LD50 Graphs & Toxicity Worksheet: High School Biology
advertisement
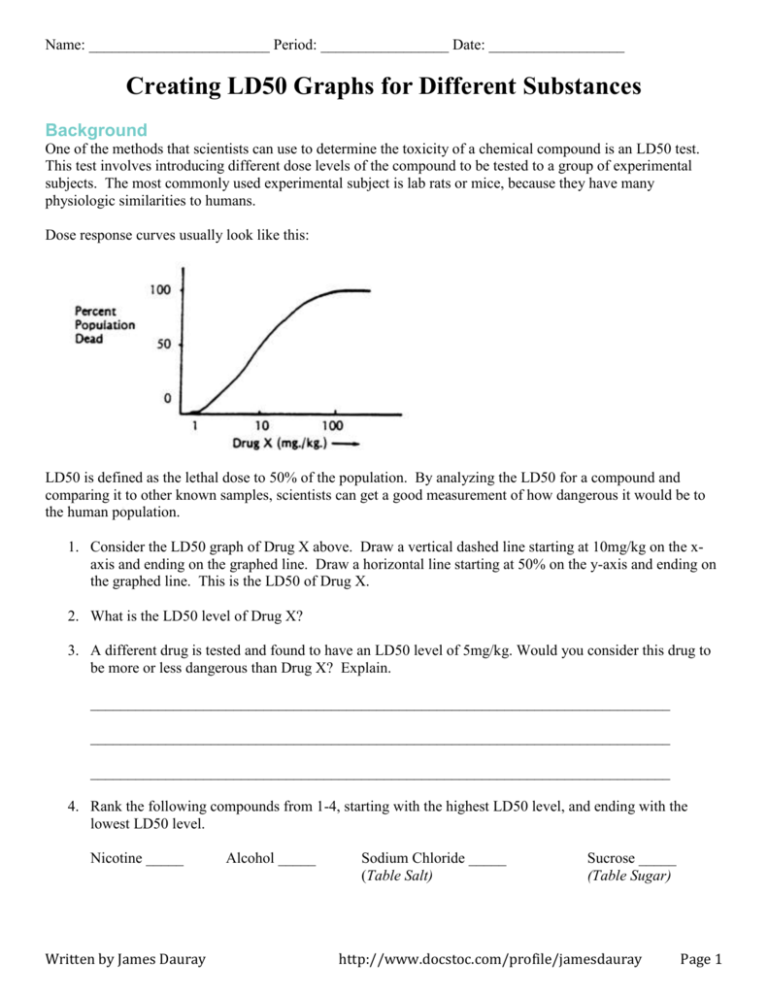
Name: ________________________ Period: _________________ Date: __________________ Creating LD50 Graphs for Different Substances Background One of the methods that scientists can use to determine the toxicity of a chemical compound is an LD50 test. This test involves introducing different dose levels of the compound to be tested to a group of experimental subjects. The most commonly used experimental subject is lab rats or mice, because they have many physiologic similarities to humans. Dose response curves usually look like this: LD50 is defined as the lethal dose to 50% of the population. By analyzing the LD50 for a compound and comparing it to other known samples, scientists can get a good measurement of how dangerous it would be to the human population. 1. Consider the LD50 graph of Drug X above. Draw a vertical dashed line starting at 10mg/kg on the xaxis and ending on the graphed line. Draw a horizontal line starting at 50% on the y-axis and ending on the graphed line. This is the LD50 of Drug X. 2. What is the LD50 level of Drug X? 3. A different drug is tested and found to have an LD50 level of 5mg/kg. Would you consider this drug to be more or less dangerous than Drug X? Explain. _____________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________ 4. Rank the following compounds from 1-4, starting with the highest LD50 level, and ending with the lowest LD50 level. Nicotine _____ Written by James Dauray Alcohol _____ Sodium Chloride _____ (Table Salt) Sucrose _____ (Table Sugar) http://www.docstoc.com/profile/jamesdauray Page 1 Data Analysis Lethal dose data is shown below for two toxic chemical compounds: arsenic and sodium cyanide. Graph each and determine their LD50 levels. Sodium Cyanide Dose Number of Deaths 1 8 2 16 3 30 4 48 5 68 6 89 7 119 8 140 9 173 10 190 Arsenic ( Sample size = 190 ) Death Rate (%) ( Sample size = 210 ) Dose Number of Deaths 2 2 4 6 6 11 8 22 10 41 12 72 14 131 16 198 18 210 Death Rate (%) 5. What is the LD50 of sodium cyanide? _____________________________________________________________________________ 6. What is the LD50 of arsenic? _____________________________________________________________________________ 7. Which is more dangerous based on the data, arsenic, or sodium cyanide? _____________________________________________________________________________ Conclusion 8. Why is LD50 data so useful in dealing with human health and environmental toxins? _____________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________ 9. In the course of measuring this data, many thousands of lab mice and rats have been killed. Do you consider this to be ethical research? Why is data collected on lab mice instead of humans? Would it be more ethical to use a species that is more closely related to us like chimpanzees? Explain your opinion. _____________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________ Further Research This is a table showing the LD50 of several substances, both toxic and non-toxic. For each substance, calculate the amount of each substance that statistically would have a 50% chance of killing you. 1. Record your weight in pounds here: __________________ 2. Convert your weight to kilograms by multiplying by 0.45: _________________ 3. Calculate your human lethal dose by multiplying your mass in kilograms by the LD50, then dividing by 1000 to convert to grams. Substance LD50 (mg/kg) Sucrose 29,700 Ethanol 7,060 Sodium chloride (table salt) 3,000 THC (found in cannabis) 1,270 (males) 730(females) Aspirin 200 Caffeine 192 Nicotine 50 Arsenic 14 Sodium cyanide 6.4 Venom of the Australian Inland Taipan snake 0.025 VX Nerve Gas 0.0023 Batrachotoxin (from Poison Dart frogs) Polonium-210 (nuclear fission waste product) 0.0020 0.00001 Lethal Human Dose (grams) = mass x LD50 / 1000