CSC 413/513 Introduction to Algorithms
advertisement

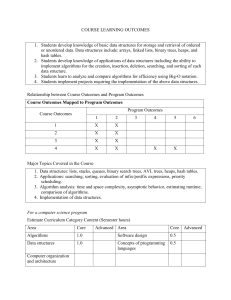
Page 1 of 3 CSC 413/513 Introduction to Algorithms Fall 2014 Instructor: Wonryull Koh Office: TEC 234 Office Hours: TBA Email: wonryull.koh@usm.edu Office Phone: (601) 266 4366 Lecture: Tuesdays, Thursdays 8:00 – 9:15 AM, TEC 202 Textbook: Introduction to Algorithms, Third Edition, by Thomas H. Cormen, Charles E. Leiserson, Ronald L. Rivest and Clifford Stein, MIT Press, 2009 Prerequisites: CSC 307 and Mat 169 or Mat 179 Overview and Objectives Design and analysis of algorithms. Complexity theory. Students learn how to analyze algorithm performance mathematically in addition to learning how a large variety of algorithms work. Students study algorithms with a variety of design strategies including iterative, divide-and-conquer, dynamic programming, and greedy algorithms, so that they will be able to Apply the big-O, Omega, Theta and small-o, omega, theta notations to evaluate and compare the asymptotic running time of different algorithms Solve simple recurrences and use recurrences to evaluate the running time of algorithms Master a variety of sorting algorithms, knowing how they work, how fast they run, how to implement them, and what algorithms should be used in different situations Use hash tables and use open addressing to resolve collisions in hash tables Understand how binary search trees handle the search, insertion, and deletion operations efficiently, and how to maintain a balanced binary search tree Master the classic algorithm design techniques including iteration, recursion, divide-and-conquer, dynamic programming, and greedy algorithms Understand a few preliminary graph algorithms and their applications in computer science, such as topological sorting, minimum spanning trees, and shortest paths Have a preliminary understanding of NP-completeness and reductions, as well as some canonical NP-complete problems Assignments and Grading There will be several programming and written assignments, a midterm exam, and a comprehensive final exam. All assignments will be announced in class. If you cannot turn in an assignment on time, discuss the situation in advance with the instructor. There will be no make-up exams and no late assignments accepted except for “documented absences that are truly beyond the student's control” per the USM Undergraduate Bulletin. Your grade will be based on the following components: assignments 50% – Homework will consist of written problems and programming assignments. Occasionally, the amount and/or type of homework may differ between CSC 413 and CSC 513; Page 2 of 3 additional homework will be assigned to students in CSC 513. exams 50% – a midterm exam and a cumulative final exam, worth 25% each, will be given. Course grades will be assigned according to the following scale: % total points letter grade 90-100 A 80-89 B 70-79 C 60-69 D < 60 F Tentative Topics 1. Foundations The concept and methodology of asymptotic running time analysis. Definitions, meaning, and computation/comparison of the family of big-O notations. Standard complexity classes. Pseudocode. 2. Recurrences Divide-and-conquer, demonstrated with merge-sort. Solving recurrences, and using recurrences to analyze divide-and-conquer algorithms. 3. Sorting Major sorting algorithms, including merge sort, heap sort, and quick sort. The lower bound of sorting. Linear time sorting. 4. Hashing Hash functions, hash tables, and open addressing schemes. 5. Binary Search Trees Binary search trees, with algorithms of search, insertion, and deletion. Balanced binary search tree, demonstrated with red-black trees. 6. Algorithm Design Techniques Dynamic programming, greedy algorithms. 7. Graph Preliminaries Graph terminologies, applications, and representation methods, depth-first search, breadth-first search, and topological sorting. 8. Graph Algorithms Minimum spanning tree: Prim’s and Kruskal’s algorithms, shortest path: Bellman-Ford’s and Dijkstra’s algorithms. 9. NP-Completeness Polynomial time vs. exponential time, NP-completeness and polynomial time reductions, classical NP-complete problems Academic honesty Students are encouraged to collaborate in preparing for the assignments in this class. However, the final work submitted must be the student's own work. A violation of academic honesty will draw severe penalties per the USM Undergraduate Bulletin. Drop Deadlines August 27: Last day to drop without academic/financial penalty; Last day to receive 100% refund; Last day to drop classes without instructor permission August 28 - October 31: All approved drops will result in grade of W within these dates Page 3 of 3 October 31: Last day to make an add/drop course request or withdraw from the University and receive a grade of W ADA Syllabus Statement A student with a disability that qualifies under the American with Disabilities Act (ADA) should contact the Office for Disability Accommodations (ODA). Address: Office of Disability Accommodations 118 College Drive #8586 Hattiesburg, MS 39406-0001 Phone: (601) 266-5024 or (228) 214-3232 Fax: (601) 266-6035 Individuals with hearing impairments can contact ODA using the Mississippi Relay Service at 1-800-5822233 (TTY), or email Suzy Hebert at Suzanne.Hebert@usm.edu