History of the Earth Guided Notes pg. 176 in Life Science Book
advertisement

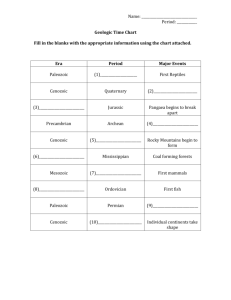
History of the Earth Guided Notes pg. 176 in Life Science Book 1. Fossils- traces or imprints of living things, such as animals, plants, bacteria, and fungi that are preserved in rock. 2. How do paleontologists figure out the age of a fossil? Relative dating or absolute dating 3. Principle of Superposition- This principle states that in a sequence of undisturbed sedimentary layers or lava flows, the oldest layers are at the bottom. 4. Relative dating- look at a cross section of sedimentary rock - Oldest layer is on the bottom - Examine the sequence of fossils starting at the bottom 5. Absolute dating- Force holds atoms together; if there isn’t enough force to hold them together, the atom is considered unstable - Unstable atoms decay by releasing energy, particles or both - Each kind of unstable atom decays at its own rate. 6. Half-life- time it takes half of the unstable atom in a sample to decay. - Half-life range from fractions of a second to billions of years 7. How do you find the half life of a fossil? Measuring the ratio of unstable atoms to stable atoms, scientist determine the approximate age 8. Geologic Time Scale- scientist use to outline the history of life on earth - Scientists used fossils and absolute dating to make this scale - Paleontologists divided the scale up into big categories called eras 9. Era- characterized by the type of animal that dominated the earth at that time - Examples: Mesozoic Era: dinosaurs reptiles (Age of the Reptile) 10. Mass extinction- large number of species died out at the same time - Scientists aren’t sure what causes a mass extinction 11. How do scientists believe mass extinction can happen? Major changes in Earth’s climate or atmosphere - Climate could have changed because of movement of continents or all dinosaurs died out because a meteorite could have collided with Earth causing major climate changes. 12. Pangaea- “supercontinent” - All the continents were together at one time 13. What do plate tectonics cause animals to do? Causes animals to adapt or they will not survive. Eras 1. Precambrian Time- 4.6 billion years ago-540 million years ago -life began and transformed the planet 2. What was the atmosphere made of during this time period? Atmosphere lacked oxygen, rich in other gases like carbon monoxide, carbon dioxide, hydrogen, and nitrogen 3. If I was to picture what earth look like at that time, what would I see? Pictured as a place of great turmoil - Meteorites crashing, violent thunderstorms and volcanic eruptions were constant - Intense radiation from the sun 4. How did the first forms of life develop during the Precambrian era? Scientists think life developed from nonliving matter -chemicals that already existed in the environment (water, clay, dissolved material, gases present) -energy was present on Earth; chemicals reacted with one another and formed complex molecules making life possible -time passed and prokaryotes formed (they have no nucleus) -these prokaryotes were anaerobic (they did not require oxygen to survive) -these prokaryotes made their own food through photosynthesis -through the process of photosynthesis, oxygen was released -this changed Earth’s atmosphere forever 5. What is a radiation shield and how does it make a huge impact on how our earth is today? As the atmosphere filled with oxygen, this helped to form the radiation shield (this is also known as the ozone layer) -the ozone layers purpose is to absorb UV radiation -before the ozone layer, underground and under the ocean was the only way for survival -ozone layer allowed thing the ability to live on land 6. By the end of the Precambrian era, what has developed on earth? -at the 1 billion years mark, eukaryotes formed (they have a nucleus, more complex structure and bigger organism) -over the next 2.5 billion years, scientists think they kept evolving to form more complexed organisms 7. Paleozoic Era- 540 million years ago-248 million years ago 8. What has developed during this era? Plants, fungi, air-breathing animals on dry land - Huge forests covered earth by the end of this era - All major plant groups besides flowering plants appeared during this era 9. By the end of this era, how has life on earth changed? Crawling insects were the first animals followed by salamander like animals -near the end of this era, reptiles, winged insects and dragonflies appeared - Largest mass extinction happened during this period where 90% of marine species died out 10. Mesozoic Era- 248 million years ago-183 million years ago 11. What has developed during this era? -Age of the Reptile because of the burst of evolution from surviving reptiles 12. This era is known as the Age of the __Reptile_________. Why? Dinosaurs dominated Earth for 150 million years 13. What made their appearances during this period? - Large marine lizards appeared - First birds appeared during this time - Most important plant was the cone-bearing seed plant formed large forests - Flowering plants made their appearance 14. What happened at the end of this era? The dinosaurs and others became extinct 15. What is the dinosaur theory? Meteorite hit Earth; this generated a giant dust cloud with enough heat to cause worldwide fires - When this happened, the dust cloud block out the sunlight from getting to the plants so they died. - After the plants died, the plant eating dinosaurs died - After the plant eating dinosaurs died, the meat eating dinosaurs died - Only species able to survive were small mammals that were able to burrow underground 16. Cenozoic era- 65 million years ago-present 17. What has developed during this era? - Fossils are embedded in rock layers so we know the most about this era - Many mammals, birds, insects, and flowering plants appeared 18. This era is considered the Age of _____Mammal_____. - Mammals came to dominate - Mastodons, saber-tooth cats, giant sloths and small horses are some examples