Critical thinking - Assuring Graduate Capabilities
advertisement

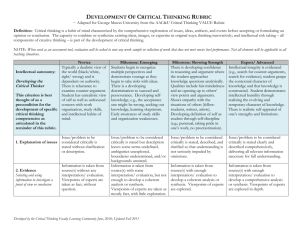
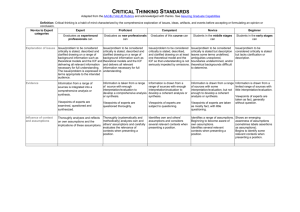
CRITICAL THINKING STANDARDS — MARKETING — UNISA Adapted from the AAC&U VALUE Rubrics and acknowledged with thanks. See Assuring Graduate Capabilities Definition: Critical thinking is a habit of mind characterized by the comprehensive exploration of issues, ideas, artifacts, and events before accepting or formulating an opinion or conclusion. Novice to Competent categories Explanation of issues Beginner Students after their first year can … Novice Students after their second year can … Identify key issues in a routine marketing-related situation, and describe and provide superficial explanation of those issues. Identify key issues in a routine marketing-related situation and provide a reasonable explanation of those issues, but not necessarily using all relevant theory to support that explanation. Evidence Obtain most relevant information from source(s), but Selecting and using information to without providing interpretation or evaluation, and investigate a point of view or conclusion without questioning viewpoints of experts. Competent Graduates can … Identify and prioritise key issues in a routine marketing-related situation, and provide a clear explanation of those issues, using relevant theory and real or hypothetical examples to support that explanation. Obtain relevant information from source(s), but Obtain relevant information from source(s), providing without providing sufficient interpretation or sufficient interpretation or evaluation to enable a evaluation to enable a coherent analysis, and with little coherent analysis or synthesis, and with appropriate questioning of viewpoints of experts. questioning of viewpoints of experts. Influence of assumptions and context Show some awareness of assumptions or context when Show reasonable awareness of assumptions and presenting an opinion. context when presenting an opinion. Student's position (perspective, hypothesis) State a specific position (perspective) which is somewhat obvious and simplistic. State a specific position which acknowledges different State a specific position (perspective or hypothesis) facets of an issue or situation. which takes into account the complexities of an issue and the viewpoints of others. Conclusions and related outcomes (implications and consequences) Provide a conclusion that is incompletely or inconsistently linked to the information provided, with related outcomes (consequences and implications) being over-simplified. Provide a conclusion that is logically linked to some of the information provided (because information is selected to fit the desired conclusion), with some related outcomes being identified. Exemplars Identify some limitations in the performance of a Read an academic article or listen to a lecture marketing campaign or salesperson within a case and identify supporting or conflicting arguments or study, having failed to recognise the importance of ideas from the course content or other sources. some key case information, and therefore providing an inadequate analysis of the overall performance. Support for this resource has been provided by the Australian Learning and Teaching Council Ltd, an initiative of the Australian Government. Identify own and others' assumptions and several relevant contexts when presenting an opinion. Provide a conclusion logically linked to the full range of information provided, including opposing viewpoints, with related outcomes being identified reasonably clearly. Collect relevant data after being presented a situation, and then provide a coherent argument to support a recommendation relevant to that situation, using the data as evidence within the argument.