AP Physics Test Review Problem #1: Either a lens or mirror. Draw
advertisement

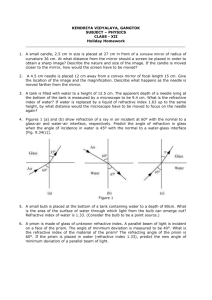
AP Physics Test Review Problem #1: Either a lens or mirror. Draw ray diagrams and use math to locate/describe image. Something similar to this one! A thin converging lens of focal length 10 cm is used as a simple magnifier to examine an object A that is held 6 cm from the lens. (a) On the figure below, draw a ray diagram showing the position and size of the image formed. (b) State whether the image is real or virtual. Explain your reasoning. (c) Calculate the distance of the image from the center of the lens. (d) Calculate the ratio of the image size to the object size. (e), The object A is now moved to the right from x = 6 cm to a position of x = 20 cm, as shown above. Describe the image position, size, and orientation when the object is at x = 20 cm Problem #2: A young’s experiment problem Light with frequency f hits 2 slits that are .3 mm apart. The resulting interference pattern is shown on a screen 4 m away. The bright bands are 2 mm apart. 1. Why is Young’s Experiment important to our understanding of light behavior? 2. What is the wavelength of the light? 3. Sketch the interference pattern and lab set up. Mark a spot with the letter P for which the path difference is 2 wavelengths. Mark another with Q that the path difference is 0.5 wavelengths. 4. How could you alter the experiment to make the bright spots father apart? Problem #3: Refraction Problem The triangular prism shown in Figure I above has index of refraction 1.5 and angles of 37°, 53°, and 90°. The shortest side of the prism is set on a horizontal table. A beam of light, initially horizontal, is incident on the prism from the left. a. On Figure I above, sketch the path of the beam as it passes through and emerges from the prism. b. Determine the angle with respect to the horizontal (angle of deviation) of the beam as it emerges from the prism. c. The prism is replaced by a new prism of the same shape, which is set in the same position. The beam experiences total internal reflection at the right surface of this prism. What is the minimum possible index of refraction of this prism? The new prism having the index of refraction found in part (c) is then completely submerged in water (index of refraction = 1.33) as shown in Figure II below. A horizontal beam of light is again incident from the left. d. On Figure II, sketch the path of the beam as it passes through and emerges from the prism. e. Determine the angle with respect to the horizontal (angle of deviation) of the beam as it emerges from the prism. Problem #4: Resonance/ like our lab problem. The room temp today is a balmy 350 C. You are doing the lab where you raise and lower the water level in a tube to find the resonances. You are using a 440 Hz tuning fork. What is the speed of sound in the room today? What is the wavelength of the sound produced by the tuning fork? How far apart will your resonances be located? If one is found at 0.25 m…where will the next one be found? MC Mirrors & Lenses: Do you know the relationship between the focus and center of curvature? Where does a very distant object produce its image? Can you correctly choose the image in a plane mirror? Do you know what an image looks like in a concave mirror when it is placed anywhere? Before F, between f and C etc. Do you know what an image looks like in a convex lens when it is placed anywhere? Before F, between f and C etc Do you know which type of lens/ mirrors in converging? Diverging? Can you use the thin lens equation to solve for image location? Can you find the magnification of a lens or mirror? Do you know the applications of lenses and mirrors? Resonance/Sound/Standing Waves Do you know the relationship between overtones and frequencies for strings, open pipes or closed pipes? What type of a wave is sound? Given a standing waves can you find wavelength? IF given frequency…then speed? Light/Interference/Waves Do you know what type of wave light is? Can you identify what two waves will look like when they interfere? Can you use the equations to determine the separation of sources for a 2-d interference pattern? Do you know what happens to a wave when it crosses a barrier? What stays the same? What changes? Are you familiar with Doppler shift? The diagrams? Use the wave equation to solve for wavelength? Know the electromagnetic spectrum? They all travel at the speed of light. Refraction Know which way light bends? Looking at which way it bends, determine larger or smaller index of refraction Solve for critical angle