Flash Cards
advertisement

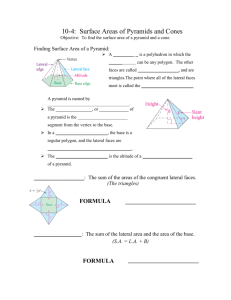
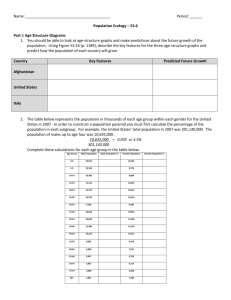
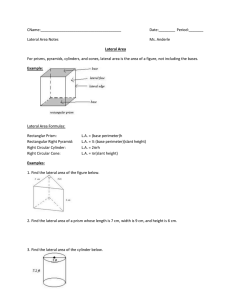
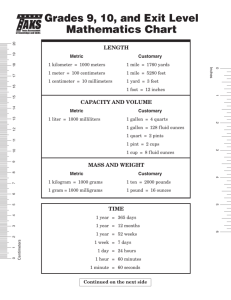
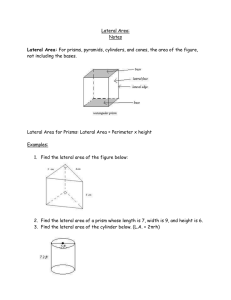
Lateral Surface Area Total Surface Area Regular Pyramid Slant Height The sum of all the areas of a solids lateral faces The sum of all the areas of a solid’s sides. A pyramid whose base is a regular polygon. The lateral faces of a regular pyramid are congruent isosceles triangles, which intersect at the pyramid’s vertex. The altitude or height of each lateral face of a pyramid. Similar Solids Solids that have the same shape and their corresponding linear measures are proportional. Outcome Any of the possible results of an action Event One outcome or collection of outcomes Sample Space An organized list of outcomes. Used to determine the total number of possible outcomes for an event. Tree Diagram A specific type of an organized list Fundamental Counting Principle Random Composite Experiment Uses multiplication of the number of ways each event in an experiment can occur to find the number of possible outcomes in a sample space. Outcomes occur at random if each outcome is equally likely to occur. An event that consists of two or more simple events. Independent Events Dependent Events Two or more events in which the outcome of the event does not affect the outcome of the other event(s) Two or more events in which the outcome of one event does affect the outcome of the other event or events Experimental Probability An estimated probability based on the relative frequency of positive outcomes occurring during an experiment Theoretical Probability Probability based on known characteristics or facts. Simulation An experiment that is designed to act out a given situation Sample A randomly-selected group chosen for the purpose of collecting data Population Unbiased Sample Simple Random Sample Stratified Random Sample The entire group of items or individuals from which the samples under consideration are taken A sample that is selected so that it is representative of the entire populations Each item or person in the population is as likely to be chosen as any other. The population is divided into similar, non-overlapping groups. A simple random sample is then selected from each group. Systematic Random Sample The items or people are selected according to a specific time or interval Biased Sample One or more parts of the population are favored over the others Convenience Sample A sample that includes members of a population that are easily accessed. Voluntary Response Sample A voluntary response sample involves only those who want to participate in the sample. Histogram A type of bar graph used to display numerical data that have been organized into equal intervals. Circle Graph A graph used to compare parts of a data set to the whole set of the data. The entire circle represents the whole set, so the percents in a circle graph add up to 100. Measure of Central Tendency Measure of Variation Numbers that describe the center of the set of data. The most common measures are: Mode: number occurring most often Mean: sum of all the data divided by the number of items in the set Range: difference between the greatest number and the least number in the set Median: middle number of an ordered set Used to describe the distribution or spread of the data set.