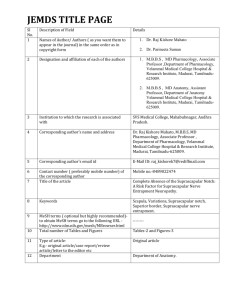
Graduate Programme in Health and Social Sciences.
advertisement
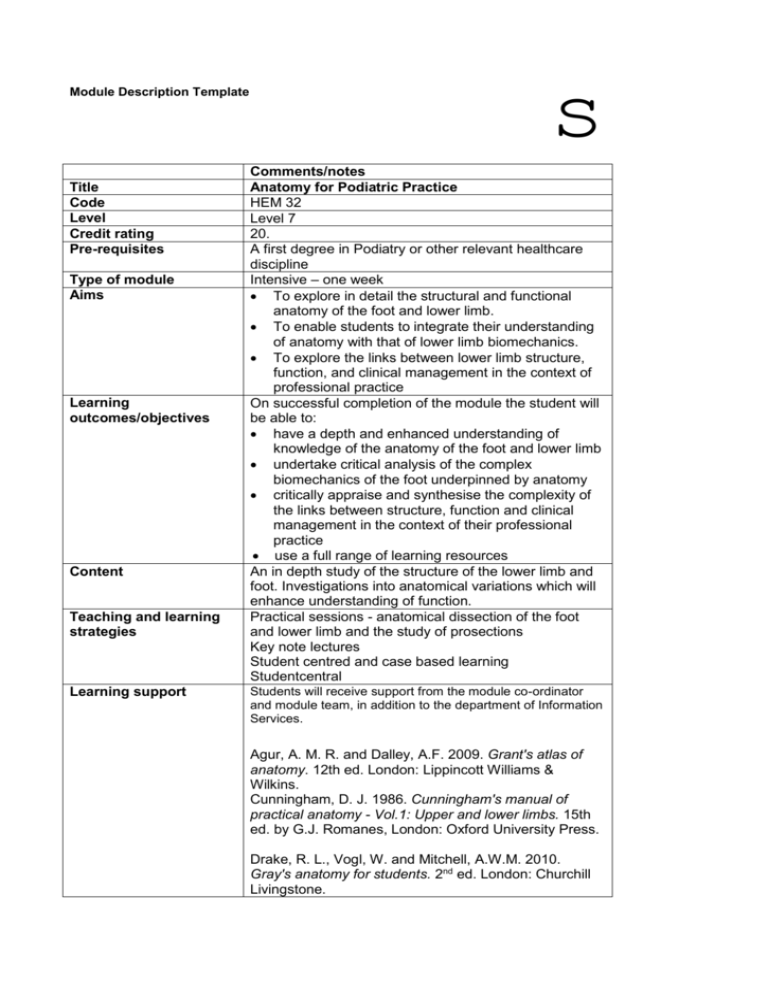
Module Description Template Title Code Level Credit rating Pre-requisites Type of module Aims Learning outcomes/objectives Content Teaching and learning strategies Learning support s Comments/notes Anatomy for Podiatric Practice HEM 32 Level 7 20. A first degree in Podiatry or other relevant healthcare discipline Intensive – one week To explore in detail the structural and functional anatomy of the foot and lower limb. To enable students to integrate their understanding of anatomy with that of lower limb biomechanics. To explore the links between lower limb structure, function, and clinical management in the context of professional practice On successful completion of the module the student will be able to: have a depth and enhanced understanding of knowledge of the anatomy of the foot and lower limb undertake critical analysis of the complex biomechanics of the foot underpinned by anatomy critically appraise and synthesise the complexity of the links between structure, function and clinical management in the context of their professional practice use a full range of learning resources An in depth study of the structure of the lower limb and foot. Investigations into anatomical variations which will enhance understanding of function. Practical sessions - anatomical dissection of the foot and lower limb and the study of prosections Key note lectures Student centred and case based learning Studentcentral Students will receive support from the module co-ordinator and module team, in addition to the department of Information Services. Agur, A. M. R. and Dalley, A.F. 2009. Grant's atlas of anatomy. 12th ed. London: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. Cunningham, D. J. 1986. Cunningham's manual of practical anatomy - Vol.1: Upper and lower limbs. 15th ed. by G.J. Romanes, London: Oxford University Press. Drake, R. L., Vogl, W. and Mitchell, A.W.M. 2010. Gray's anatomy for students. 2nd ed. London: Churchill Livingstone. Assessment tasks Brief description of module content and/or aims (maximum 80 words) Area examination board to which module relates Module coordinator Semester offered, where appropriate Site where delivered Date of first approval Date of last revision Date of approval of this version Version number Replacement for previous module Course(s) for which module is acceptable and status in that course School home External examiner Gilroy, A. M., MacPherson, B. R., and Ross, L. M. 2008. Atlas of Anatomy. New York: Thieme. Gosling, J.A., Harris, P.F., Willan, P.L.T. and Whitmore, I. 2008. Human anatomy. 5th ed. London: Mosby-Wolfe. Logan, B. M., Singh, D. and Hutchings, R. T. 2004. McMinn's color atlas of foot and ankle anatomy. 3rd ed. London: Mosby. Palastanga, N, Field D. and Soames R.W. 2006. Anatomy and human movement: structure and function. 5th ed. Oxford: Butterworth-Heinemann. Schuenke, M., Schulte, E., and Schumacher, U. 2006. Atlas of Anatomy series: General anatomy and musculoskeletal system. New York: Thieme. Students will be required to submit a 3000 word portfolio comprising two case studies which will critically evaluate the anatomical considerations which may influence surgical or other intervention. (100% of final weighting) This assessment will cover all the learning outcomes. A detailed understanding of the anatomy of the lower limb and foot is a fundamental component of clinical competency for many healthcare practitioners. This module enables students to gain enhanced knowledge and understanding of the anatomy of the lower limb and foot in the context of foot biomechanics, surgical intervention and other clinical management. Graduate Programme in Health and Social Sciences Maria Young, Kate Carter Semester 2 Eastbourne December 2000 September 2007 June 2011 3 MSc in the Principles of Podiatric Surgery- core module PGCert/PGDip/MSc Podiatry PGDip/MSc Podiatry with Clinical Biomechanics PGDip/MSc Podiatry with diabetes PGDip/MSc Podiatry with rheumatology – option module School of Health Professions Dr Campbell Wareham 2009-2013 Module Description Template s Title Clinical Pharmacology Code HEM31 Level 7 Credit rating 20 Pre-requisites A first degree in a relevant healthcare discipline Type of module Intensive – one week Aims To enable students to appraise their understanding of the pharmacology of a diverse range of drugs. To allow students to evaluate the process of drug history taking understand the safe, legal and effective access & supply of approved prescription only medicines Learning outcomes/objectives On successful completion of the module students will be able to; 1. review drug prescription in the management of local and systemic disease; 2. analyse critically pharmacological management in the context of professional practice 3. explain the mechanisms underlying adverse drug reactions and recognise the potential for, and the implications of, drug interactions in clinical practice, 4. appreciate their role and the legal implications of administration and supply of approved POM’s to patients Content Relevant ‘normal’ physiology Pharmacokinetics - pharmacokinetic parameters, drug administration, absorption, clearance & excretion Pharmacodynamics - drug receptors and other target molecules - dose / response relationships - agonists and antagonists - therapeutic window - inter-individual variation in drug response, General considerations - adverse drug reactions, drug interactions - drug overdose and poisoning, drug dependency and abuse - effects of disease state on drug response - POM’s and the law - writing orders for drugs, drug schedules, labelling, storage and handling Cardiovascular pharmacology - cardiac glycosides, anti-arrhythmic drugs - diuretics, anti-hypertensive drugs and vasodilators - anti-platelet drugs, anticoagulants -- drugs used in the management of hyperlipidaemia Respiratory pharmacology - bronchodilator drugs - drugs used in asthma prophylaxis - drugs used in the treatment of allergy - respiratory stimulants Endocrine disorders - drugs used in the management of endocrine disorders - use of corticosteroid drugs as replacement therapy Musculo-skeletal disorders simple analgesics, anti-inflammatory analgesics, opioid analgesics - non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs - disease modifying anti rheumatic drugs Antimicrobial drugs - principles of therapy - factors influencing drug selection and route of administration - systemic and topical preparations, spectrum of activity & appropriate drug use Indicative Reading Books Current British National Formulary Neal MJ 2009 Medical Pharmacology at a glance. Wiley-Blackwell Publications Page CP Hoffman B, Curtis M, Walker M, 2006 Integrated Pharmacology'. Mosby, Harcourt Publishers Rang HP, Dale MM, Ritter JM et al, 2011 Rang & Dales Pharmacology Elsevier Articles McInnes IB, O’Dell JR 2011 State-of-the-art: rheumatoid arthritis Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases 69 1898-1906 29 National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence (NICE) 2009 NICE clinical guideline 79 – Rheumatoid arthritis www.NICE.org.uk/CG79 Stumvoll M, Goldstein BJ, Haeften TW 2005 Type II diabetes: principles of pathogenesis and therapy The Lancet 365 1333-46 Williams B, Pulter NR, Brown MJ et al. 2004 Guidelines for management of hypertension: report of the fourth working party of the British Hypertension Society, 2004 BHS IV Journal of Hypertension 18 139-185 Websites www.fleshandbones.com; www.freemedicaljournals.com; www.bnf.org Teaching and learning Seminars and case presentations strategies Key note lectures Student cantered and case based learning Student central Learning support Students will receive support from the module co-ordinator and module team, in addition to Information Services and student central Assessment tasks Optional for podiatrists requiring HPC entitlement to administer & supply approved POMs □ A 1 hour MCQ examination Mandatory all students wishing to achieve 20 M level credit must pass the following written assessment (LO 1-4) □ A 3000 word case study, discussing the pharmacological management of a patient in their care. Brief description of module This module enables students to study the pharmacology of a broad content and/or aims range of drugs and to consider the relevance of drug prescription in (maximum 80 words) a podiatric context. Successful completion will allow POM entitlement on the HPC register Area examination board to Graduate Programme in Health and Social Sciences. which module relates Module coordinator Simon Otter, Ms Rosie Furner Semester offered, where Semester 1 appropriate Site where delivered Eastbourne Date of first approval December 2000 Date of last revision July 2006 Date of approval of this July 2011 version Version number 3 Replacement for previous module Field for which module is Graduate Programme in Health and Social Sciences acceptable and status in that field Course(s) for which PGCertificate in Podiatric Theory – compulsory module module is acceptable and PGCert/PGDip/MSc Podiatry – option module status in course MSc Podiatry with Clinical Biomechainics/Diabetes/Rheumatology option module School home School of Health Professions External examiner Dr Campbell Wareham 2009-2013