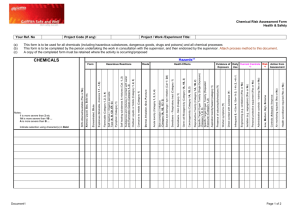
Biological Evaluation Main Focus This section focuses on the results
advertisement

Biological Evaluation Main Focus This section focuses on the results of different in vitro biological experiments of several drugs. B.1 Chronic Aerobic Toxicity Chronic aerobic cytotoxicities were determined to be the maximal concentration of drug showing no toxicity towards CHO cells after 8 day exposure period. o Cells suspended in 1ml growth medium o Same number cells per well o Drug solutions made in phosphate buffer and added to every other well for control o After 8 days excess fluid poured off and cells stained with methylene blue Retention of stain indication of viable cell colony First well to retain full stain is considered to be the maximum concentration with no cytotoxicity. The more toxic a compound is, the lower the concentration required to give toxicity. P-series (alkyl phenanthridinium DNA targeting moieties alone) exhibited increasing toxicity with increasing chain length. 2-NLP series show decreasing toxicity op to a chain length of 4 carbon atoms separating the DNA binding phenanthridinium group from the nitroimidazole. Compounds designed to test the effects of electron affinity and structure on biological function showed that nitrofuran derivatives are the most toxic, while the least toxic are the 4nitroimidazoles. B.2 Acute Aerobic and Hypoxic Toxicity Acute toxicities measured at 0.5mM drug concentrations Used clonogenic assay (ability of cells to form colonies after exposure to xenobiotic agent)under both aerobic and hypoxic conditions. Aliquots of cells removed every 30min or hour and diluted to essentially zero drug concentration in fresh growth medium; then incubated in petri dishes for eight days before staining. Comparison of time of drug exposure to 10% survival was graphed, shorter times indicate greater toxicity. DNA targeting moieties o Toxicity seen in two compounds with longest chain length, with P-6 being more toxic than P-5. o No appreciable toxicity in the rest. o No selective toxicity due to lack of bioreductible moiety (comparison between aerobic and hypoxic) DNA targeted 2-nitroimidazole drugs o Significant level of hypoxia selective toxicity o Under both conditions toxicity appears to decrease with increasing chain length Trend mostly observed, 2-NLP-6 is an exception Compounds testing reduction potential o Nitrofuran derivative has no aerobic toxicity but high hypoxic toxicity o Amide analogue is more toxic in air and only slightly more toxic in hypoxic conditions o FEP-2, FAP-2, 2-NLP-3, and 5-NLP-3 show good selectivity to hypoxic conditions B.3 Radiosensitization CHO cells exposed to 0.5mM drug solutions shortly prior to irradiation with 60Co gamma ray Cells collected and plated DNA targeting moieties o P-2 to P-6 showed no radiosensitization o The rest of the compounds show significant radiosensitization at 0.5mM B.3.1 Radiosensitizing Efficiency – C1.6 Concentration of radiosensitizer required to enhance ratios of 1.6 Lower value means the more efficient a compound is at making tumor susceptible to radiation 2-NLP-2 to 2-NLP-4 have lowest C1.6 mM values, apporx 0.1mM FEP-2 has the greatest, least efficient. Approx. 0.38mM Oxygen has a C1.6 of 0.005mM B.4 In Vitro Therapeutic Index (chronic aerobic toxicity/C1.6) Higher the ratio the larger margin between concentrations that are required to give a defined level of radiosensitization and unwanted toxicity Results show 2-NLP-4 as most promising compound in terms of therapeutic index, approx. 2 FEP-2 has the poorest, approx. 0.3