RESPIRATORY CARE PHARMACOLOGY
advertisement

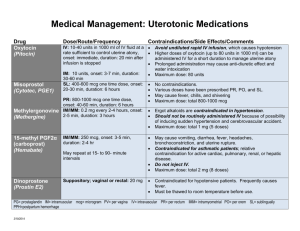
RESPIRATORY CARE PHARMACOLOGY RT205b Adrenergic Agents: Adrenergic – Term applied to nerve fibers that, when stimulated, release epinephrine at their endings. Includes nearly all sympathetic postganglionic fibers except those innervating sweat glands. Adrenergic neuron-blocking agents – Substances that inhibit transmission of sympathetic nerve stimuli regardless of whether alpha- or beta-adrenergic receptors are involved Sympathomimetic – Are substances that mimic the effects of the hormone epinephrine (adrenaline) and the hormone/neurotransmitter norepinephrine (noradrenaline). They all raise blood pressure and are all weak bases. 1. Short-acting beta-2 agonist (SABA) a. Albuterol Sulfate (s-albuterol) (Proventil, Ventolin, ProAir) SVN: Proventil, Ventolin 1. (Unit Dose 0.083%) 2.5 mg in 3.0ml 2. Dilute 0.5 milliliter (2.5mg) of the 0.5 % solution with 2.5 ml of sterile 9% normal saline solution. 3. TID, QID, Q4WA, Q4, Q2 (crisis), Continuous (crisis) 4. Time course: a. Onset: 5 minutes b. Peak: 30-60 minutes c. Duration: 4-6 hours MDI: ProAir HFA, Proventil HFA, Ventolin HFA, Airet 5. 90 ug/puff 6. 2-3 puffs TID, QID 7. Time course a. Onset: 5 minutes b. Duration: 4-6 hours b. Levalbuterol hydrochloride (r-albuterol) (Xopenex) B2 – Bronchodilator SVN: Xopenex 1. Unit Dose: a. .31 mg/3 ml; 6-11 years b. .63 mg/3 ml; 6 years - older c. 1.25 mg/3 ml; 12 years – older 2. Q 4-8 hours 3. Time course a. Onset: 5-10 minutes b. Duration: 5-8 hours MDI (Levalbuterol tartrate): Xopenex HFA 4. 90 ug/puff 5. 1-2 puffs Q 4-6 Hours 6. Time course a. Onset: 5-10 minutes b. Duration: 5-8 hours c. Pirbuterol acetate (Maxair) i. B2 – Bronchodilator ii. MDI: Maxair 1. 0.2 mg/puff 2. 2 puffs Q 4-6 Hours 3. Time course a. Onset: 5 minutes b. Duration: 5-6 hours d. Terbutaline sulfate – (Brethine, Bricanyl, Brethaire) USED TO STOP UTERINE CONTRACTIONS TO PREVENT EARLY DELIVERY i. B2 – Bronchodilator ii. SVN: Bricanyl, Brethine 1. Unit dose 2.5 mg/ml 2. Q 4-6 Hours 3. Time course a. Onset: 5 minutes b. Duration: 4-8 hours MDI: Terbutaline (Brethine, Bricanyl) 4. 0.2 mg/puff 5. 2 puffs Q 4 -6 Hours 6. Time course a. Onset: 5 minutes b. Duration: 4-8 hours DPI: Bricanyl 7. 0.5 mg/dose 8. 1 inhalation Q 4-6 Hours 9. Time course a. Onset: 5 minutes b. Duration: 4-8 hours e. Bitolterol mesylate – (Tornalate) B2 – Bronchodilator SVN: Image not available at this time 1. 2.5 mg 2. Q 6-8 Hours 3. Time course a. Onset: 4 minutes b. Duration: 6-8 hours 2. Long-acting beta-2 agonist (LABA) a. Salmeterol xinafoate – (Serevent) B2 – Bronchodilator MDI: Servent 1. 25 ug/puff 2. 2 puffs BID 3. Time course a. Onset: 10-20 minutes b. Duration: 12 hours DPI: (Serevent Diskus) 4. 50 ug/puff 5. 1 puff BID 6. Time course a. Onset: 10-20 minutes b. Duration: 12 hours b. Formoterol fumarate - (Foradil) B2 – Bronchodilator SVN: Perforomist NEW FALL 2007! 1. (Unit Dose) 20 ug in 2 ml solution? 2. 1 vial Q 12 Hours DPI: (Foradil) 3. 12 ug/inhalation 4. BID 5. Time course a. Onset: 15 minutes b. Duration: 12 hours c. Arfomoterol tartrate (Brovona) SVN Inhalation Solution (unit-dose vial for nebulization): 15 mcg/2 mL solution Some fast acting response, but dosed BID for COPD as a LABA only 3. Ultra-short-acting beta-2 agonist (USABA) a. Racemic epinephrine – (Vaponefrin, MicroNefrin, Asthma Nefrin) Moderate A – Increases blood pressure Moderate B1 – Increases heart rate Moderate B2 – Bronchodilation SVN: Image not available at this time. 1. Unit dose 2. (2.25% solution) 0.25 – 0.75 (5.63-11.25 mg) ml in 2.5 to 3 ml normal saline solution 3. Onset: 10 minutes 4. Duration: 1-4 hours b. Isoetharine mesylate – (Bronkosol, Bronkometer, Arm-A-Med, Isoetharine HCl) Moderate B1 – increases heart rate Strong B2 – bronchodilator SVN: No image at this time. 1. (1% solution) 0.25-0.50 ml (2.5-5.0 mg) Q 4-6 hour 2. Time course a. Onset: 5 minutes b. Duration: 4 hours c. Epinephrine – (Adrenalin Cl, Adrenalin) Strong A – increased blood pressure Strong B1 – increases heart rate Strong B2 – Bronchodilation SVN: No image available at this time. 1. (1% solution) 0.25-0.5 ml (2.5-5.0 mg) 2. Time course a. Onset: 1-2 minutes b. Duration: 1-3 hours Tablets: Bronkaid 3. 1 caplet ever 4 hours 4. Not to exceed 6 caplets in 24 hours d. Isoproterenol hydrochloride – (Isuprel, Isuprel Mistometer, Isoprenaline) Warning! Isoproterenol is no longer available in the United States. Strong B1 – Increases heart rate Strong B2 – Bronchodilation SVN: Isuprel 1. (0.5% solution) 0.25 – 0.50 ml (1.25-2.50 mg) in 2.5 to 3 ml normal saline solution 2. Time course a. Onset: 1-5 minutes b. Duration: 1-2 hours Anticholinergic Agents: Anticholinergic – Impeding the impulses of cholinergic, esp. parasympathetic, nerve fibers. An agent that blocks parasympathetic nerve impulses. SYN: parasympatholytic. Parasympatholytic – Having a destructive effect on or blocking parasympathetic nerve fibers. 1. Bronchodilators a. Ipratropium bromide – (Atrovent) Used as maintenance drug for COPD including chronic bronchitis and emphysema. Intensifies bronchodilator (acts stronger and longer) Do not give to patients with glaucoma or peanut allergy! SVN: 1. Unit Dose – 0.5 mg/ 2.5 ml (2% solution) 2. QID or Q 6 Hours 3. Time course a. Onset: 20 minutes b. Duration: 5-8 hours MDI: 4. 2 puffs QID or Q 6 Hours 5. Time course: a. Onset: 20 minutes b. Duration: 5-8 hours b. Tiotropium bromide – (Spiriva HandiHaler) Careful handling of drug! Wash hands! Getting medication in eyes can cause blurring of vision, pupil dilation and glaucoma. Dry Powder Inhaler (DPI); MDI IS NEW! Using HandiHaler Device Capsules packaged 6 – 30 count. MDI: 1. 9 mcg/puff 2. QD 3. Time course – unknown at this time. DPI: 4. 18 ug per inhalation 5. Once a day (best taken in AM) 6. Time course a. Onset: 20 minutes b. Duration: 24 hours c. Atropine sulfate SVN: 1. 1mg per dose QID 2. Time course a. Onset: 5-20 minutes b. Duration: 1-4 hours Combination Drugs: 1. Bronchodilators a. DuoNeb Warning! Do not give to patient’s who are allergic to soybean and peanuts. (Ipratropium bromide component) SVN 1. 3 mg Albuterol sulfate & 0.5 mg Ipratropium bromide 2. 5-15 minute treatment 3. QID 4. Time course a. Onset: Albuterol sulfate 5 min. Ipratropium bromide 20 min. b. Duration: Albuterol sulfate 4 -6 hr. Ipratropium bromide 5 -8 hr. b. Combivent Ipratropium bromide is an anticholinergic with bronchodilator activity. Albuterol sulfate is a B2 selective adrenergic bronchodilator. Contraindications: Patients with seizures, narrow angle glaucoma, Soya lecithin allergy (soybean or peanuts) MDI 1. 90 mcg Albuterol sulfate & 18 mcg Ipratropium bromide 2. 2 puffs Q6 or QID 3. Max. 20 puffs daily 4. Time Course a. Onset: Albuterol sulfate 5 min. Ipratropium bromide 20 min. b. Duration: Albuterol sulfate 4 -6 hr. Ipratropium bromide 5 -8 hr. c. Advair Serevent and Fluticasone Dipropionate (Long-acting bronchodilator + corticosteroid) 3 doses (500/50, 250/50, 100/50) steroid being the changing dose 1. 1 Puff BID (Must have patient rinse mouth after administration of meds to decrease chances of “Thrush” (oropharyngeal candidiasis or yeast infection) d. Symbicort Contains formoterol, a long-acting beta2-adrenergic agonist (LABA) and budesonide (steroid); given BID, two doses 160/4.5 mcg, 80/4.5 mcg; MDI e. Dulera (mometasone furoate/ formoterol fumarate dihydrate) BID, 100/5 or 200/5 mcg dose MDI Xanthine Drugs: Xanthine – A nitrogenous extractive contained in muscle tissue liver, spleen, pancreas, and other organs, and in the urine. It is formed during the metabolism of nucleoproteins. The three methylated xanthines are caffeine, theophylline, and theobromine. Trimethyl xanthine = caffine. Dimethyl xanthine = Theobromine 1. Dimethyl xanthines a. Theophylline – Theo-Dur, Theolair, Theovent, SloBid, Aerolate, Bronkodyl, Elixophylin, Uniphyl, Quibron-T Belongs to a class of drugs called phosphodiesterase inhibitors. These drugs inhibit the breakdown of cyclic 3’-5’ AMP to 5’ AMP by the enzyme phosphodiesterase which causes bronchoconstriction—end result is Bronchodilation Narrow therapeutic index: 1. 10-20 mg/L needed for Bronchodilation with minimum side effects. 2. Above 20 mg/L associated with unacceptable incidence of adverse effects 3. Above 35 mg/L associated with seizures and cardiac arrhythmias. P.O. (Tablet or Liquid) 4. 13 mg/kg per dose or 900 mg divided into even doses Q 6-8 Hours. 5. Average is 400 mg per day 6. Time course a. Onset: 15-60 minutes b. Duration: varies b. Aminophylline – Phyllocontin, Truphylline Prevent and relieve symptoms of acute bronchial asthma, and treatment of bronchospasm associated with chronic bronchitis and emphysema. Unlabeled uses: respiratory stimulant to cheyne-stokes respiration. Treatment of apnea and bradycardia in premature babies. Cardiac stimulant and diuretic treatment of CHF. SVN: Aminodic 1. 0.25 gm/ 1.0 ml (25% solution) Tablets: Aminophylline 2. 100 mg anyhydrous equivalent of 85 mg theophylline 3. 200 mg anyhydrous equivalent of 170 mg theophylline 4. 300 mg anyhydrous equivalent of 236 mg theophylline 5. All doses based on weight Example: Adult dose – 200 mg tab – 1 capsule TID 6. Maintenance therapy; 13 – 24 mg/kg/day 7. Q 6-8 Hours 8. Time course a. Onset: 30 minutes b. Duration: varies IV: Aminophylline 9. Must be given slowly (can cause cardiac arrest) 10. Emergency: 4.4 - 7 mg/kg followed by maintenance dose 11. Maintenance: 0.5 – 0.0 mg/kg/hr 12. Smoker: 0.75 mg/kg/hr 13. Time course a. Onset: 5 – 15 minutes b. Duration: varies Corticosteroid Agents: Corticosteroid – Any of a number of hormonal steroid substances obtained from the cortex of the adrenal gland. They are classified according to their biological activity as glucocorticoids, mineralocorticoids, and androgen. Adrenal corticosteroids do not initiate cellular and enzymatic activity but permit many biochemical reactions to proceed at optimal rates. Corticosteroids: used widely in the management of the inflammatory process associated with asthma, reactive airway disease, and other pulmonary disorders. Helps prevent mast cell degranulation that leads to the inflammatory response. 1. Anti-inflammatory Drugs a. Beclomethasone – Beclovent Rotacaps, Beclodisk, Vanceril, QVAR HFA MDI a. 40-80 ug/puff b. 2 puffs TID or QID c. 2-4 puffs BID (max 20 puffs/day) d. Time course: i. Onset: Varies ii. Duration: Varies b. Budesonide – Pulmicort i. SVN: Pulmicort Respule a. Used to prevent asthma attacks—not to treat them. b. c. d. e. Unit dose: 0.5 mg/ml BID 1 mg is total daily dose Time course: i. Onset: within 24 hours ii. Duration: varies DPI: Pulmicort Turbuhaler f. 200 ug/puff g. 1 – 3 puffs BID h. Time course: i. Onset: within 24 hours ii. Duration: Varies c. Dexamethasone – Decadron, Dexasone, Diodex, Hexadrol, Maxidex, Dexamehasone Sodium Phosphate, Dexamethason Acetete. Dexamethasone is a synthetic glucocorticoid. Its naturally occurring counterparts are hydrocortisone and cortisone. Although the drug is used in a variety of ways, in general, it reduces inflammation and depresses the immune system. Decreases inflammation by suppression of neutrophil migration, decreased production of inflammatory mediators, and reversal of increased capillary permeability; suppresses normal immune response. MDI: 1. 84 ug/puff. 2. 2-3 puffs BID or QID 3. Time course a. Onset: 1 Hour b. Duration: 2-3 Days Tablets: Dexamethasone 1. Decadron 0.25 mg – orange, scored, five-sided tablet 2. Decadron 0.50 mg – yellow, scored, five-sided tablet 3. Decadron 0.75 mg – bluish-green, scored, five-sided tablet 4. Decadron 1.50 mg – pink, scored, five-sided tablet 5. Decadron 4.00 mg – white, scored, five-sided tablet 6. Decadron 6.00 mg – green, scored, five-sided tablet Injectables: Dexafort 1. 2 mg/ml 2. 4 mg/ml 3. 8 mg/ml 4. 10 mg/ml 5. 16 mg/ml 6. 20 mg/ml 7. 24 mg/ml Liquid preparation: Dexamethasone 1. 0.5 mg/ml Flunisolide – Aerobid Similar to Azmacort, but said to have a longer duration time. MDI a. 250 mcg/puff b. 2 puffs BID c. Max 8 puffs/day d. Time course i. Onset: Varies ii. Duration: Varies e. Fluticasone MDI: Flovent HFA a. 44, 110, 220 ug/puff b. 2 puffs BID c. Time course i. Onset: 24 hours ii. Duration 2-3 days DPI: Flovent (Rotadisk) a. 50, 100, 250 ug/blister b. 100-1000 ug BID (titrated dose) c. Time course i. Onset: 24 hours ii. Duration: 2-3 days f. Triamcinolone – Azmacort Indicated for the maintenance of asthma and as prophylactic therapy. Azmacort may reduce or eliminate the need for systemic corticosteroids Pulmonary function improvements seen after 1-2 weeks. It is desirable to titrate the lowest effective dose. MDI a. 100 mcg/puff b. 2-4 puffs c. BID or QID d. Max 16 puffs/day g. Prednisone – Prednisone, Deltasone, Meticorten, Orasone, Sterapred Reduces inflammation and enhances the actions of Sympathomimetic agents. Effective as an immunosuppressant and affects virtually all of the immune system Many side effects include weight gain and “moon face”. Tablet or Liquid a. 5-60 mg dose b. QD c. Time course i. Onset: Varies ii. Duration: Varies h. Hydrocortisone Is a corticosteroid similar to a natural hormone called cortisol produced by the adrenal glands Commonly used as a replacement therapy in adrenocortical deficiency states. Tablet – Cortef i. 5 -30 mg j. BID or QID k. Time course i. Onset: varies Intravenous/Intramuscular (IV or IM) – Solu-Cortef l. 4 mg/kg m. Q 4-6 Hours n. Time course Methylprednisolone a. Prevents mast cell degranulation b. PO (by mouth): Medrol 4-48 mg/daily Time course 1. Onset: 1-3 hours 2. Duration: 1-2 days IV (intravenously): Solu-Medrol 1-2 mg/kg Q 4-6 Hours Time course 3. Onset: rapid 4. Duration: 7 days c. IM (intramuscular): Solu-Medrol 10-250 mg/kg Q 6 Hour Time course 1. Onset: 4-8 days 2. Duration: 1-5 weeks Mucolytics & Wetting Agents: Mucolytics are used to thin & liquefy thick, tenacious secretions. Mucolytics increase the production of respiratory tract fluids & reduce viscosity of secretions. Secretions can then be more easily expectorated or suctioned. Many Mucolytics can cause bronchospasms, which can be minimized or avoided by giving a bronchodilator just before or with mucolytic, depending on compatibility. Mucolytic – Breakdown of mucus 1. Mucoactive Agents a. Acetylcysteine - Mucomyst 10% & 20 %, Mucosil 10 & 20 i. Breaks disulfide bonds in mucus & decreases viscosity. ii. Give with bronchodilator to prevent bronchospasm. iii. Store in refrigerator after opening. iv. Also used with acetaminophen overdose as an antidote. v. Mist may set off fire alarm systems. vi. Smells like “rotten eggs” v. SVN 1. 1-20 mL of 10% solution 2. 1-10 mL of 20% solution 2. TID or QID PRN b. Dornase alfa – Pulmozyme i. Mucolytic-hydrolyzes sputum DNA, & decreases mucous viscosity & elasticity. ii. Used to treat CF or other infection or disease with purulent mucus, iii. Can cause pharyngitis & cough. iv. Do not mix with other drugs. v. SVN (use Hudson Updraft, Pari LC plus or Marquest Acorn II) 1. 2.5 mL of 1 mg/ml solution 2. QD PRN c. Aqueous aerosols; water, saline (0.45%, 0.9%, 3%-10%) i. (2-5 ml) 0.45% used with ultrasonic nebulizer to humidify and thin secretions. 1. Deposits more distally. 2. Less irritating to mucosa than 0.9% NS via ultrasonic. ii. (2-5 ml) 0.9% used via SVN or instilled intratracheally PRN to humidify and thin secretions. 1. Also used as a diluent for full strength bronchodilators 2. Isotonic NaCl iii. (2-5 ml) 3%-10% used to induce sputum. 1. Irritant to lung 2. Given with Neb PRN 3. Used with caution for patients with edema or salt restrictions. 4. Hypertonic NaCl d. Sodium bicarbonate – NaHCO3 i. 2-5 ml of 2%-7.5% solution via Neb or instilled intratracheally PRN ii. Breaks saccharide chains in mucus, lowers surface tension and decreases adhesiveness. iii. Give bronchodilator to reduce bronchospasm iv. Caution in edema, salt restrictions, or metabolic alkalosis Aerosolized Anti-Infective Medications: 1. Anti-Infectives a. Tobramycin – Nebcin, TOBI i. Antibiotic used to treat CF & many bacterial pulmonary infections ii. Give B2 bronchodilator first to prevent bronchospasms. iii. May need to increase flow rate to 8-12 lpm depending on solution viscosity. iv. SVN 1. 80 mg dose 2. BID for 28 days b. Pentamidine isethionate – NebuPent, Pentam 300, Pentacarinat i. Effective against Pneumocystis Carinii ii. Give bronchodilator before Pentamidine to prevent bronchospasm iii. RCP should wear mask as protective barrier iv. Drug delivered with Respirgard II nebulizer (See Image) v. SVN: NebuPent 1. 300 mg dose 2. 35-40 minute treatment 3. Administered Q 4 week c. Ribavirin – Virazole Neuromuscular Blocking Agents: 1. Neuromuscular Blockers a. Succinylcholine chloride – Anectine (Depolarizing) b. Pancuronium – Pavulon (Nondepolarizing c. Tubocurarine chloride – Tubarine (Nondepolarizing) d. Vecuronium bromide – Norcuron (Nondepolarizing) Leukotriene Inhibitors: 1. Leukotrienes a. Montelukast Sodium - Singulair b. Zafirlukast - Accolate c. Zileuton - Zyflo Cromolyn & Nedocromil: Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). Inhibiting mast cell degranulations during antigen-antibody reaction. Prevents the release of chemical mediators, including histamine, serotonin, & slow-reacting substances of anaphylaxis (SRS-A). These mediators cause inflammation and bronchospasm. More beneficial to children than adults. Cromolyn Sodium – Intal, Crolom SVN 20 mg/ 2 mL NS QID Time course Onset: 20-30 minutes Duration: 2-6 hours MDI 800 mcg/puff (age 4 and older) 2 puffs QID Time course Onset: 20-30 minutes Duration: 2-6 hours DPI (Spinhaler) 20 mg/capsule QID Time course Onset: 20-30 minutes Duration: 2-6 hours Nedocromil sodium - Tilade Surfactant Agents: 1. Surfactants a. Beractant – Survanta b. Colfosceril - Exosurf c. Calfactant – Infasurf d. Poractant alfa - Curosurf e. Lusupultide – Venticute