Engineering
advertisement

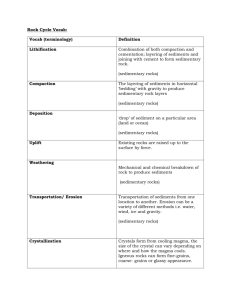
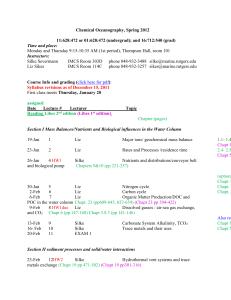
Identification Subject Department Program Term Instructor E-mail: Phone: Classroom/hours Prerequisites Language Compulsory/Elective Required textbooks and course materials Geology for Petroleum Engineering (3 KU/6 ECTS credits) Petroleum Engineering Undergraduate Spring, 2013 Gasham Zeynalov gzeynalov@khazar.org (+994 12) 421-79-16 (ext. 243 ) 11 Mehseti str. (Neftchilar campus), Room #403N, Wednesday 13.40-17.30 Office hours Consent of instructor English Required Core textbook: 1.Charles C. Plummer, David McGeary and Diane H.Carlson, Physical Geology, McGraw-Hill Higher Edication, 2001 2.Reineck H.E., Singh I.B., Depositional Sedimentary Environments, Springer-Verlaq, 1989 3. HW Petroleum Geoscience, 2003 Course website Course outline Course objectives Learning outcomes This course is prepared to gain high knowledge about Geology for Petroleum Engineering discipline. The course combines theoretical foundations with practical applications. We will begin with a general overview in each topic and then go into more detail on several concepts. Finally, we will create ability to carry out geological analysis and make optimization on Depositional Environments of sediments and their source rock and reservoir quality for exploration and appraisal program of the oil and gas fields. This course is a basic subject of a Petroleum Engineering. In this course will be covered a lot of topics of Geological sciences. General Objectives of the Course: to meet curriculum requirements of the School of Engineering and Applied Sciences Specific Objectives of the Course: - to support students academically, to provide background understanding about Earth, Earth structure and how it works - to encourage students participation and interaction and fostering and atmosphere of to learn and respect - focus on aspects that are important to exploration and production activities in Petroleum Industry By the end of the course the students should be able: - to understand importance of Geology, including Earth structure and processes; - different rock types and their cycles, - Sedimentary rocks and their pore fluids - Plate tectonics of the Lithosphere; - Sedimentation processes in the basins; - Petroleum Play and System concepts, - Clastic and carbonate depositional environments and their importance in hydrocarbon system; - different types of geologic and structural mapping in the Petroleum Engineering. - to integrate these sounds with Petroleum Engineering subjects Teaching methods x x x x x Evaluation Lecture Group discussion Experiential exercise Simulation Case analysis Course paper Others Methods Policy Midterm Exam Case studies Class Participation Assignment and quizzes Project Presentation/Group Discussion Final Exam Others Total Preparation for class Date/deadlines Percentage (%) 30 10 10 10 40 100 The structure of this course makes your individual study and preparation outside the class extremely important. The lecture material will focus on the major points introduced in the text. Reading the assigned chapters and having some familiarity with them before class will greatly assist your understanding of the lecture. After the lecture, you should study your notes and work relevant problems . Withdrawal (pass/fail) This course strictly follows grading policy of the School of Engineering and Applied Science. Thus, a student is normally expected to achieve a mark of at least 60% to pass. In case of failure, he/she will be required to repeat the course the following term or year. Cheating/plagiarism Cheating or other plagiarism during the Quizzes, Mid-term and Final Examinations will lead to paper cancellation. In this case, the student will automatically get zero (0), without any considerations. Professional behavior guidelines The students shall behave in the way to create favorable academic and professional environment during the class hours. Unauthorized discussions and unethical behavior are strictly prohibited. Week Tentative Schedule 1 Date/Day (tentative) Topics Introduction to the Geology: Key elements in geological studies Importance of Geology in the Petroleum Engineering Textbook/Assi gnments Chapt. 1(1) 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 Geological images at different scales Formation of the Earth, origin of life Evolution, Nature and Composition of the Earth Rock cycle models Basic rock types and their identification Igneous, Metamorphic and Sedimentary rocks Silici-clastic and carbonate sedimentary rocks Description of the rocks and their identification and characterization (mineralogy composition and rock types) Earth processes: Plate Tectonics and evidence for plate tectonic theory Types of plate margins (spreading and subduction zones) and associated basins Chapt.1 (1) Sedimentary Basins: basin formation in divergent and convergent margins Controls on sedimentary deposition in basins Sedimentary rocks and their mineral composition and their pore fluids Transgression, regression, onlap and offlaps Stratigraphy and Geologic time scale Unconformity formation in sedimentation process Interpretation of SEM and photomicrograph images (petrography) Mid -term Examination Chapt.6,8,10 (1) Petroleum Play concept, Petroleum play key elements Risk analysis in exploration of oil and gas fields Petroleum Systems: Elements and processes Source rocks deposition environments and maturation characteristics Identification trapping mechanisms in oil fields Sedimentology and classification of sedimentary rocks, Sediment textures: grainsize, fabric, packing and morphology variations Porosity and permeability, Controls on Porosity and Permeability Compaction and cementation in detrital sediments Stratigraphic and geologic time scale characteristic of the basin (in example of the South Caspian and Kura basins) Transportation and deposition of sediments and their different models Sedimentary processes and rock facies, Sedimentary structures and bedforms Identifying bedforms, sedimentary structures on outcrop and well data Facies and Facies sequences, Walter law Clastic depositional Environments: Aeolean, fluvial, deltaic, coastal and deep water sediments, Identifying bedforms, Chapt. 2(3) chapt.3,6,7 (1) chapt.19 (1) Chapt.6 (1). Part 1 (2) Chapt. 2(3) Chapt.6 (1) Part 1 (2) Chapt.6 (1) Part 1 (2) Chapt.9,10 (1) sedimentary structures on outcrop and well data Carbonate Sediments : Carbonate grains and minerals, classification of carbonate sediments Carbonate depositional Environments, Porosity in carbonate rocks 13 14 15 16 Chapt.9,10 (1) Part II (2) Structural geology: structural features( faults, folds, fractures, diapirs and their interactions) Contractional and extensional structures Identifying Structural features on well log data Chapt.14 , 15 (1) Mapping: contouring and structural mapping Manual and computer contouring, fault mapping Constructing a contour map of spatial data using manual and mechanical contouring Final Examination Chapt.15(1) TBA This syllabus is a guide for the course and any modifications to it will be announced in advance.