Plasmids and Plasmid Mapping Handout
advertisement

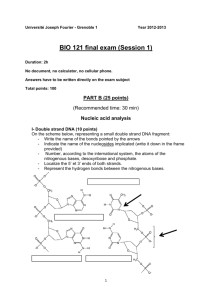
Plasmids and Plasmid Mapping What are Plasmids? Plasmids are circular double stranded molecules of deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) which exist independently from a cell as they can easily move from one organism to another allowing them to spread quickly. Plasmids are relatively small with only a few thousand base pairs and a few genes. They have only one origin site of replication. Plasmids are not required within an organism but are adopted by them to provide a biological advantage. There are two classes of Plasmids: Col factors (colicinogenic factors) and R factors. Col factors influence the production of proteins which have antibiotic properties and thus kill other bacteria. R factors allow the bacteria to create a defense mechanism against antibiotics. The more identical plasmids in an organism, the more that trait will be expressed by the cell. Application In biotechnology plasmids are used to engineer desired characteristics to be included with an organism’s genetic material. A geneticist would make specific cuts along a plasmid to introduce the desired gene(s) to be expressed and using a process called transformation the plasmid would be inserted into a bacteria. This allows for the mass production of proteins or genes and the bacteria with the new plasmids have medical applications as antibiotics, proteins such as insulin or human gene therapy. Plasmid Mapping Geneticist use plasmid mapping to figure out where the plasmid would be cut if a new gene was inserted. It is important for the Geneticist to know where the cuts will be made to insure that it will not disturb any genes that are already present on the plasmid. Plasmid Review Questions: True or False: 1. ______ Plasmids are only found in prokaryotes 2. ______ The genetic information on a plasmid replaces the genetic information found in DNA Multiple Choice: 1. What are Plasmids? a. Nucleotides with the base pairs adenine, uracil, cytosine and guanine. b. Molecules of DNA that can move easily from one bacteria to another c. Segments of base pairs that attach to the DNA of an organism d. Circular structured molecules of DNA that replace the genes already in an organism e. All of the above 2. The main function of Plasmids is… a. To create a selective advantage b. To allow the organism to develop characteristic so that it may kill other organisms c. To allow the organism to resist being killed d. All of the above e. None of the above Practice Problem: (for more problems see pg. 316 of the textbook) 1. Draw a Plasmid Map given the information in the chart below: BamHI 2890 bp pAMP 200 bp 2690 bp BamHI + pAMP 200 bp 1030 bp 1660 bp Extend: Will a 1000 bp long gene be expressed if it is located 600 bp away from the 2890 bp cut?