IB MATH HL 12th grade Course Guidelines 2014

IB MATH HL 12
th
grade
Course Guidelines 2014-2015
Instructor:
Bojana Trninic-Radja e-mail: bradja@uplifteducation.org
facebook: MATHHL IBPHYSICS
Tutorials: any time by appointment
Course Description:
This course is designed for the most successful mathematics students who either have a genuine interest in mathematics and enjoy meeting its challenges and problems, or need such mathematics for further studies or related subjects such as physics, engineering, and technology at university level.
This is the second year of the two year IB MATH High Level course, and will cover following topics:
Core
• Algebra
• Functions and equations
• Circular functions and trigonometry
• Matrices
• Vectors
• Statistics and probability
• Calculus
Options
• Statistics and probability
• Sets, relations and groups
• Series and differential equations
• Discrete mathematics
Portfolio
Two individual pieces of work based on mathematical investigation and mathematical modeling
All seven core subjects are required and one of the four options must be chosen.
Assessment:
In High Level IB Math students will be assessed using tests (multiple choice, short- and extended response questions ), quizzes and homework. Students can expect tests to be of same level as the IB examination.
Grading:
Homework Quizzes: 20 %
Major Quizzes: 20 %
Exams: 60 %
Homework
The homework grade: you’ll have quiz on the homework. That will be student’s homework grade.
Major Quizzes and Exams:
Major assessments will most commonly consist of IB-style assessments. Major assessments will receive both a North Hills grade on a 100 point scale and an IB grade on a 7 point scale. The 100-point scale grade is
calculated as part of the quarterly course average and will be posted on Powerschool.. The IB 7 point scale grade is not calculated into the course average, but is included as a predictor as to how students are likely to perform on the IB Math exam in May.
In accordance with NHP’s assessment policy, if a student fails his/her exam they may schedule a re-test to earn up to a
70%. If a student retakes an exam, their second score will stand (up to a 70% max), even if the score is lower than the
first exam score.
Grading:
Homework Quizzes:
Quizzes:
20 %
20 %
Exams: 60 %
IB Assessment
Students’ success in the mathematics higher level course is measured by combining their grades on external and internal assessment. The internal assessment is of each student’s portfolio, which consists of two pieces of work demonstrating ability in mathematical investigation, to highlight that investigation is fundamental to the study of mathematics; and mathematical modeling, to translate a real-world problem into mathematics.
IB External Assessment: (conducted externally by IBO – 80%)
▪ Paper 1 (HL ) 30% of the IB External Assessment grade.
Short- and extended response questions on the core (no calculator allowed)
Time: 120 minutes
▪ Paper 2 (HL) 30% of the IB External Assessment grade.
Short- and extended response questions (with graphic display calculator required)
Time: 120 minutes
▪ Paper 3 (HL) 20% of the IB External Assessment grade.
Option
IB Internal Assessment: 20% of the IB grade.
Tutorials:
Students are strongly encouraged to seek tutorial help the moment they realize they are not mastering key knowledge and skills.
Unit Syllabi:
Unit syllabi covering class activities, exams, projects, readings and other homework for each unit are available online on the IB MATH HL web page. In addition, the syllabus for the first unit is attached to these course guidelines.
Course Web Page:
The course web page is located at www.northhillsprep.org. Simply click on the “Faculty” tab, then
“Radja, Bojana”. In addition to syllabi, class notes, markschemes (rubrics), guidance on the IB MATH
Portfolio, and a variety of other resources are available on the course web page.
TENTATIVE SYLLABUS for first nine weeks
Exponents and logarithms first 2 weeks
▪ Change of base
▪ Laws of Exponents; laws of logarithms
▪ Graph exponential and logarithmic functions
▪ Solve both exponential and logarithmic functions.
Complex numbers next: 3 weeks
▪ real part, imaginary part, conjugate, modulus and argument
▪ Cartesian form z=a + ib (2-D vectors)
▪ Modulus-argument form (polar form)
▪ Sums, products and quotients of complex numbers
▪ De Moivre’s theorem
▪ Powers and roots of a complex number
▪ Conjugate roots of polynomial equations with real coefficients
Mathematical Induction: a week
▪ Proof by mathematical induction (Process of induction and principle od induction)
▪ Indirect proof
▪ Forming conjectures to be proved by mathematical induction
Vectors and planes, Solution of system of linear equations 5 weeks
Solution of Linear Equations
▪Unique solution
▪No solution
▪Infinity of solutions
▪Find solution(s), if any exist, of a set of linear equations using matrix techniques.
▪Write solution(s) as a point, line, or plane.
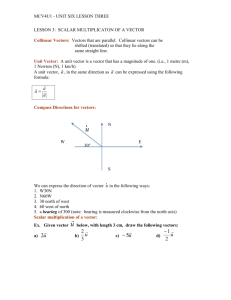
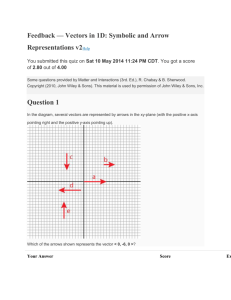
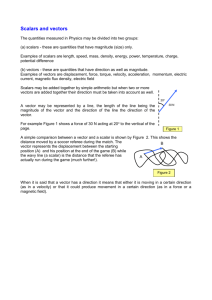
Vectors in Two and Three Dimensions
▪Graph vectors in 2 and 3 dimensions.
▪Represent vectors using vector notation.
Components of a Vector
▪Identify the components of a vector.
Addition and Multiplication of Vectors
▪Add vectors.
▪Multiply vectors by a scalar.
▪Graph the resultant vector.
Length of Vector
▪Calculate the length (magnitude) of a vector.
▪Write down the unit vector for a given vector.
Scalar Products and Projections
▪Calculate the scalar product.
▪Find the angle between 2 vectors using scalar product formula.
▪Prove orthogonality.
Vector Products
▪Calculate the vector product of 2 vectors.
▪Find a 3rd vector that is perpendicular to 2 other vectors.
Geometric Application of the Vector Product
▪Use of the formula involving vector product, magnitudes, and sine of the angle.
Algebra of Scalar and Vector Products .
▪Show that two vectors are orthogonal.
▪Use the formula magnitude of cross product equals the product of the squared magnitudes minus the square of the dot product.
Lines and Planes
▪Express equations of lines and planes in parametric, cartesian, and normal form.
Intersections of:
▪Two lines
▪Line with a plane
▪Two planes
▪Three planes
Distances in Three Dimensions
▪Write expressions and calculate the distance between 2 objects (points, lines, or planes) in 3-d.