What you need to know
advertisement

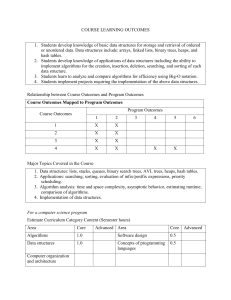
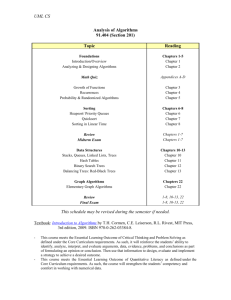
Computing and Algorithms: What you Need to Know Items in blue color have been discussed in previous courses Items with yellow background have been discussed this semester A. Computers and Programming a. Von Neumann architecture b. Number systems, Binary number system, c. Basic idea what operating systems do d. Basic idea how programs are executed e. If statements, while, do-while and for loops (150) f. Array processing, 1D and 2D (150) g. Classes and objects, return values, pass by reference, pass by value (150, 155) h. Static and non-static methods i. Recursive methods (150, 155) (150, 155, 250) B. Data structures Be able to describe the defining features of each structure, its basic operations and their complexity, how it can be implemented a. Linked lists, doubly linked lists. Basic operations, complexity (155) b. Stacks, with linked nodes and with arrays, Basic operations, complexity of basic operations (155) c. Queues, linked nodes and with arrays Basic operations, complexity of basic operations (155) d. Circular arrays (155) e. Trees, Binary trees, Binary search trees, tree traversals Binary nodes, basic operations (155) 1 f. Sets, Bags, Maps, Dictionaries (155) g. AVL trees (250) h. Hash tables, creating and search, complexity (250) i. Binary heaps, priority queues implemented with binary heaps, Basic operations, complexity (250) j. Graphs, graph representation, graph algorithms (see C(c) below) (250) C. Algorithms Be able to describe how each algorithm works and its complexity. Be able to identify algorithms given their pseudocode. a. Search: linear search and search in a sorted array, Binary tree search (150, 155) b. Sorting Be able to state the application of each algorithms, whether it is recursive or not, and memory requirements i. Simple sorts: insertion, selection, bubble sort ii. Advanced sorting: 1. Merge sort 2. Quick sort 3. Heap sort 4. Shell sort (150, 155) (155) (155 ) (250) (250) c. Graph algorithms i. Topological sort and scheduling networks ii. Shortest path algorithms iii. Minimal spanning trees (250) (250) (250) d. Huffman codes e. Set algorithms – subset generation (250) (250) 2 D. Design methods (250) Be able to describe each design method and give examples of algorithms developed with that method a. b. c. d. e. f. g. h. i. j. Brute force and exhaustive search Divide and conquer Decrease and conquer Transform and conquer Genetic algorithms Greedy algorithms Branch and bound Dynamic programming Iterative improvement Space and time tradeoffs E. Algorithm analysis a. b. c. d. e. (250) Big O notation, Theta and omega, be able to manipulate Big O expressions Analyzing loops Analyzing recursive methods with recurrence relations Solving recurrence relations NP problems F. Some other stuff, not studied in cmsc 250 a. Databases b. Web programming, client-server computing, networking c. Basic idea about methods in Artificial Intelligence d. Basic idea about computability, Finite State Automata, Turing machines 3