SET1 USHA RAMA COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING & TECHNOLOGY
advertisement

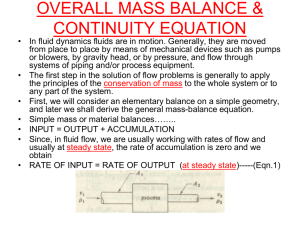
SET1 SET1 USHA RAMA COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING & TECHNOLOGY Branch:CIVIL Subject:FM I - MID EXAM Year/Sem:II/I Max Marks: 40M Time: 2 Hours Answer all questions All Questions carry equal marks 1 1 a) Define density, specific volume, weight density 2 3 4 and specific gravity. b) Determine the density, specific weight and specific volume of air if the specific gravity with water as reference fluid) is 0.011614. Find the total pressure and position of centre of pressure on a triangular plate of base 2.4m and height 3.6m which is immersed in water in such a way that the plan of the plate makes an angle of 60 0 with the free surface of the water. The base of the plate is parallel to water surface and is at a depth of 3.0m from water surface. A 30 cm diameter pipe, conveying water, branches into two pipes of diameters 20 cm and 15 cm respectively. If the average velocity in the 30 cm diameter pipe is 2.5 m/s, find the discharge in this pipe. Also determine the velocity in 15 cm pipe if the average velocity in 20 cm diameter pipe is 2 m/s State and derive Bernoulli’s theorem, mentioning clearly the assumption underlying it. USHA RAMA COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING & TECHNOLOGY Branch:CIVIL Subject:FM I - MID EXAM Year/Sem:II/I Max Marks: 40M Time: 2 Hours Answer all questions All Questions carry equal marks 1 1 a) Define density, specific volume, weight density 2 3 4 and specific gravity. b) Determine the density, specific weight and specific volume of air if the specific gravity with water as reference fluid) is 0.011614. Find the total pressure and position of centre of pressure on a triangular plate of base 2.4m and height 3.6m which is immersed in water in such a way that the plan of the plate makes an angle of 60 0 with the free surface of the water. The base of the plate is parallel to water surface and is at a depth of 3.0m from water surface A 30 cm diameter pipe, conveying water, branches into two pipes of diameters 20 cm and 15 cm respectively. If the average velocity in the 30 cm diameter pipe is 2.5 m/s, find the discharge in this pipe. Also determine the velocity in 15 cm pipe if the average velocity in 20 cm diameter pipe is 2 m/s State and derive Bernoulli’s theorem, mentioning clearly the assumption underlying it. SET2 SET2 USHA Branch:CIVIL Subject:FM I- MID EXAM Year/Sem: II/I Max Marks: 40 M Time: 2 Hours Answer all questions All Questions carry equal marks A space between two square plate (50 cm × 50 cm) is filled with 1 2 3 4 USHA RAMA COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING & TECHNOLOGY oil of 1cm thickness. The upper plate moves with constant velocity of 2.5 m/s under a force 10 N. Determine the dynamic and kinematic viscosities of the oil in poise and stokes respectively. Take specific gravity as0.95 Obtain simplified expressions for the centre of pressure of vertical planes. i) Plate, ii) Circle and iii) triangle. A velocity potential function for two dimensional steady state flows is given by φ = x (2y-1) Find out the velocity at the point P (2, 3) .Also find out the value of stream function passing through the point P. A Water pipe changes in diameter from 400mm at section A to 800mm at section B which is 7 m above. The pressures at A and B are 100 KPa and 75 KPa respectively. The discharge is 400 litres/sec. Find the direction of flow. RAMA COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING & TECHNOLOGY Branch: CIVIL Subject:FM I- MID EXAM Year/Sem:II/I Max Marks: 40 M Time: 2 Hours Answer all questions All Questions carry equal marks A space between two square plate (50 cm × 50 cm) is filled with 1 2 3 4 oil of 1cm thickness. The upper plate moves with constant velocity of 2.5 m/s under a force 10 N. Determine the dynamic and kinematic viscosities of the oil in poise and stokes respectively. Take specific gravity as0.95 Obtain simplified expressions for the centre of pressure of vertical planes. i) Plate, ii) Circle and iii) triangle. A velocity potential function for two dimensional steady state flows is given by φ = x (2y-1) Find out the velocity at the point P (2, 3) .Also find out the value of stream function passing through the point P A Water pipe changes in diameter from 400mm at section A to 800mm at section B which is 7 m above. The pressures at A and B are 100 KPa and 75 KPa respectively. The discharge is 400 litres/sec. Find the direction of flow. SET3 USHA Branch:CIVIL I - MID EXAM Max Marks: 40M Subject:FM Year/Sem:II/I Time: 2 Hours Answer all questions All Questions carry equal marks 1 a) Explain surface tension? Derive the expression for 2 3 4 SET3 RAMA COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING & TECHNOLOGY excess pressure in a soap bubble. b) Find the height through which water rises by capillary action in a glass tube of 2mm bore if the surface tension at the prevailing temperature is 0.075 N/m. Derive an expression for total pressure and the depth of centre of pressure from free surface of liquid of an vertical plane surface submerged in the liquid. Distinguish between: i) Steady flow and un-steady flow, ii) Uniform and non-uniform flow, iii) Compressible and incompreesible flow and iv) Rotational and irrotational flow 30 cm x 15 cm venturimeter is provided in a vertical pipe line carrying oil of specific gravity 0.9, the flow being upwards. The difference in elevation of the throat section and entrance section of the venturimeter is 30 cm. the differential U tube mercury manometer shows a gauge deflection of 25 cm. Calcualte the (i) the discharge of oil, and (ii) the pressure diffrenece between the entrance section and throat section. Take the coefficient of meter as 0.98 and specific gravity of mercury as 13.6. USHA RAMA COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING & TECHNOLOGY Branch:CIVIL I - MID EXAM Max Marks: 40M Subject:FM Year/Sem:II/I Time: 2 Hours Answer all questions All Questions carry equal marks 1 a) Explain surface tension? Derive the expression for 2 3 4 excess pressure in a soap bubble. b) Find the height through which water rises by capillary action in a glass tube of 2mm bore if the surface tension at the prevailing temperature is 0.075 N/m. Derive an expression for the depth of centre of pressure from free surface of liquid of an inclined plane surface submerged in the liquid. Distinguish between: i) Steady flow and un-steady flow, ii) Uniform and non-uniform flow, iii) Compressible and incompreesible flow and iv) Rotational and irrotational flow 30 cm x 15 cm venturimeter is provided in a vertical pipe line carrying oil of specific gravity 0.9, the flow being upwards. The difference in elevation of the throat section and entrance section of the venturimeter is 30 cm. the differential U tube mercury manometer shows a gauge deflection of 25 cm. Calcualte the (i) the discharge of oil, and (ii) the pressure diffrenece between the entrance section and throat section. Take the coefficient of meter as 0.98 and specific gravity of mercury as 13.6.