Standards 8.EE.2 - CMS Secondary Math Wiki
advertisement

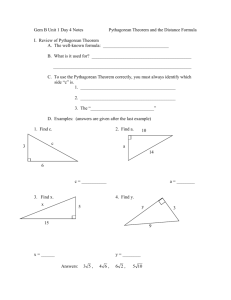
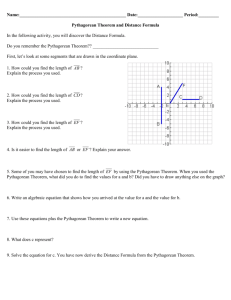
7th Grade Honors Unit 5 Exponents Enduring understanding (Big Idea): Students will learn the properties of exponents and how to use numbers written in powers of tens to solve problems. Students will learn the Pythagorean Theorem and how to solve problems using Pythagorean Theorem. Essential Questions: How can you represent very large and very small numbers? How can you simplify expressions involving exponents? What are the characteristics of exponential functions? Why is the Pythagorean Theorem useful? How can patterns help you simplify expressions involving zero and negative exponents? Why should you use powers of ten to write and organize numbers? How do properties of exponents make problems solving easier? Why should you use properties of exponents to simplify a power raised to a power or a product raised to a power? How are the properties of dividing powers and multiplying powers similar? Why should you graph exponential functions? BY THE END OF THIS UNIT: Students will know… Students will be able to… Zero and negative exponents Rules for multiplying and dividing powers The Pythagorean Theorem Scientific Notation Vocabulary: Scientific Notation Unit Resources Learning Task: Concept Byte 10-1 Distance and Midpoint Formula Performance Task: Pages 79-80 in Teacher resources CMP2 Resources: 8th Grade CMP2 Looking For Pythagoras (All Investigations) Write numbers in scientific notation Define and use zero and negative exponents Multiply powers with the same base Divide powers Solve for lengths of missing sides of right triangles Solve problems using the Pythagorean Theorem Simplify expressions involving zero and nonnegative exponents Write numbers in scientific and standard notation and compare their values Raise a power to a power Raise a product to a power To divide powers with the same base To raise a quotient to a power Graph and evaluate exponential functions Mathematical Practices in Focus: 12345678- Make sense of problems and persevere in solving them Reason abstractly and quantitatively Construct viable arguments and critique the reasoning of others Model with mathematics Use appropriate tools strategically Attend to precision Look for and make use of structure Look for and express regularity in repeated reasoning Successive pages contain an unpacking of the standards contained in the unit. Standards are listed in alphabetical and numerical order not suggested teaching order. Teachers must order the standards to form a reasonable unit for instructional purposes 7th Grade Honors Unit 5 Exponents Standards Chapter and Section Suggested Homework Standard 8.EE.1 7-1 Problems 1-4, Exs. 9-27 odd, 28-48 even, 50-66 Standard 8.EE.3 7-2 Problems 1-3, Exs. 11-23 odd, 24-34 even, 35-59 Standard 8.EE.4 7-3 Problems 1-4, Exs. 8-24 even, 25-31,32-40 even, 41-48, 54-69 Standard 8.EE.4 7-4 Problems 1-5, Exs 10-28 even, 30-43, 46-66 Standard 8.EE.4 7-5 Part 1 Problems 1-2, Exs. 8-26 even, 27-29, 70-86 Part 2 Problems 3-4 Exs. 30-46 even, 47-55, 59,61,62, 65-67 Standard 8.F.3 7-6 Problems 1-3 Exs. 8-25, 26-38 even, 39-52 Standard 8.G.7, 8.EE.2 10-1 Problems 1-3, Exs. 6-19, 20-28 even, 29-40 Standard 6.NS.6 Investigation 1 Coordinate Grids Standard 8.EE.2 Investigation 2 Squaring Off 8th Grade CMP2 Looking For Pythagoras Investigation 1 8th Grade CMP2 Looking For Pythagoras Investigation 2 1.1: ACE 1-7, 26-28, 30, 35, 36 1.2: ACE 8-14, 29, 31, 37 1.3: ACE 15-25, 32-34, 38, 39 2.1: ACE 1-3, 42, 47-48 2.2: ACE 4-34 2.3: ACE 35-41, 43-46, 49-53 Common Core Investigations 1.2 Cube Roots Common Core Investigations 1.2: ACE 40-52 Successive pages contain an unpacking of the standards contained in the unit. Standards are listed in alphabetical and numerical order not suggested teaching order. Teachers must order the standards to form a reasonable unit for instructional purposes 7th Grade Honors Unit 5 Exponents Standards 8.EE.2; 8.G.6; 8.G.7; 8.G.8 8th Grade CMP2 Looking For Pythagoras Investigation 3 3.1:ACE 1-14 3.2:ACE 18-23, 26 3.3:ACE 24. 27-35 3.4:ACE 15-17, 25 Standards 8.NS.1; 8.NS.2; 8.EE.2; 8.G.7 8th Grade CMP2 Looking For Pythagoras Investigation 4 4.1:ACE 1. 2. 13-16 4.2:ACE 3-9. 17-25, Successive pages contain an unpacking of the standards contained in the unit. Standards are listed in alphabetical and numerical order not suggested teaching order. Teachers must order the standards to form a reasonable unit for instructional purposes 7th Grade Honors Unit 5 Exponents CORE CONTENT Cluster Title: Understand and Apply the Pythagorean Theorem Standard 8.G.6: Explain a proof of the Pythagorean Theorem and its converse. Concepts and Skills to Master • Know that in a right triangle a² + b² = c² (the Pythagorean Theorem). • Understand and explain a proof of the Pythagorean Theorem. • Understand and explain a proof of the converse of the Pythagorean Theorem. SUPPORTS FOR TEACHERS Critical Background Knowledge Understand the relationship between a and a2, b and b2, c and c2. Understand the relationship between squares and square roots. Academic Vocabulary right triangle, leg, hypotenuse, square, Pythagorean Theorem Suggested Instructional Strategies Resources Textbook Correlation Consider introducing this with an application regarding o Looking for Pythagoras (CMP2) distance. Explore various proofs of the Pythagorean Theorem and discuss the logic within each. Investigations 3 MARS Tasks (HS): E04: Proofs Of The Pythagorean Theorem E08: Pythagorean Triples MARS Problem Solving Lesson (HS):Proofs of the Pythagorean Theorem Texas Instrument 8.G.6 Lessons CMP2 Resources Sample Formative Assessment Tasks Skill-based Task Problem Task Explain the logical reasoning behind a proof of the Pythagorean Theorem. Investigate the historical context of one of the proofs of the Pythagorean Theorem and present the proof in context to the class. Successive pages contain an unpacking of the standards contained in the unit. Standards are listed in alphabetical and numerical order not suggested teaching order. Teachers must order the standards to form a reasonable unit for instructional purposes 7th Grade Honors Unit 5 Exponents CORE CONTENT Cluster Title: Understand and Apply the Pythagorean Theorem Standard 8.G.7: Apply the Pythagorean Theorem to determine unknown side lengths in right triangles in real-world and mathematical problems in two and three dimensions. Concepts and Skills to Master • Use the Pythagorean Theorem to solve for a missing side of a right triangle given the other two sides. • Use the Pythagorean Theorem to solve problems in real-world contexts, including three-dimensional contexts. SUPPORTS FOR TEACHERS Critical Background Knowledge •Solve an equation using squares and square roots. • Use rational approximations of irrational numbers to express answers. Academic Vocabulary right triangle, leg, hypotenuse, Pythagorean Theorem, square, square root, Suggested Instructional Strategies Resources Textbook Correlation Find and solve right triangles in career situations o Looking for Pythagoras (CMP2) such as construction. Investigations 3 and 4 o Foundations of Algebra Chapter 10-1 Texas Instrument 8.G.7 Lessons CMP2 Resources Sample Formative Assessment Tasks Skill-based Task If the height of a cone is 10 meters and the radius is 6 meters, what is the slant height? Problem Task TVs are measured along their diagonal to find their dimension. How does a 52-inch HD (wide-screen) TV compare to a traditional 52-inch (full screen) TV? Successive pages contain an unpacking of the standards contained in the unit. Standards are listed in alphabetical and numerical order not suggested teaching order. Teachers must order the standards to form a reasonable unit for instructional purposes 7th Grade Honors Unit 5 Exponents CORE CONTENT Cluster Title: Understand and apply the Pythagorean Theorem. Standard 8.G.8: Apply the Pythagorean Theorem to find the distance between two points in a coordinate system. Concepts and Skills to Master • Calculate the distance between two points in a coordinate system using the Pythagorean Theorem. SUPPORTS FOR TEACHERS Critical Background Knowledge •Use the Pythagorean Theorem to solve for the hypotenuse of a right triangle. Academic Vocabulary right triangle, distance formula, leg, hypotenuse, Pythagorean Theorem, square, square root, , Suggested Instructional Strategies Resources Textbook Correlation Overlap a map with a coordinate grid and use the o Looking for Pythagoras (CMP2) Pythagorean Theorem to find the distance between two Investigations 3 locations. Investigate the relationship between the Pythagorean Texas Instrument 8.G.8 Lessons Theorem and the distance formula. Use the Pythagorean Theorem to explore and categorize CMP2 Resources triangles and quadrilaterals on a coordinate system. Sample Formative Assessment Tasks Skill-based task Using the Pythagorean Theorem, find the distance between (4,2) and (7,10). Problem Task List 3 coordinate pairs that are 5 units away from the origin in the first quadrant. Describe how to find the points and justify your reasoning. (Note: Points on the axes are not in the quadrant.) Successive pages contain an unpacking of the standards contained in the unit. Standards are listed in alphabetical and numerical order not suggested teaching order. Teachers must order the standards to form a reasonable unit for instructional purposes 7th Grade Honors Unit 5 Exponents CORE CONTENT Cluster Title: Define, evaluate, and compare functions. Standard 8.F.3: Interpret the equation y = mx + b as defining a linear function, whose graph is a straight line; give examples of functions that are not linear. Concepts and Skills to Master Distinguish between linear and non-linear functions given their algebraic expression, a table, or a graph. Recognize that functions written in the form y = mx + b are linear and that every linear function can be written in the form y = mx + b. SUPPORTS FOR TEACHERS Critical Background Knowledge Generate and plot ordered pairs from an equation. Understand linear slope as a constant rate of change. Academic Vocabulary collinear, linear, nonlinear Suggested Instructional Strategies Resources Examine constant and non-constant rates of Textbook Correlation change in tables of values. o Algebra 1 Foundations Chapter 7-6 Explore growing patterns, generated from a Grapher variety of contexts to explore linear and CMP2 Resources nonlinear relationships. Line Plotter MARS Concept Assessment Task Lessons (MS): A05: Baseball Jerseys; A17: Linear Graphs, A19: Meal Out MARS Concept Formative Assessment Lessons (MS): Modeling Situations With Linear Texas Instrument 8.F.3 Lessons Successive pages contain an unpacking of the standards contained in the unit. Standards are listed in alphabetical and numerical order not suggested teaching order. Teachers must order the standards to form a reasonable unit for instructional purposes 7th Grade Honors Unit 5 Exponents CORE CONTENT Cluster Title: Expressions and Equations: Work with radicals and integer exponents. Standard 8.EE.1: Know and apply the properties of integer exponents to generate equivalent numerical expressions. For 1 1 example: 3² x3−5 = 3−3 = = 3³ 27 Concepts and Skills to Master Know the properties of integer exponents. Apply the properties of integer exponents to simplify and evaluate numerical expressions. SUPPORTS FOR TEACHERS Critical Background Knowledge Understand exponents as repeated multiplication. (6.EE.1) Compute fluently with integers (add, subtract, and multiply). Academic Vocabulary exponent, base, power, integer Suggested Instructional Strategies Resources Use repeated multiplication and division to Textbook Correlation informally derive the exponent rules. Foundations of Algebra Chapter 7-1 Have students examine equivalent numerical expressions with exponents. Sample Formative Assessment Tasks Skill-based Task Simplify 57 ( ( (2)²)²)² −50 2−2 * 4 3 MARS AssessmentTask (HS): E06: “Ponzi” Pyramid Schemes Texas Instrument 8.EE.1 Lessons CMP2 Resources Problem Task Explain why 35 * 32 = 37 and not 97 . 5 Write three expressions equivalent to 32 * 92 . Successive pages contain an unpacking of the standards contained in the unit. Standards are listed in alphabetical and numerical order not suggested teaching order. Teachers must order the standards to form a reasonable unit for instructional purposes 7th Grade Honors Unit 5 Exponents CORE CONTENT Cluster Title: Expressions and Equations: Work with radicals and integer exponents. Standard 8.EE.2:Use square root and cube root symbols to represent solutions to equations of the form x 2 = p and x3 = p, where p is a positive rational number. Evaluate square roots of small perfect squares and cube roots of small perfect cubes. Know that √2 is irrational. Concepts and Skills to Master Evaluate the square roots of small, perfect squares and cube roots of small perfect cubes. Represent the solutions to equations using square root and cube root symbols. Understand that all non-perfect square roots and cube roots are irrational. SUPPORTS FOR TEACHERS Critical Background Knowledge Understand and use inverse operations to solve equations. Academic Vocabulary square, square root, , cube, cube root, , radical Suggested Instructional Strategies Resources Textbook Correlation Use the geometric representations of square area and o Looking for Pythagoras (CMP2) cube volumes and their relation to the side length. Use the idea of inverse operations to introduce the concept of roots. Investigations 2, 3, and 4 Foundations of Algebra Chapter 10-1 Squares, Square Roots and Exponential Expressions MARS Formative Assessment Lesson (MS): The Pythagorean Theorem: Square Areas CMP2 Resources Texas Instrument 8.EE.2 Lessons Sample Formative Assessment Tasks Skill-based Task If a square has an area of 9/16 square inches, what is the length of a side? If a cube has a volume of 0.125 cubic meters, what are the dimensions of the cube? Problem Task Is the square root of a number always smaller than the number itself? Explain. Successive pages contain an unpacking of the standards contained in the unit. Standards are listed in alphabetical and numerical order not suggested teaching order. Teachers must order the standards to form a reasonable unit for instructional purposes 7th Grade Honors Unit 5 Exponents CORE CONTENT Cluster Title:Work with radicals and integer exponents. Standard 8.EE.3: Use numbers expressed in the form of a single digit times an integer power of 10 to estimate very large or very small quantities, and to express how many times as much one is than the other. For example, estimate the population of the United States as 3 × 8 9 10 and the population of the world as 7 × 10 , and determine that the world population is more than 20 times larger. Concepts and Skills to Master • Estimate numbers as a product of a single digit and a power of ten. • Compare numbers expressed as a product of a single digit and a power of ten by a scale factor. SUPPORTS FOR TEACHERS Critical Background Knowledge • Understand properties of integer exponents. • Use and understand powers of ten and place value. • Estimate and round numbers. Academic Vocabulary powers of ten, estimate Suggested Instructional Strategies Resources Textbook Correlation • Use large and small real-life numbers (e.g. national debt). Foundations of Algebra • Use base 10 blocks. Chapter 7-2 • Write numbers as repeated multiplication or as the value MARS AssessmentTask (MS): of a power of 10.(e.g. 7∙103→7∙1000 𝑜𝑟 A02: 100 People ; A03: A Million Dollars 7000 →7∙1000→7∙(10∙10∙10)) Texas Instrument 8.EE.3 Lessons CMP2 Resources Sample Formative Assessment Tasks Skill-based Task The mass of the earth is 6×1024kg. The mass of the moon is 7×1022kg. How many times bigger is the mass of the earth than the mass of the moon? A proton has 2 x 10 -27 kg mass and an electron has 9×10-14kg mass. How many times smaller is the electron than the proton? Problem Task Provide two (2) original (not teacher-given) real-life situations that could be illustrated using powers of ten, one that describes a very small number and one that describes a very large number. Estimate how much larger one is than the other. Successive pages contain an unpacking of the standards contained in the unit. Standards are listed in alphabetical and numerical order not suggested teaching order. Teachers must order the standards to form a reasonable unit for instructional purposes 7th Grade Honors Unit 5 Exponents CORE CONTENT Cluster Title: Cluster Title: Work with radicals and integer exponents. Standard 8.EE.4: Perform operations with numbers expressed in scientific notation, including problems where both decimal and scientific notation are used. Use scientific notation and choose units of appropriate size for measurements of very large or very small quantities (e.g., use millimeters per year for seafloor spreading). Interpret scientific notation that has been generated by technology. Concepts and Skills to Master • Add, subtract, multiply and divide with numbers expressed in scientific notation and decimal notation. • Represent very large and small quantities in scientific notation and use appropriate units. • Convert between decimal notation and scientific notation. • Interpret numbers expressed in scientific notation, including numbers generated by technology. SUPPORTS FOR TEACHERS Critical Background Knowledge • Use rules of exponents. • Understand powers of ten and place value. Academic Vocabulary scientific notation, decimal notation, power of ten, units of measure Suggested Instructional Strategies Resources Textbook Correlation • Use examples found in science to create authentic reasons Foundations of Algebra to use scientific notation. Chapter 7-3, 7-4, 7-5 MARS AssessmentTask (HS): A18: Giantburgers MARS Formative AssessmentLesson (MS): Estimating Length Using Scientific Notation Scientific Notation (Includes a Smartboard Lesson) Scientific Notation (WebQuest) Scientific Notation (Card Game) Texas Instrument 8.EE.4 Lessons Successive pages contain an unpacking of the standards contained in the unit. Standards are listed in alphabetical and numerical order not suggested teaching order. Teachers must order the standards to form a reasonable unit for instructional purposes 7th Grade Honors Unit 5 Exponents Sample Formative Assessment Tasks Evaluate and express your answers in scientific notation. • (3×105 )+ (5.54×107 ) • (4.2×10−2 )–(7.4×102 ) Problem Task Express your age at your last birthday in each of the following units: years, months, weeks, days, hours, minutes and seconds. Which values would be useful to write in scientific notation? Justify your reasoning. • (3×108 )(500) Compare your age to that of the 4.5 billion year old earth. • 30 1.5 𝑥10−4 Multiply 345,328,004 x 234 on your calculator and write the answer in scientific notation. Successive pages contain an unpacking of the standards contained in the unit. Standards are listed in alphabetical and numerical order not suggested teaching order. Teachers must order the standards to form a reasonable unit for instructional purposes