Full Description - Faculty of Information Technology Multimedia
advertisement

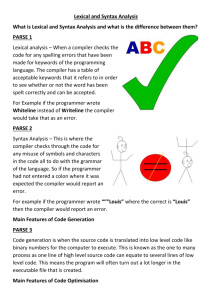
COURSE/MODULESUMMARY OF INFORMATION ON EACH COURSE/MODULE 1. Version July 2009 (state the date of the last Senate approval) 2. Pre-Requisite/Requirement for Registration TCP1201 Object-Oriented Programming and Data Structures 3. Name(s) of academic/teaching staff Dr. Yeoh Eng Thiam Mr. Nathar Shah 4. 5. Trimester 1 (Delta Level) Semester and Year offered Objective of the course/module/subject in the programme : To provide a thorough introduction to the theory and practice of programming language translation and to provide extensive hands-on experience with compiler construction tools and techniques. 6. Justification for including the subject in the program : This subject trains the student on the application of theoretical concepts and also provides a hands-on development of a complicated software application. The student will learn to develop a software by systematically separating it into individual components and also learn techniques that are applicable in developing other types of software. 7. Subject Learning Outcomes : LO1. Explain the process of translating a program from one language to another language Domain Cognitive Level 2 LO2. Apply lexical and syntax analysis techniques on a given context free grammar Cognitive 3 LO3. Design lexical and syntax analyser phases of a Cognitive compiler LO4. Explain the processes of semantic checking, code Cognitive generation and optimization in a compiler Mapping of Learning Outcomes to Programme Outcomes : Learning Outcomes PO1 PO2 PO3 PO4 PO5 LO1 LO2 LO3 LO4 Assessment Methods and Types : Method and Type Description/Details Assignments Practical work Quiz Written Tutorial Practical work Test Written Final Exam Written Details of Subject 6 8. 9. 10. 2 PO6 PO7 x PO8 x x x Percentage 20% 5% 10% 15% 50% Topics Mode of Delivery (eg : Lecture, Tutorial, Workshop, Seminar, etc.) Indicate allocation of SLT (lecture, tutorial, lab) for each subtopic Lecture 2 1. Introduction to Language Translation Lab Tutorial 2 Language translation systems: interpreters, compilers and assemblers; Language translation phases; Machine-dependent and machineindependent aspects of translation; Main components in compilers; Review of programming language concepts. 2. Lexical Analysis 6 6 8 8 4 4 2 2 Role of lexical analyzer; Specification and recognition of tokens; Application of regular expressions in lexical scanners; Implementation of finite-state automata; Handling lexical errors. 3. Syntax Analysis Role of parsers; Formal definition of context free grammars; Parse tree vs. abstract syntax tree; Recursive-descent parsing; Shift-reduce parsing; Construction of parsing tables; Eliminating ambiguity, left recursion and left factoring; Precedence and Associativity; Syntaxdirected translation; Handling parsing errors. 4. Semantic Analysis Role of semantic analyzer; Symbol table management; Declaration models: binding, visibility, scope, and lifetime; Inherited and synthesized attributes; Annotated syntax tree and dependency graphs; Bottom-up and Top-down evaluation of Attributes; Data type as set of values with set of operations; Semantic models of user-defined types; Equivalence of types; Type-checking models; Type conversion; Type-checking algorithms. 5. Code Generation Role of code generator; Interrmediate code generation; Intermediate representations; Issues in the design of code generator. Instruction selection and register allocation; Addresses in target code; Basic blocks and flow graphs; Run-time environment; Generating codes for arithmetic expressions, Boolean expressions, control structures, and procedure calls. 6. Optimization 2 2 4 4 Local and global optimization; Peep Hole optimization; Optimization of basic blocks; Optimizing using Directed Acyclic Graphs; Global redundancy and data flow analysis; Looping improvement. 7. Tools for language translation Automated generation of lexical and syntax analyzers; Specifying regular expressions for scanner generation; Specifying grammar for parser generation; Handling ambiguities and conflicts; Combining tools for an integrated compiler. Overview of automation tools: Lex, 11. 12. 13. YACC, JLex, Java CUP. Total Student Face to Face Learning Time (SLT) 28 Lecture 28 Tutorials Laboratory/Practical Quiz 0 Assignment 1 Mid Term Test 2 Final Exam 59 Sub Total Total SLT Credit Value Reading Materials : Textbook Aho, Lam, Sethi, Ullman, Compilers: Principles, Techniques, & Tools, 2nd Ed., Addison-Wesley, 2007. Independent Learning 28 28 9 12 4 20 101 160 4 Reference Materials Michael L. Scott, Programming Language Pragmatics, 3rd Ed., Morgan Kaufman, 2009. Keith D. Cooper, Linda Torczon, Engineering a Compiler, Morgan Kaufman, 2003. D. Grune, H. Bal, C. Jacobs, K. Langendoen, Modern Compiler Design, Wiley, 2000. 14. Appendix (to be compiled when submitting the complete syllabus for the programme) : 1. Mission and Vision of the University and Faculty 2. Programme Objectives or Programme Educational Objectives 3. Programme Outcomes (POs) Programming Language Translation 15. Name of Course/Module/Subject 4. Mapping of POs to the 8 MQF domain 5. Mapping of Los to the POs 6. Summary of the Bloom’s Taxonomy’s Domain Coverage in all the Los in the format below : Subject Bloom’s Taxonomy Domain Learning Outcomes Affective Cognitive Psychomotor (please state the learning outcomes) TSE2101 Learning 2 Outcome 1 Learning 3 Outcome 2 Learning 5 Outcome 3 Learning 2 Outcome 4 7. Summary of LO to PO measurement 8. Measurement and Tabulation of result for LO achievement 9. MeasurementTabulation of result for PO achievement Mapping Assessment to Learning Outcomes No. A1 Assessment Assignment (20%) LO1 LO2 X A2 Quiz (5%) X X A3 Tutorial (10%) X X A4 Test (15%) X X A5 Final Exam (50%) X X LO3 X LO4 X X X X X 16. 17. 18. Course /Subject SUMMARY Code Status of Subject MQF Level/Stage TCP2451 ON EACH OF INFORMATION Elective Bachelor - MQF Level 6