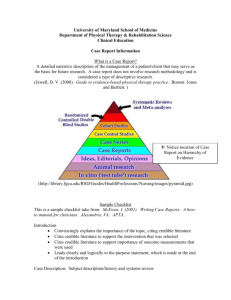
Executive Overview - Aerospace Industries Association
advertisement

Aerospace Industry Guideline for Developing a Security Plan for Unclassified Data Version 1.3 March 20, 2012 Developed By: Electronic Enterprise Integration Committee Aerospace Industries Association, Inc. Important Disclaimer: The Aerospace Industries Association of America, Inc. (“AIA”) has no intellectual property or other interest in this Aerospace Industry Guideline for Developing a Security Plan for Unclassified Data. By developing this Aerospace Industry Guideline for Developing a Security Plan for Unclassified Data Plan and making it freely available to anyone, AIA assumes no responsibility for this Guideline’s content or use, and disclaims any potential liability associated therewith. 2 Executive Overview From time to time an AIA member company may be requested to provide the DOD, a prime contractor or an industry partner an Information Technology Security Plan for unclassified data. This security plan could be required at the enterprise, program or application level depending on the unique requirements of the request. This request might be challenging for those members that have never been required to provide such a document. This “Aerospace Industry Guideline for Developing a Security Plan for Unclassified Data” provides a template and guidance to assist member companies in the development of a security plan to meet their customers or partners needs. Please keep in mind that this document is provided as a guideline and not a mandatory standard. AII member companies are encouraged to use this guideline. Use of this industry-wide best practice will provide the following benefits: 1. Simplify development of the security plan by the provider to meet the needs of the requester 2. Ensure consistent formats across the industry to simplify assessment by the requester 3. Reduce the cost of compliance for both requester and provider The trend is for the NIST SP 800-53 recommendation to be the basis for security planning. Our guideline is based on the NIST SP 800-53 policy for identifying security controls. The following is the prologue taken directly from the NIST Special Publication 800-53 Revision 3: “ “…Through the process of risk management, leaders must consider risk to US interests from adversaries using cyberspace to their advantage and from our own efforts to employ the global nature of cyberspace to achieve objectives in military, intelligence, and business operations… “ “…For operational plans development, the combination of threats, vulnerabilities, and impacts must be evaluated in order to identify important trends and decide where effort should be applied to eliminate or reduce threat capabilities; eliminate or reduce vulnerabilities; and assess, coordinate, and deconflict all cyberspace operations…” “…Leaders at all levels are accountable for ensuring readiness and security to the same degree as in any other domain…" -- THE NATIONAL STRATEGY FOR CYBERSPACE OPERATIONS OFFICE OF THE CHAIRMAN, JOINT CHIEFS OF STAFF, U.S. DEPARTMENT OF DEFENSE” 3 Company Name System Name Security Plan for Unclassified Data Version 1.2 March 08, 2012 Signatures: ____________________________________Date: ___________ xxxxx Project Manager ____________________________________Date: ___________ yyyyy Enterprise Information Security Table of Contents 1. Project Overview: ................................................................................................................................ 3 2. Information Technology Security Plan ............................................................................................. 3 1. 2. 3. Introduction.................................................................................................................................... 3 Objectives ...................................................................................................................................... 3 Company Security Policies ........................................................................................................... 3 Security Roles and Responsibilities ................................................................................................. 3 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Project Lead/Manger Add responsibilities ..................................................................................... 4 Enterprise Information Security Add responsibilities .................................................................... 4 Systems/Network Administration Add responsibilities .................................................................. 4 Support Team Add responsibilities ............................................................................................... 4 Development /Testing Team Add responsibilities ......................................................................... 4 Policy and Operational Controls ....................................................................................................... 4 1. 2. 3. Personnel Security ........................................................................................................................ 4 Physical and Environmental Protections ....................................................................................... 4 Data Security Controls .................................................................................................................. 4 3. 4. a. b. 4. Personally Identifiable Information (PII) ....................................................................................... 4 User vs. System Administrator Authentication............................................................................. 5 Hardware and Software Maintenance ........................................................................................... 5 a. b. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. System Documentation and Source Code .................................................................................... 5 Configuration Management.......................................................................................................... 5 Security and Privacy Awareness, Training, and Education .......................................................... 5 Incident Response Capability........................................................................................................ 5 Security Advisory Alert Handling ................................................................................................... 5 Monitoring...................................................................................................................................... 5 Acceptable Use Policies ................................................................................................................ 5 a. b. c. d. E-Mail ............................................................................................................................................ 5 Internet Access.............................................................................................................................. 6 Digital Media ................................................................................................................................. 6 Social Media .................................................................................................................................. 6 10. Mobile Devices .............................................................................................................................. 6 11. Peer-to-Peer Networking and Instant Messaging ......................................................................... 6 12. Separation of Duties ...................................................................................................................... 6 13. Least Privilege ............................................................................................................................... 6 14. Remote Access/End Point Security .............................................................................................. 6 5. Policy on Technical Controls ............................................................................................................. 6 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 6. Identification and Authentication ................................................................................................... 6 Audit Records ................................................................................................................................ 7 Remote Access ............................................................................................................................. 7 Vulnerability Testing ...................................................................................................................... 7 Encryption ..................................................................................................................................... 7 Malicious Code Protection ............................................................................................................ 7 Patch Management ....................................................................................................................... 7 Trusted Internet Connection.......................................................................................................... 7 Wireless and Physical Network Connection ................................................................................. 7 References ........................................................................................................................................... 7 2 1. Project Overview: Provide an overview of the subject for which this security plan is written, such as an enterprise, program, project or interface. 2. Information Technology Security Plan 1. Introduction This introduction is a sample and can be customized by the owner for whoever needs it regardless of whether it is the DOD or prime contractor. The plan should be as general as possible so that it can be reused. Any specific restriction on the scope of this plan should be documented here. For example: “The purpose of this Security Plan is to document the security procedures in place to comply with federal regulations and DLA Transactions Services requirement for the exchange of unclassified information between entity XXX and DLA Transactions Services instances of the Global EXchange (GEX).” 2. Objectives Identify the objectives of the company’s security plan for itself and its customers and partners. 3. Company Security Policies Identify any external sources of policies or guidelines that form the basis of these security policies. For example: “All entity XXX Security Policies are based on NIST Special Publication 800-53 (Current Revision) regarding Security Controls and Assessment Procedures for Federal Information Systems and Organizations.” 3. Security Roles and Responsibilities This chapter explains what the responsibilities are for the different roles. Samples of the most common roles are listed below. Customize the list as needed to meet the specific requirements of this security plan. 3 1. Project Lead/Manger Add responsibilities 2. Enterprise Information Security Add responsibilities 3. Systems/Network Administration Add responsibilities 4. Support Team Add responsibilities 5. Development /Testing Team Add responsibilities 4. Policy and Operational Controls This chapter explains what controls are in place. 1. Personnel Security This section describes the controls related to employees and other users, such as the need to perform appropriate background checks. Controls must also be in place to ensure that network accounts of terminated employees and other users are closed, prohibiting access to any company system or application. 2. Physical and Environmental Protections This section describes the physical controls such as locks and guards and environmental controls for temperature, humidity, lighting, fire and power. It is only necessary to describe controls for those areas within a facility that directly provide protection and support for the system(s) defined within the scope of this document. This includes IT assets such as communications equipment, workstations, servers, data centers, network and firewall infrastructure. 3. Data Security Controls This section describes the controls for confidentiality, authentication, non-repudiation, access and integrity for both internal and external data. These controls will ensure that information stored in any form is protected against unauthorized access, tampering, alteration, loss, and destruction during creation, use, handling, storage and preservation. It also includes special controls and procedures needed for: a. Personally Identifiable Information (PII) The security of Personally Identifiable Information (PII) must be handled with special care. Identify here the policies in place to insure that data is handled appropriately. 4 b. User vs. System Administrator Authentication General User authentication is often handled differently from System Administrator authentication. Explain here the authentication policies in place for both System Administrators and General Users. Explain how Systems Administrator rights are controlled. Other levels of access right can be defined as needed and the policies and controls for those additional levels will need to be added here. 4. Hardware and Software Maintenance This section describes the controls for ensuring that hardware and software remains secure, approved and operational through the appropriate maintenance procedures such as hardware upgrades, software patching and license management. It also includes special controls and procedures needed for: a. System Documentation and Source Code Describe here the policies and controls that restrict access to system documentation and source code. b. Configuration Management Describe the system configuration management plan that is used to manage the source code and documentation from system design and development, through implementation and maintenance. 5. Security and Privacy Awareness, Training, and Education This section describes the appropriate security and privacy awareness, training and education policies that are in place for employees and other users. This training should include security awareness training to instruct users how to promptly report suspected vulnerabilities, security violations and security incidents. Identify any special training that is required for different levels of information and system access. 6. Incident Response Capability This section describes what policies are in place for detecting, reporting, and responding to security incidents relating to unauthorized access to network, systems and data. 7. Security Advisory Alert Handling This section describes the policies in place to perform ongoing monitoring, analysis and alert handling of security vulnerabilities and incidents published by the information security/information assurance community. It also serves to assess their relevance and potential impacts on network and system infrastructures. 8. Monitoring This section describes the policies and controls in place to monitor application, network and system logs for security anomalies. 9. Acceptable Use Policies a. E-Mail Define any policies and controls that are in place for employees or other users. This includes required training and other account specific permissions. 5 b. Internet Access Define any policies and controls that are in place for employees or other users. This includes required training and other account specific permissions. c. Digital Media Define what policies and controls are in place for employees and others users to ensure they abide by software and digital media copyright laws and do not obtain, install, replicate or use unlicensed software and digital media. d. Social Media Define what policies and controls are in place for employees and others users to ensure they are aware of the risks of social media, such as the release of sensitive information and/or the compromise of the company brand. 10. Mobile Devices This section describes the policies and controls over the use of mobile devices such as laptops, tablets and smart phones on the network. 11. Peer-to-Peer Networking and Instant Messaging This section describes the policies and controls for using peer-to-peer networking and instant messaging across internal and external networks. 12. Separation of Duties This section describes the Separation of Duties policies in place to ensure that no individual or group has unilateral access to network, system and data resources or business functions. 13. Least Privilege This section describes the policies and controls that ensure system access is only granted to the minimum level to accomplish that task. For example General Users should not have System Administrator elevated privileges. 14. Remote Access/End Point Security This section explains the policies and controls established for employees and other users to remotely access the network using either a wireless or physical connection. 5. Policy on Technical Controls This chapter explains how the controls defined in chapter 4 are implemented. 1. Identification and Authentication This section explains how employees and other users are verified for system access and how policies are enforced. This can be done through the use of account/password, smart cards, 3D facial scan. 6 2. Audit Records This section explains how system access and usage is logged and monitored for suspicious activity. 3. Remote Access This section explains how remote access to networks is restricted and secured using enterprise approved identification and authentication methods. This includes detection of intrusion attempts and protection against unauthorized access. 4. Vulnerability Testing This section explains how protection controls are routinely tested for robustness. 5. Encryption This section explains how information is protected using encryption technologies during processing, transfer and storage. 6. Malicious Code Protection This section explains how enterprise systems enforce protections to minimize the risk of introducing malicious code (e.g., viruses, worms, spyware, Trojan horses) into enterprise systems and networks. It should also explain how often virus signatures are updated. 7. Patch Management This section explains how patches are managed and implemented on all system components in a timely manner. 8. Trusted Internet Connection This section explains how Internet access is controlled, such as through the use of proxy servers, VPN, and firewalls. 9. Wireless and Physical Network Connection This section explains how network access controls are implemented for both wireless and physical connections from internal and external locations. 6. References National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) Special Publication 800-53 - Recommended Security Controls for Federal Information Systems and Organizations http://csrc.nist.gov/publications/nistpubs/800-53-Rev3/sp800-53-rev3-final_updatederrata_05-01-2010.pdf 7