Curriculum 4 Year plan
advertisement

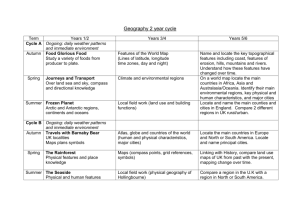
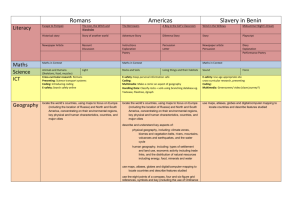
Key Stage 2 History & Geography Curriculum 4 Year plan Autumn Term 2014 Title: ‘Time Machine: 19142014’ History Geography Spring Term 2015 Title: ‘Tell Me a Story’ British History An extended period study, e.g. - The changing power of monarchs - Significant turning points in British history - Crime & punishment - Leisure A local history study linked to areas of British History studied, tracing how several aspects of national history are reflected in the locality Use maps, atlases, globes and digital/computer mapping to locate countries and describe features studied. Summer Term 2015 Title: ‘Fantastic Physical Feats’ British History Stone Age to Iron Age Britain, including: - hunter-gatherers and early farmers - Bronze age religion, technology & travel - Iron age hill forts Locate the world’s countries using maps to focus on Europe, and North and South America, concentrating on their environmental regions, key physical and human characteristics, countries, and major cities. Identify the position and significance of latitude, longitude, Equator, Northern Hemisphere, Southern Hemisphere, the Tropics of Cancer and Capricorn, Arctic and Antarctic Circle, the Prime/Greenwich Meridian and Key Stage 2 History & Geography Curriculum 4 Year plan time zones (including day and night). Key Stage 2 History & Geography Curriculum 4 Year plan Autumn Term 2015 Title: ‘Around the World’ History Spring Term 2016 Title: ‘Age of Empires’ Summer Term 2016 Title: ‘Olympics’ The Roman Empire and its impact on Britain, including Ancient Greece – a study of Greek life and achievements and their influence on the western world. - Julius Caesar’s attempted invasion in 55-54 BC - the Roman Empire by AD 42 and the power of its army - successful invasion by Claudius and conquest, including Hadrian’s Wall - British resistance, for example, Boudica - ‘Romanisation’ of Britain: sites such as Caerwent and the impact of technology, culture and beliefs, including early Christianity Geography Locate the world’s countries, using maps to focus on Europe (including the location of Russia) and North and South America, concentrating on their environmental regions, key physical and human characteristics, countries, and major cities Identify the position and significance of latitude, longitude, Equator, Northern Hemisphere, Southern Hemisphere, the Tropics Name and locate counties and cities of the United Kingdom, geographical regions and their identifying human and physical characteristics, key topographical features (including hills, mountains, coasts and rivers), and land-use patterns; and understand how some of these aspects have changed over time. Locate the world’s countries, using maps to focus on Europe (including the location of Russia) and North and South America, concentrating on their environmental regions, key physical and human characteristics, countries, and major cities. Identify the position and significance of latitude, longitude, Equator, Northern Hemisphere, Southern Hemisphere, the Tropics Key Stage 2 History & Geography Curriculum 4 Year plan of Cancer and Capricorn, Arctic and Antarctic Circle, the Prime/Greenwich Meridian and time zones (including day and night). of Cancer and Capricorn, Arctic and Antarctic Circle, the Prime/Greenwich Meridian and time zones (including day and night). Understand geographical similarities and differences through the study of human and physical geography of a region of the United Kingdom, a region in a European country, and a region within North or South America Use maps, atlases, globes and digital/computer mapping to locate countries and describe features studied. Use maps, atlases, globes and digital/computer mapping to locate countries and describe features studied. Key Stage 2 History & Geography Curriculum 4 Year plan Autumn Term 2016 Title: ‘Ununited Kingdom’ OR ‘Invaders and Settlers’ History Britain’s settlement by Anglo Saxons and Scots, including: -Roman withdrawal from Britain in c. AD 410 and the fall of the western Roman Empire - Scots invasions from Ireland to north Britain (now Scotland) - Anglo-Saxon invasions, settlements and kingdoms: place names and village life - Anglo-Saxon art and culture - Christian conversion – Canterbury, Iona and Lindisfarne The Viking and Anglo-Saxon struggle for the Kingdom of England to the time of Edward the Confessor, including: -Viking raids and invasion - resistance by Alfred the Great and Athelstan, first king of England - further Viking invasions and Danegeld - Anglo-Saxon laws and justice - Edward the Confessor and his death in 1066 Spring Term 2017 Title: ‘Disaster!’ Summer Term 2017 Title: ? A non-European society that provides contrasts with British history – one study chosen from: early Islamic civilization, including a study of Baghdad c. AD 900; Mayan civilization c. AD 900; Benin (West Africa) c. AD 900-1300. Key Stage 2 History & Geography Curriculum 4 Year plan Geography Human geography, including: types of settlement and land use, economic activity including trade links, and the distribution of natural resources including energy, food, minerals and water. Physical geography, including: climate zones, biomes and vegetation belts, rivers, mountains, volcanoes and earthquakes, and the water cycle. Locate the world’s countries, using maps to focus on Europe (including the location of Russia) and North and South America, concentrating on their environmental regions, key physical and human characteristics, countries, and major cities. Identify the position and significance of latitude, longitude, Equator, Northern Hemisphere, Southern Hemisphere, the Tropics of Cancer and Capricorn, Arctic and Antarctic Circle, the Prime/Greenwich Meridian and time zones (including day and night). Use maps, atlases, globes and digital/computer mapping to locate countries and describe features studied. Key Stage 2 History & Geography Curriculum 4 Year plan Autumn Term 2017 Title: ‘Ancient Civilizations’ History Spring Term 2018 Title: ‘Map It!’ The achievements of the earliest civilizations – an overview of where and when the first civilizations appeared and a depth study of one of the following: Ancient Sumer; The Indus Valley; Ancient Egypt; The Shang Dynasty of Ancient China. Summer Term 2018 Title: ‘Exmouth Now and Then’ British History An extended period study, e.g. - The changing power of monarchs - Significant turning points in British history - Crime & punishment - Leisure A study over time tracing how several aspects of national history are reflected in the locality. Geography Locate the world’s countries, using maps to focus on Europe (including the location of Russia) and North and South America, concentrating on their environmental regions, key physical and human characteristics, countries, and major cities. Identify the position and significance of latitude, longitude, Equator, Northern Hemisphere, Southern Hemisphere, the Tropics of Cancer and Capricorn, Arctic and Name and locate counties and cities of the United Kingdom, geographical regions and their identifying human and physical characteristics, key topographical features (including hills, mountains, coasts and rivers), and land-use patterns; and understand how some of these aspects have changed over time. Use the eight points of a compass, four and six-figure grid references, A study of an aspect of history that is significant in the locality. Use fieldwork to observe, measure, record and present the human and physical features in the local area using a range of methods, including sketch maps, plans and graphs, and digital technologies. Human geography, including: types of settlement and land use, economic activity including trade links, and the distribution of natural resources including energy, food, minerals and water. Key Stage 2 History & Geography Curriculum 4 Year plan Antarctic Circle, the Prime/Greenwich Meridian and time zones (including day and night). symbols and key (including the use of Ordnance Survey maps) to build their knowledge of the United Kingdom and the wider world. Use maps, atlases, globes and digital/computer mapping to locate countries and describe features studied. Human geography, including: types of settlement and land use, economic activity including trade links, and the distribution of natural resources including energy, food, minerals and water. Physical geography, including: climate zones, biomes and vegetation belts, rivers, mountains, volcanoes and earthquakes, and the water cycle. Physical geography, including: climate zones, biomes and vegetation belts, rivers, mountains, volcanoes and earthquakes, and the water cycle.