Methods and Materials in Special Education
advertisement

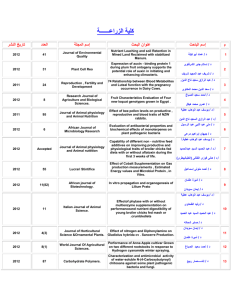
INSTRUCTOR: Batoul M. Khalifa OFFICE NUMBER: 218 PHONE:44035221 EMAIL: Batoul@qu.edu.qa OFFICE HOURS: Wednesday 2-3 p.m. -77280600 COLLEGE OF EDUCATION CONCEPTUAL FRAMEWORK Together We Shape the Future through Excellence in Teaching, Scholarship, and Leadership. COLLEGE OF EDUCATION UNIT LEARNING OUTCOMES (Checked if addressed in this course) Teaching 1. Content: Demonstrate a deep and thorough understanding of the key theories and concepts of the subject matter. 2. Pedagogy: Ensure effective planning for instruction and the use of multiple learning and pedagogical content strategies to maximize student learning and promote critical thinking. 1 3. Technology: Evaluate and use current and emerging technologies in instructionally powerful ways and to assist in the management of educational environment. 4. Diversity: Respond to every student’s uniqueness and foster successful learning experiences by meeting individual differences. Scholarship 5. Scholarly Inquiry: Understand the tools and methods of inquiry and use data-driven decision making to maximize teaching and learning. 6. Problem Solving: Gather, analyze, and plan a sequence of steps to achieve learning objectives: process a variety of factors in identifying solutions and making sound, well-informed decisions. Leadership 7. Ethical Values: Apply professional ethics in all educational contexts and have enduring respect for self-confidence in teaching as a profession. 8. Initiative: Demonstrate the qualities of effective leadership to plan with vision and reason, collaborate with all stakeholders, and communicate effectively in interpersonal and public contexts. COURSE DESCRIPTION: This course focuses on the instructional skills necessary for teaching students with high incidence disabilities (LD, E/BD, and ID) who receive special education services. Topics of primary emphasis include, developing effective individualized education plans; preparing and delivering exemplary lesson plans; and identifying instructional strategies that promote effective classroom learning. Research-based methodology will be emphasized. Three credits 2 COURSE OBJECTIVES 1) Sources of specialized materials, curricula, and resources for individuals with disabilities. 2) Strategies for integrating student-initiated learning experiences into ongoing instruction 3) Use strategies to facilitate integration into various settings 4) Select, adapt, and use instructional strategies and materials according to characteristics of the individual with exceptional learning needs 5) Organize, develop, and sustain learning environments that support positive intercultural and intercultural experiences. 6) Identify and prioritize areas of the general curriculum and accommodations for individuals with exceptional learning needs. 7) Prepare IEP and lesson plans. 8) Interpret sensory, mobility, reflex, and perceptual information to create or adapt appropriate learning plans COURSE LEARNING OUTCOMES: Upon completion of this course, students will be able to 1) Use effective, research-based instructional strategies and practices to meet the individual needs of individuals with disabilities. 2) Identify and implement the principles of effective teaching for students with mild/moderate disabilities in content area curriculum. 3) Document student progress and use student data to monitor progress and facilitate decision-making. 4) Develop and evaluate IEP's for students with mild/moderate disabilities. 5) Perform a task analysis of basic daily living skill. 3 6) Demonstrate the ability to implement specific instructional strategies, materials, and curriculum for students with mild/moderate disabilities, as appropriate. 7) Describe the elements of curriculum as they apply to special education and how this fits with Qatari curriculum standards and national examinations. 8) Plan, organize, and implement educational programs appropriate to the cognitive and affective needs of individuals with disabilities 9) Use effective instructional strategies to assist individuals with disabilities to detect and correct errors in oral and written language. 10) Use appropriate instructional strategies to teach math skills and concepts according to the characteristics of the learner and patterns of error. 11) Modify pace of instruction and use organization cues. 12) Integrate appropriate teaching strategies and instructional approaches to provide effective instruction in academic and nonacademic areas for individuals with disabilities TEXTBOOKS & READINGS Weinbrenner, S. (2006). Teaching children with learning difficulties in the regular classroom: Strategies and techniques every teacher can use to challenge and motivate struggles students. (Translated into Arabic in UAE: 2008) Bateman, B. D. & Herr, M.H. (2006). Writing measurable IEP, Goals & objectives. IEP Resources. (e-book: desk copy) Harwell, J. M. (2008). Learning disabilities Handbook. New 3rd edition. JosseyBoss publication. ISBN: 978-0-7879-9755-7 Bender, W. N. (2008). Differentiating Instruction for Students With Learning Disabilities: Best Teaching Practices for General and Special Educators. 2nd edition, 4 Crown Press. Council for Exceptional Children, California. ISBN-13: 9781412954464 . مطبعة علي بن علي: الدوحة، صعوبات التعلم بين النظرية والتطبيق.)2007( براندا، شريفة & الزوراس، العلي، بتول،خليفة Recommended 1. http://www.ehow.com/students-with-learning-disabilities/ 2. http://helpguide.org/mental/learning_disabilities.htm 3. http://nichcy.org/wp-content/uploads/docs/bib15.pdf 4. http://helpguide.org/mental/adhd_add_teaching_strategies.htm COURSE REQUIREMENTS Use of Blackboard COURSE MATRIX Unit Learning QNPS Outcomes 1. Content Course Course Learning Outcomes Assessment Objectives 1 1 10 (Tasks/Artifacts) 1. Use effective, research-based instructional strategies and practices Web-quest Reflective journal to meet the individual needs of individuals with disabilities. 1 Content 1 1 5 Scholarly 2 3 Inquiry 2. Identify and implement the Report principles of effective teaching for Reflective journal 7 students with mild/moderate Team work 9 disabilities in content area Quiz curriculum. 2 Pedagogy 6 Problem Solving 6 3 7 4 9 3. Document student progress and use student data to monitor progress and Report facilitate decision-making Site visit report 10 In-class assignments, 2 Pedagogy 2 6 6 Problem Solving 3 7 9 10 Note book (IEP) 4. Develop and evaluate IEP's for Note book (IEP) students with mild/moderate Observation student in disabilities. school In-class assignments. 5 2 Pedagogy 2 1 3 Technology 3 3 7 5 9 1 Content 3 5 2 Pedagogy 4 6 10 5. Perform a task analysis of basic daily living skill. 6. Demonstrate the ability to Note Book (task analysis) Reflective Journal Note Book (design implement specific instructional strategy) strategies, materials, and curriculum Note book (lesson plan: for students with mild/moderate IEP) disabilities, as appropriate. In-class assignments, 7. Describe the elements of curriculum Note Book (task analysis) as they apply to special education Reflective Journal and how this fits with Qatari Note Book (design curriculum standards and national strategy) examinations. Note book (lesson plan) Exam quiz 8. Plan, organize, and implement 2 Pedagogy 2 4 6 Problem 3 5 educational programs appropriate to Reflective Journal Solving 4 6 the cognitive and affective needs of Note Book (design individuals with disabilities strategy) 3 Technology 11 Note Book (task analysis) Note book (lesson plan) Exam quiz 1 Content 1 6 9. Use effective instructional strategies 2 Pedagogy 2 7 to assist individuals with disabilities strategy) 8 Initiative 3 to detect and correct errors in oral Note book (lesson plan) and written language. Exam quiz 1 Content 2 2 Pedagogy 3 8 10. Use appropriate instructional Note Book (design Note Book (design strategies to teach math skills and strategy) 7 Ethical Values concepts according to the Note book (lesson plan) 8 Initiative characteristics of the learner and Exam quiz patterns of error. Open book exam In-class assignments, 1 Content 7 6 2 Pedagogy 12 7 11. Modify pace of instruction and use organization cues. Note book (IEP) Report Class activities 2 Pedagogy 7 2 12. Integrate appropriate teaching 7 Ethical Values 11 3 strategies and instructional an instructional method; 8 Initiative 12 8 approaches to provide effective Note book (IEP) instruction in academic and Report nonacademic areas for individuals Class activities: with disabilities. Observation student in Mini researches report-on school 6 COURSE OUTLINE Week 1 Course overview and syllabus Course introduction, syllabus review Special education and inclusive schooling Computer -research expedition Week 2 Creating Learning Opportunities for Students With Severe Disabilities in Inclusive Classrooms Applications. Providing Support for Student Independence Through Scaffolded Instruction Video. Course Participation routine Week 3 Models of Teaching Children with disabilities. (Cooperative Groups Engaging Elementary Students With Pragmatic Language Impairments) Strategies for Tactile Learners. Video Week 4 Instructional strategies ( IPE) how to write the IEP Application, Sample of case study, training to write the IEP in class Week 5 & 6 7 Planning for lesson in ED. Goal, ILOs. Application for Lesson Plan. Video Demystifying the IEP Process for Diverse Parents of Children With Disabilities Week 7 How to reach teach children with ADD/ ADHD Practical techniques, strategies and interventions Video Week 8 Mid Semester Examination Helping Students Who Are Deaf or Hard of Hearing Succeed Week 9 Instructional strategies for the autistics children, Reading, Differentiated instruction concept (Autism, Autobiography, and Adaptations) Developing Children’s Oral Language Skills Through Dialogic Reading Training in class to design the strategies. Application( case study, lesson plan) Week 10 Instructional strategies in the content areas, Writing , (Direct Teaching), Content Enhancement Routines Week 11 Teaching adolescents with special needs 8 Course, unit, and lesson organizers Self-advocacy strategy, Reciprocal Teaching. Watching Video Week 12 Mathematics Teaching Strategies, (going beyond math wars) Linking assessment to strategies in special education Enhancing Core Mathematics Instruction for Students At Risk for Mathematics Disabilities Cooperation Building Strategies Students Presentations, sharing Week 13 Remedial Teaching. Resources Room. Students Presentations, sharing Week 14 Final Exam 9 Web-quest 5% TaskStream IEP 10% TaskStream Three strategies & 15% TaskStream Task analysis 2 Reflective Journals 5% observation 10% Quiz 10% Mid exam 15% Final exam 30% GRADING SYSTEM A = 100 - 90 B+ = 89.99 - 85 B = 84.99 - 80 C+ = 79.99 - 75 C = 74.99 - 70 D+ = 69.99 - 65 D = 64.99 - 60 F = 59.99 - 0 10 SPECIAL NEEDS In accordance with Law No 2 of the year 2004, and Article 49 in the Constitution of Qatar: "Education is the right of all.", and "the State shall extend efforts to achieve fair and appropriate access in education for all". Qatar University seeks to ensure fair and appropriate access to programs, services, facilities, and activities for students with special needs. Any student who feels s/he may need an accommodation based on the impact of a disability should contact the instructor privately to discuss your specific needs. Please contact the Office for Disability Services to coordinate reasonable accommodations for students with documented disabilities. Special Needs Section Student Activities building Men’s Campus: 44033854, Fax: 44838925; Women’s Campus: 44033843, Fax: specialneeds@qu.edu.qa; Office hours: 7:30 AM – 2:30 PM 44839802; Email: STUDENT COMPLAINTS POLICY Students at Qatar University have the right to pursue complaints related to faculty, staff, and other students. The nature of the complaints may be either academic or non-academic. For more information about the policy and processes related to this policy, you may refer to the students’ handbook. ACADEMIC HONESTY Qatar University is an academic community actively engaged in scholarly pursuits. As members of this community, students are expected to recognize and honor standards of academic and intellectual integrity. The College of Education supports the ideals of scholarship and fairness by rejecting all dishonest work when it is submitted for academic credit. Qatar University encourages students to be responsible and accountable for their decisions and actions. Any attempt by students to present the work of others as their own or to pass an examination by improper means is regarded as a most serious offense and renders those students who do so liable to disciplinary action. Assisting another student in any such dishonesty, or knowing of this dishonesty and not reporting it, is also considered a grave breach of honesty. Academic dishonesty and plagiarism are described on page 37 in the Qatar University Student Handbook. LEARNING SUPPORT Qatar University operates Learning Support Centers on each campus to provide services to students to supplement their in-class instruction and ability to meet course requirements. These services include tutoring, acquiring efficient learning skills and strategies, academic and learning assessment (in conjunction with the Counseling Center), and writing labs and workshops. Information about the Learning Center may be found at: http://www.qu.edu.qa/students/services/slsc/ REFERENCES Patricia Howlin, Simon Baron-Cohen & Julia Hadwin (2006).Teaching Children with Autism to Mind – Read, a Practical Guide. New York, Willy & Sons Press. Philip Abrams & Leslie Henrique (2006). The Autistics Spectrum, A work book of you and your child. Berkeley, CA, Ulysses Press. Polloway, E. A., Patton, J. R., and Serna, L. (2005). Strategies for teaching learners with special needs, 8th Ed. Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA: Allyn & Bacon Co. Putnam, J. W. (2001). Cooperative Learning and Strategies for Inclusion. Celebrating Diversity in the Classroom. 2nd, Brookes Publishing. Sabornie, E. J. & de Bettencourt, L .U. (2004). Teaching students with mild and high-incidence disabilities at the secondary level, 2nd Ed. Upper Saddle River, NJ. USA: Pearson, Merrill/ Prentice- Hall Co. السططلة: الريططا. ط وع، اططباب، وحططر ال رألططة لططدب اه ططاج، اضطططران ص ططن ااصتبططاط.)2002( جمددال مامددد، الحامددد .إصدارات ألاديمية التربية الخاصة . عالم الكتب: ال اهرة. االيب التعلم لأل اج ذوي ااحتيا ات الخاصة.)2005( رفعت محمود بهجات . دار ال ح: دبي. ال راءة والكتابة، صعوبات التعلم.)2006( صالح عميرة علي عبد الناصر أنيس عبدد الوادا ( .)2003الصطعوبات الخاصطة حطي الطتعلم ،اهاطظ النظريطة والت.خيصطية .السطلة اطيكولو ية اه اج غير العاديين( ،)1ال اهرة :دار الوحاء لدصيا الطباعة والن.ر. كمال عبد الحميد زيتون( .)2003التدريظ لذوي ااحتيا ات الخاصة .ال اهرة :عالم الكتب. محمد عبد المطلب جاد( .)2003صعوبات التعلم حي اللغة العربية .ال اهرة :دار ال كر العربي. عبد الفتاح مافظ ،نبيل ( .)2002صعوبات التعلم ،والتعليم الع ي ،ال اهرة :مكتبة زهراء ال.رق. مورتيمير ،انا ( .)2004تعليم ذوي ااحتيا ات حي انوات العمر اهولى .تر مة\ : \ خالد توحيق & خميظ حسن .ال اهرة :ه للن.ر والتوزيع ( .سلسلة كتب في موضوعات تعليم ذوي االمتياجات الخاصة) القبالي ،يحيى ( .)2004مدخل إلى صعوبات التعلم. ،2ال اهرة :دار الطريق للن.ر والتوزيع. Web sites www.athealth.com http://www.werathah.com http://www.vocationallearning.org.u http://www.ldresources.com http://www.idebate.org/main/home.asp http://www.psychtest.com http://www.ldonline.org http://www.lewisschool.org http://www-hoover.stanford.edu http://www.nild.net Disclaimer instructor may modify the syllabus if it is in the best interest of the students Qatar National Professional Standards for Teachers 1) Structure innovative and flexible learning experiences for individuals and groups of students. 2) Use teaching strategies and resources to engage students in effective learning. 3) Foster language literacy and numeracy development. 4) Create safe, supportive, and challenging learning environments. 5) Construct learning experiences that connect with the world beyond school. 6) Apply information and communication technology in managing student learning. 7) Assess and report on student learning. 8) Apply teaching/subject area knowledge to support student learning. 9) Work as a member of professional teams. 10) Build partnerships with families and the community. 11) Reflect on, evaluate, and improve professional practice. In accordance with Law No 2 of the year 2004, and Article 49 in the Constitution of Qatar: "Education is the right of all.", and "the State shall extend efforts to achieve fair and appropriate access in education for all". Qatar University seeks to ensure fair and appropriate access to programs, services, facilities, and activities for students with special needs. Any student who feels s/he may need an accommodation based on the impact of a disability should contact the instructor privately to discuss your specific needs. Please contact the Office for Disability Services to coordinate reasonable accommodations for students with documented disabilities.