Earthquake Epicenters - Lincoln Park Public Schools
advertisement
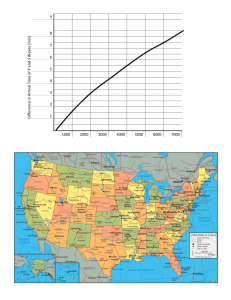
Name ________________________ Class _____________ Date _____________ Inquiry Lab DATASHEET A Earthquake Epicenters The energy from an earthquake travels as seismic waves in all directions through Earth. P waves, or primary waves, travel more quickly than S waves, or secondary waves, do. That’s why P waves are always detected first. The average speed of P waves in Earth’s crust is 6.1 km/s. The average speed of S waves in Earth’s crust is 4.1 km/s. The difference in arrival time at a seismometer station between P waves and S waves is called lag time. In this lab, you will use the lag time to determine the epicenter of an earthquake. OBJECTIVES Demonstrate the method scientists use to determine an earthquake’s epicenter. MATERIALS calculator (optional) compass ruler, metric SAFETY INFORMATION PROCEDURE 1. The illustration below shows seismometer records made at three seismometer stations following an earthquake. The jagged line marks the arrival of waves. The seismometer traces begin at the left, where the arrival of P waves at each seismometer station is shown at time zero. The second set of waves on each record shows the arrival of S waves. Name ________________________ Class _______________ Date ___________ Earthquake Epicenters continued 2. Write your data in the data table below. EPICENTER DATA TABLE City Austin, TX Lag time (s) Distance to epicenter (km) Bismarck, ND Portland, OR 3. Use the seismograms to find the lag time between the P waves and the S waves for each city. To find the lag time, add the S wave arrival time to the P wave time (0). Record these data in your table. 4. The average speed of P waves is 6.1 km/s. The average speed of S waves is 4.1 km/s. Use the following equation to calculate how long each wave type takes to travel 100 km: Show your work below. 5. To find the lag time for earthquake waves at 100 km: Subtract the time P waves take to travel 100 km from the time S waves take to travel 100 km. Record the lag time. Show your work below. 6. Use the following formula to find the distance from each city to the epicenter: In your data table, record the distance from each city to the epicenter. Show your work below. Name__________________________ Class_______________ Date___________ Earthquake Epicenters continued 7. Use the map above to find the epicenter of the earthquake. 8. Use the scale in the map to determine the distance from each city to the epicenter. Put the point of the compass on the zero. Stretch the pencil on the scale to equal the distance of the epicenter from Austin. 9. Put the point of your compass at Austin on your map, and draw a circle. 10. Repeat steps 8 and 9 for Bismarck and Portland. The epicenter of the earthquake is located near the point where the three circles meet. ANALYZE THE RESULTS 11. Analyzing Data The longer the lag time between the P wave and the S wave, the greater the _____ to the epicenter of the earthquake. DRAW CONCLUSIONS 12. Drawing Conclusions Which city on the map is located closest to the epicenter? BIG IDEA QUESTION 13. Drawing Conclusions Why is it important to locate the epicenter of an earthquake?