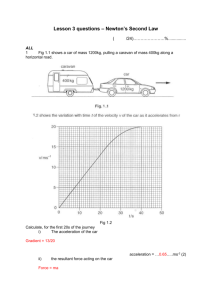
Rate of change of velocity
advertisement

Intro to Physics Midterm Review & Study Guide Mrs. DiOrio & Mr. Dougherty Unit 1 Try these conversions, using the ladder method. 1000 mg = ____1___ g 1 L = _____1000__ mL 160 cm = ___1600____ mm 14 km = ___14000____ m 3 109 g = ____.109___ kg 250 m = ____.250___ km Compare using <, >, or =. 56 cm ___<___ 6m 7 g __>____ 698 mg Unit 2 1. What is speed? Speed = Distance/Time 2. If you are traveling around the Somerville circle at 25 mph what stays constant? Speed 3. When you are graphing, what variable goes on the x-axis? Time 4. What tool do you use to measure instantaneous speed? a. speedometer b. tape measure c. stop watch d. odometer 5. What tool do you use to measure how far your trip was? a. speedometer b. scale c. stop watch d. odometer 7. Name 3 units of speed. a. __________________________Miles per hour b. __________________________Meters per second c. __________________________Inches per hour 8. What is the formula for acceleration? Change in velocity / Change in time 9. Define independent and dependent variable. Independent is manipulated by the researcher, the dependent is what comes out. 10. Two cars are traveling in opposite directions going 60 mph. Do they have the same velocities? No, velocity is a speed and a direction. 11. What is the formula for speed? Speed = Distance * Time 12. What is the formula for distance? Distance = Speed / Time 13. See # 11 & know the formula for speed. Thank you. 14. What does a speedometer in a car tell you? Instantaneous Speed 15. What is acceleration? Rate of change of velocity 16. What is the difference between speed and velocity? Velocity has a specific direction. 17. What is the formula for acceleration? Change in acceleration / change in time 18. What is free fall? A fall where only the weight of the object is present. 19. A ball is thrown upwards and caught when it comes back down. In the absence of air resistance, the speed of the ball when caught would be; the same as, faster than, or less than when thrown upwards? 20. An object is in free fall. For each second the object is falling, what happens to its speed? It increases 21. If you drop a feather and a coin at the same time in a tube filled with air, which one will reach the bottom of the tube first? Why? Coin, feather will hit resistance. 22. Please see #13. Know the formula for speed. Thank you. 23. Please see #22. Know the formula for speed. Thank you. 24. What is the value for gravity on the Earth’s surface? 9.8 : a 25. Which unit is more accurate? The centimeter or the millimeter? Millimeter 26. What is the correct order of metrics going from the largest to the smallest? KHD B DCM 27. 1000 mg = ________1_____ g 28. 160 cm = _______1600_______ mm 29. 109 g = _______.109_______ kg 30. Determine the percentage error in: Experimental Value 135.2, Accepted Value 133.4. Accepted Value – Experimental Value * 100 Accepted Value 1.35% 31. Please see # 23. Know the formula for speed. Thank you. 32. What are the SI base units for: Distance: Meter Mass: Gram Time: Seconds Unit 3 Newton’s Laws 1. What does Newton’s 1st Law say? An object at rest will stay at rest, and object in motion will stay in motion. 2. What is a force? A push. 3. Define: Inertia The tendency of an object to resist change wheter it is in motion or motionless. 4. Name 4 types of friction. 1. Sliding 2. Rolling 3. Fluid 4. Static 5. What does Newton’s 2nd Law say? The net force is equal to the acceleration placed on the mass. 6. What is the formula for Force? F=M*A 7. What is the unit of measure for force? N 8. What is the difference between mass and weight? Mass is the amount of matter an object has while weight is a measure against gravity. 9. What is the formula for Weight? W=M*A 10. How is gravity represented and what is it’s value? A, 9.8 11. What does Newton’s 3rd Law say? For every action on an object there is an equal and opposite reaction. 12. Describe how a fish moves through water using Newton’s 3rd Law. The force against the water from its fins is using the reactive force from the water to move forward. Thinking Questions: 13. Suppose you stand on a scale in the weight room and the scale reads 110N. Now, if you were to stand on two scales next to each other at the same time, what would each scale say? 55N 14. How does mass effect acceleration? The more mass an object has the more acceleration it will need to move. 15. Mrs. DiOrio is pushing a box in one direction with 200 N of force. Mr. Dougherty is pushing on a box in the opposite direction with 200 N of force. Which way is the box going and why? Nowhere, the forces acting on it are the same each way. 16. What causes a moving object to change direction? Acceleration 17. A bus is cruising along a dark desert highway when all of the sudden a bug splatters across the windshield. Which force is greater, the bus hitting the firefly or the firefly hitting the bus? It’s the same. 18. If the force on an object is doubled, the acceleration will change by how much? 2x 19. How does a rocket move through space? It brings its own oxygen supply and the fuel burns, producing a disaplcement of gas that pushes it forward. 20. What is the reaction force of a ball dropping from the air? The bounce Mathematic Section 21. If a woman has a mass of 50 kg, calculate her weight in Newtons. 50 * 9.8 = 490 N 22. Susie Smart weighs 300N. Calculate her mass. 300 / 9.8 =30.61 23. What is the weight of 2 kilograms of yogurt in Newtons? 2 * 9.8 = 19.6 24. A little boy who weighs 40 kg is riding in a wagon pulled by a horse. What is the acceleration of the wagon if the horse pulls with a force of 30 N? 30 / 40 = .75 25. A racecar breaks down. It weighs 700 kg. The driver can push with an acceleration of .05 m/s2. How much force is he putting on the car? 700 * .05 = 35 N 26. A 1500kg car accelerates at a rate of 4.0 m/s2. How much force is the car’s engine producing? 1500 * 4.0 = 6000 N 27. A golf ball, weighing .34 kg is accelerated at a rate of 174 m/s2. What force does the golfer’s club put in the ball? .34 * 174 = 59.16 28. A bottle of Gatorade weighing 1.4 kg is tossed to you at a rate of 14 m/s2. You miss it and it hits you with how much force? 1.4 * 14 = 19.6 29. A woman is pushing a shopping cart with 18 N of force. The cart weighs 28 kg. What is her acceleration? 18 / 28 = .64 30. A speedboat pulls 2 water skiers, each with a mass of 55 kg. What is the total weight of the water-skiers in Newtons? 110 * 9.8 = 1078 Cumulative Review Questions 31. 1000mg = _______1_____ g 32. Determine the percent error of Accepted Value: 134.2 and Experimental Value 165.9. 23% 33. How do you define acceleration? Rate of change of speed / time 34. When measuring, which ruler is more accurate, the centimeter or the millimeter? mm 35. 109 g = ____.109________ kg Momentum 1. What are the two variables that momentum depends on? Mass & velocity 2. Momentum can be defined as The quantity of motion of an object, mass in motion. 3. Which of the following is the correct symbol for momentum? a. M b. Mom c. P d. F 4. List the units for each variable: P= kg * ms^2 M= kg V= ms^2 5. The momentum of an object at rest is _________0___________ . 6. Which has a greater amount of momentum, a mack truck going 40 m/s2 or a skateboarder going 40 m/s2? Mack truck, because it has more mass. 7. To stop an object, we have to apply a force over a period of ____time_____________ . 8. What is the formula for impulse? Impulse = Force * Change in time 9. What are the units for impulse? N*S 10. The greater the time over which the collision occurs, the smaller the ___________force____ acting on the object. 11. In order to minimize the effect of the force on an object involved in a collision, what can you do? Increase the time 12. What does the law of conservation of momentum state? No net external force acting on a system = Momentum before = momentum after 13. Describe the kinetic energy in an elastic collision. Give an example of an elastic collision. Kinetic energy is conserved KE before = KE after, crazy ball bouncing, electrons scattering. 14. Describe the kinetic energy in an inelastic collision. Give an example of an elastic collision. Kinetic energy is NOT conserved KE before does not = KE after. Catching a baseball, football tackle, cars colliding 15. Choose whether each collision in elastic or inelastic. I = Inelastic ____I____ raquet) E = Elastic A tennis player returning a serve. (Specifically, the ball on _____I___ A truck crashing into a bridge. _____I___ An egg falling and cracking on the ground. _____E___ Billiards balls colliding. 16. A 185.25 kilogram motorcycle is moving at a speed of 87.75 m/s. What is the momentum of the cycle? 185.25 * 87.75 = 16255.69 17. If the motorcycle above crashes into a wall and stops in a time of 0.05 seconds, how much force acted on the cycle to bring it to a stop? 16255.69 * .05 = 812.78 18. Calculate the momentum of a 1200 kg car with a velocity of 25m/s. 1200 * 25 = 30,000 19. What is the momentum of a child and wagon if the total mass of the child and wagon is 22kg and the velocity is 1.5m/s? 22 * 1.5 = 33 20. The parking brake on a 1200kg automobile has broken, and the vehicle has reached a momentum of 7800kg.m/s. What is the velocity of the vehicle? 7800 / 1200 = 6.5 21. A roller coaster climbs up a hill at 5 m/s2 and then zips down the hill at 40 m/s2. When is momentum greater: going up the hill or going down the hill? Downhill 22. A soccer ball crashes into another soccer ball at rest. Does the total momentum of the balls increase, decrease or stay the same? Stays the same 23. What would you need to do to increase the momentum of a golf ball? Hit it harder, increase mass of golf ball 24. Why are dashboards padded in cars? To increase the time over which the impact occurs, lessen force 25. A freight train rolls down the track. If it were to keep rolling at the same speed, but had twice as much mass, its momentum would be __________2x___________________. 26. What is the momentum of a 10 kg bowling ball at 2 m/s2? 10 * 2 = 20 27. What impulse occurs when an average force of 13 N is exerted on a cart for 4 seconds? 13 * 4 = 52 N*S 28. What is the momentum of a 60 kg carton that slides at 4 m/s across an icy surface? 60 * 4 = 240 kg*m/s 29. How much momentum does a 3000 kg truck have traveling at 25 m/s? 3000 * 25 =75000 30. A halfback (m = 60 kg), a tight end (m = 90 kg), and a lineman (m = 120 kg) are running down the football field. Consider their ticker tape patterns below. Compare the velocities of these three players. How many times greater are the velocity of the halfback and the velocity of the tight end than the velocity of the lineman? Which player has the greatest momentum? Explain. Lineman = 120 * 3 = 360 Tight End = 90 * 6 = 540 Halfback = 60 * 9 = 540