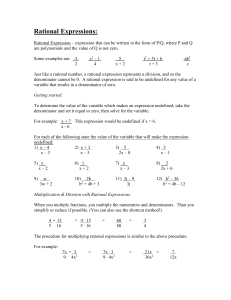
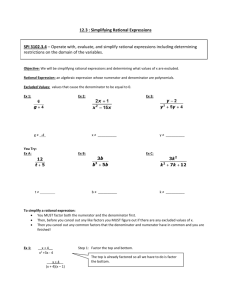
Simplifying and Multiplying Rational Expressions
advertisement
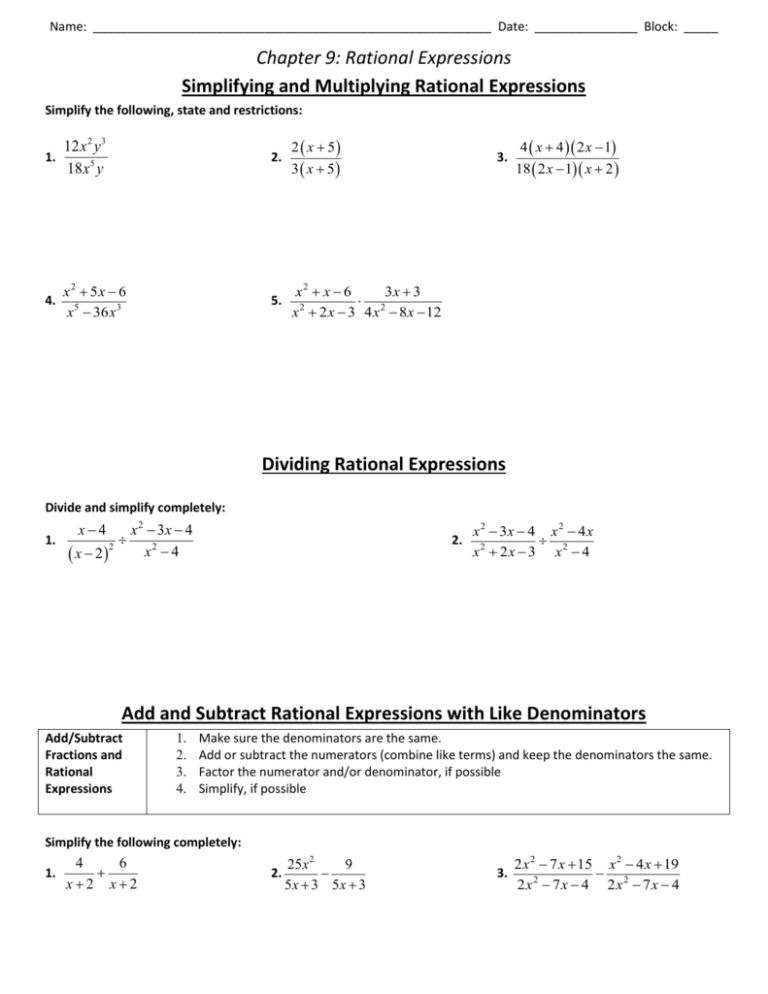
Name: __________________________________________________________ Date: _______________ Block: _____ Chapter 9: Rational Expressions Simplifying and Multiplying Rational Expressions Simplify the following, state and restrictions: 12 x 2 y 3 1. 18 x5 y 4. x2 5x 6 x5 36 x3 2. 2 x 5 3 x 5 5. x2 x 6 3x 3 2 2 x 2 x 3 4 x 8 x 12 3. 4 x 4 2 x 1 18 2 x 1 x 2 Dividing Rational Expressions Divide and simplify completely: 1. x4 x 2 2 x 2 3x 4 x2 4 2. x 2 3x 4 x 2 4 x x2 2x 3 x2 4 Add and Subtract Rational Expressions with Like Denominators Add/Subtract Fractions and Rational Expressions 1. 2. 3. 4. Make sure the denominators are the same. Add or subtract the numerators (combine like terms) and keep the denominators the same. Factor the numerator and/or denominator, if possible Simplify, if possible Simplify the following completely: 1. 4 6 x2 x2 2. 25 x 2 9 5x 3 5x 3 3. 2 x 2 7 x 15 x 2 4 x 19 2 x2 7 x 4 2 x2 7 x 4 Name: __________________________________________________________ Date: _______________ Block: _____ Add and Subtract Rational Expressions with Unlike Denominators Add/Subtract UNLIKE Rational Expressions 1. Determine the least common multiple to get a common denominator! You might need to factor each denominator first… 2. Figure out which factor is missing and multiply the numerator and denominator by the missing factor(s). 3. Simplify the numerator (FOIL, distribute, combine like terms, etc). 4. Factor the numerator, if possible. 5. Simplify, if possible. Simplify the following rational expressions. 1. 3x 2 4 x 5 4 8 2. 7 1 2 3x 9 x 3. 4. 6x 4x 3x 1 2 x 5 5. x 5 2 x 3 x 6x 9 6. 3 5 x2 x4 x 1 3 x2 2 x2 x2 x 4 Solving Rational Equations Solving a Rational Equation • • • • Find the least common denominator (LCD) FRACTION BUSTERS: multiply every term by the LCD to eliminate the denominators Solve the new equation and check to make sure your solution works Be sure to watch for domain restrictions. – Values of x that are not possible Solve: 1. x 1 x6 x4 2. x 2x 18 2 x 3 x 3 x 9 3. 3 12 1 2 x2 x 4 x2 4. x 1 2 x x 1 x x 1 Name: __________________________________________________________ Date: _______________ Block: _____ Restrictions of Rational Functions Finding Restrictions • Remember that domain tells you what x-values can be substituted into the equation. • For example, for f ( x ) • don't want the denominator to become zero! So the restriction is: x ≠ 0 In general, to find the restrictions of a rational function, figure out what number(s) would cause the denominator to become zero. 1 you can substitute in any number in for x except x = 0 because we x Find the restrictions of each function: 1. f x 1 x4 2. f x 3x 1 x 2 x 3 4 x 7 3. f x x 2 7 x 12 x 2 9 x 20 HORIZONTAL ASYMPTOTES Horizontal Asymptotes • (HA) y= • A Horizontal Asymptotes tells the end behavior of a function. To determine the y-value of the HA, we need to compare the powers of the numerator and denominator. • • • If the powers are the same, divide the coefficients. If the powers are larger in the denominator, the HA is y = 0. If the powers are larger in the numerator, there is no HA. Determine the y value of the horizontal asymptote: 2 x2 3 3x 2 4 x 5 2. g x 3x 2 3 4 x3 1 x 1 2 x 3 x 1 x 4 4. f x 3x3 4 x 2 x 1 1. f x 3. y VERTICAL ASYMPTOTES AND HOLES Vertical Asymptotes Holes (VA) x= • If a factor CANNOT be canceled and remains in the denominator, it creates a vertical asymptote. • If a factor CAN be canceled from the numerator and denominator, then it creates a hole. Name: __________________________________________________________ Date: _______________ Block: _____ • REMEMBER—YOU MUST FACTOR COMPLETELY FIRST! Determine the x-values for any holes or asymptotes: 1. f x 4. y x3 x 3 x 2 3x 1 3x 2 x 2. g x x 1 x 2 x 1 3. h x 5. f x x2 6 x 8 x 2 16 6. y x x x 1 x 2 10 x 21 x7 Translations f ( x) a k xh Translations: h ~ the horizonal shift k ~ the vertical shift a ~ the stretch ( a >1), shrink (0 < a < 1), or reflection (a < 1) Describe the translations of the following functions. 1. f ( x ) 3 4 x2 2. f ( x) 1 1 x5 horizontal shift:______________ horizontal shift:______________ vertical shift:______________ vertical shift:______________ stretch, shrink, and/or reflection:_______________ stretch, shrink, and/or reflection:_______________ 3. f ( x ) 1 3 x 4. f ( x) 1 x6 horizontal shift:______________ horizontal shift:______________ vertical shift:______________ vertical shift:______________ stretch, shrink, and/or reflection:_______________ stretch, shrink, and/or reflection:_______________