic function, you vertex form? In standard form? must set the equation equal to zero. The quadratic formula can be used to find zeros. The discriminant of a quadratic formula can tell the number and nature of the roots. Completing a perfect square trinomial allows you to factor the completed trinomial as the square of a binomial. In the graph of 𝑓(𝑥) = 𝑎(𝑏(𝑥 + 𝑐))2 + 𝑑, a is a vertical dilation or reflection, b is a horizontal dilation or reflection, c is a horizontal slide, and d is a vertical slide of 𝑓(𝑥) = 𝑥 2 . Unit Objectives: Students will be able to understand and graph key features of quadratic equations. Students will be able to solve quadratic equations graphically and algebraically (factoring, square roots, completing the square, and using the quadratic formula). Students will be able to state the number and nature of the roots of a quadratic using the discriminant. Students will be able to apply the techniques for finding zeros of a quadratic to real-world problems. Evidence of Learning Formative Assessments: SMART Response questions used throughout the unit. 6 Quizzes Summative Assessment: Unit Test Algebra II – Quadratics ~2~ NJCTL.org Lesson Plan Topics Timeframe (days) Topic #1: Key terms, Identify Quadratic Functions, and Explain Characteristics Topic #2: Combining Transformations Topic #3: Graph Quadratic Functions Quiz 1 Quadratic Functions Topic #4: Solve Quadratic Functions: Graphically Quiz 2 Solve Quadratics by Graphing Topic #5: Solve Quadratic Functions: Factoring Topic #6: Application of the Zero Product Property Topic #7: Solve Quadratic Functions: Square Roots Topic #8: Solve Quadratic Functions: Completing the Square Quiz 3 Solve Quadratics Algebraically Topic #9: Solve Quadratic Functions: Quadratic Formula Topic #10: The Discriminant Quiz 4 Discriminant/Quadratic Formula Topic #11: Vertex and Standard Form Quiz 5 Vertex and Standard Form Topic #12: More Application Problems Lab: Roller Coaster Quiz 6 Application of Quadratics Review and Unit Test Curriculum Resources: www.njctl.org/courses/math/algebra2/ 0.5 Algebra II – Quadratics ~3~ 0.5 0.5 0.5 0.5 0.5 1 0.5 1 1.5 0.5 1 0.5 0.5 1.5 0.5 1.5 0.5 2 NJCTL.org