Unit 3: Part 1 Notes Monomials
advertisement

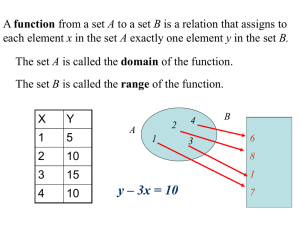
Unit 3: Part 1 Exponents Name: ___________________________ 3-1 Notes -4a Base – Exponent – 3 Coefficient – Exponents are used when we _____________ a number or variable repeatedly. Examples: Write each expression using exponents. 1. 5∙5∙5 3. d∙d∙d∙d∙d∙d 2. p 4. (6)(6)(-7)(-7)(-7)(-7)(-7) * Put negative bases in parentheses. Examples: Write each power as a multiplication expression. 5. 64 6. (-h)3 7. 7a3b2 8. (7a)3 Keystone Questions: Ex 1. What is the value of -4g3h2 when g = 2 and h = 4? Ex 2. What is the value of 2|𝑥 2 + 1| when x = -8? Unit 3: Part 1 Exponents Ex 3. Which of the following inequalities is true when x = 2? A. 2x3 + 5 > 3x2 + 10 B. 4x2 > 4x2 C. 2x2 > (x + 1)2 D. x4 < 3x3 3-1 Practice Write each expression using exponents. 1) 6 ∙ 6 ∙ 6 ∙ 6 ∙ 6 2) 8 x 8 3) x ∙ x 4) (-4)(-4)(-4) 5) a ∙ a ∙ a ∙ b ∙ b 6) 4 ∙ 4 ∙ x ∙ x ∙ y Write each power as a multiplication expression. 7) 93 8) (-5)5 9) 43 ∙ 23 10) m5n3 11) (2x)2 12) 3x2y4 Evaluate each expression if x = 2 and y = -2. 13) x2 14) y2 15) x3 16) y3 17) 2(x + 3)2 18) 4|𝑦| Unit 3: Part 1 Exponents 3-1 Practice Continued Simplify each expression. Show each step. 19) 4(62 - 4∙4)2 21) 52 +15 5+3 20) 8|23 − 32 | 22) 4∙32 – 20 Unit 3: Part 1 Exponents 3-2 Notes Zero Exponent: Anything raised to the power of zero is _____________. 1) 40= 2) x0 = 3) (4xy)0 = 4) (-216)0 = Negative Exponent: A negative exponent is the ______________ of a positive exponent. Since we use positive exponents when we multiply, a negative exponent means to ____________________. 1) 8-1 2) 2-4 3) x-2 4) 2-2 Main Idea. To evaluate a negative exponent, take the __________________ 1 −2 5) ( ) 2 1 −3 6) ( ) 3 Unit 3: Part 1 Exponents “Can’t I just use my calculator?!” Yes.. If you know how to use your calculator correctly. Evaluate each expression using just your calculator. Give each answer as a fraction. 1 2 1. -24 4. 2. 4( ) 3. 4-1 5. 4(2√4)-2 6. ( ) 2 2+7 2−5 1 −2 2 Practice: Set up each problem. Then evaluate each expression for x = 5, y = -1 and z = 4. 1) y 4 2) 3x3 3) 2y 2 4) z 2 5) yz 6) yx 7) x 2 z 2 8) y x 2 3 Unit 3: Part 1 Exponents 3-3 Notes: Multiplying Monomials Write each power as a multiplication expression. 1. Multiply x3 ∙ x4 2. Multiply c2 ∙ c Product of Powers Pattern: When you _________________ powers with the same base you __________________ the exponents. Remember: 1. If you do not see an exponent for a variable there is really a _________ there. 2. Coefficients get _________________ by other coefficients. Examples: Simplify each expression. 1. (21c6)(c7) 2. 8x4 • 3x 3. (2a4)(2a3b2)(-3ba2) Unit 3: Part 1 Exponents You Try! Simplify 1. c4 • c7 2. a • a9 3. c4 • c3 4. c10 • 4c2 5. (-2c 3)(3c12) 6. g(g5) 7. (d2)(d3)(d4) 8. 3y2xy2 9. 4a6b • 2a3 10. p • 3p4 11. yx4 • 3x3y 12. 3m2 • 2m 13. (4a2)(3ba4)(3ab4) 14. x • x3 15. (3n)n2 16. 3k3 • 3k3 17. 2v3 • 4uv 18. (b3)b Unit 3: Part 1 Exponents 3-4 Notes: Power Raised to a Power Write each power as a multiplication expression. 1. (x3)5 2. (2c2)4 Power to a Power Pattern: When you raise a power to a power you __________________ the exponents. Remember: Coefficients must be _____________ to the ___________. GET RID OF ANY EXPONENTS OUTSIDE OF PARENTHESES FIRST! Examples: Simplify each expression. 1. (2x4)3 2. (-2t4)5 3. (a4)(a7) 4. (2p3)2 5. (x4y5)2(-5xy) 6. (3x2y3)(-2x3y4)2 7. (-5mn)2(2mn4)2 8. (-u)4 Unit 3: Part 1 Exponents 3-2 Practice Simplify. 1) (3k)2 2) (3p2)2 3) (x3)2 4) (2n3)2 5) (r2)5 6) (2x2)2 7) (a4b2)2 8) (y2)4 9) (-3m)2 10) (3x4y4)4 11) (4m)4 12) (2yx3)4 13) (2v3)4v2 14) (-2a4)2 ∙ 2a4 15) -2x2 ∙ (2x2)4 16) (2x4)2 17) k4(2k4)4 18) (2a2)3 19) 2vu2 ∙ (v3)4 20) (y3)2 ∙ -2x3y3 21) (-u4)4 ∙ 2uv3 22) yx2 ∙ (yx4)3 23) a2b3 ∙ (2a2b4)4 24) (2x4y3)3 ∙ x2y4 Unit 3: Part 1 Exponents 3-5 Notes Write each power as a multiplication expression. 1. 4c5 = 2c 2 6 x6 y = 8x4 y3 2. Rule: When dividing monomials: ___________ or ________________ the coefficients ________________ the exponents. If the result is a negative exponent move the monomial to where the ____________________ exponent was. Get rid of any exponents ____________ of the parentheses first! Examples: 1. 3. 8m 7 n 5 6mn 2 4𝑎8 𝑏3 𝑐 2 −28𝑎5 𝑏6 𝑐 3 2. 4. 34 a 2b3 32 a5b 16(𝑐 −2 𝑑−1 )−3 4𝑐 3 𝑑3 Unit 3: Part 1 Exponents Recall: Zero Exponent: Anything raised to the zero power is _________. Ex 1. 𝑥2 𝑥2 Ex 2. (3𝑥)0 4 You Try! 1. 3. 3𝑥 5 𝑦2 9𝑥 2 𝑦 5 −10𝑎2 𝑦 5 2𝑎𝑏2 2. 4. −9𝑥 8 𝑦 3 −3𝑥 3 𝑦 3 4𝑥𝑦 2 8𝑥 2 𝑦5 Unit 3: Part 1 Exponents 3-5a Notes: Recall negative exponents. 1) 4-1 2) n-1 Dealing with negative exponents: If the negative exponent is in the numerator, move it to the __________________. If the negative exponents is in the denominator, move it to the ___________________. Simplify each expression. Your answer should contain only positive exponents. 1. 3u 5v 2 = 4vu 3 2. 5 x 4 y 0 = 5x4 3. 16u 2 v = 4u 4 v 4 4. 3x5 y 3 = 4 x 4 y 4 Unit 3: Part 1 Exponents 5. 3a 4b4 = a 2b 6. 4x 4 y 4 = x4 7. 5 p3 15 pm2 q 2 8. 11xy 3 = 22 x3 z 2 9. 5mp 5 pm4 n3 10. 5 x 4 y 5 z 5 = 2 x 2 y 3 z 3 11. 2 xz 4 = 4 x3 y 4 z 5 12. 5 p 4 q5r 0 = 5rq 5 13. x 4 y 3 z 2 3zx 2 y 2 14. 2 a 3b 5 c 5 = 4a 2b 2 Unit 3: Part 1 Exponents Unit 3: Part 1 Exponents