Chemistry of Life & Macromolecules Study Guide
advertisement

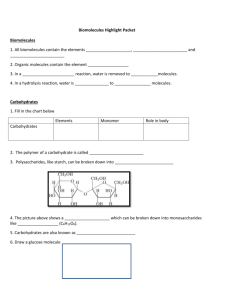
Name: _____________________________________ TOC:___ Chemistry of Life Unit Test Study Guide Below is the proficiency scale for CH 2: Chemistry of Life and LS 1A: Macromolecules. For each part it is broken down what exactly this means, and where you can find the information in your TOC. For each section, highlight the parts you think you should study the most. Then complete the review questions for each section. Remember, part of the unit test grade comes from completing your project. Everything may NOT be covered in this study guide. This information should HELP you answer every question on the test, but not give you the answers! CH 2: Chemistry of LIfe Level 2 ● Identifies that carbon, hydrogen, nitrogen, oxygen, phosphorus, and sulfur are the most abundant elements in proteins, carbohydrates, lipids, and nucleic acids. ○ Remember our acronym CHNOPS? ○ Make sure you know which atoms are in which macromolecules ● Identifies the monomers and polymers of proteins, carbohydrates, lipids and nucleic acids. This is just memorization! You gotta just do it! ● Provides examples of proteins, carbohydrates, lipids and nucleic acids. ○ You should make sure you know both examples in food and examples in the body Level 3 ● Describes the unique bonding properties of carbon that permits the formation of proteins, carbohydrates, lipids, and nucleic acids. ○ You need to make sure you understand carbons structure and its ability to bond ● Describes the structure, properties, and functions of proteins, carbohydrates, lipids, and nucleic acids. ○ Structure: make sure you understand the overall structure of macromolecules. You also need to understand that monomers bond together to form polymers and how that is made and broken. ○ Properties/Functions: You need to know all the general functions of each macromolecule. You also need to know what the functions. Yes ALL of them. Level 4 ● Distinguishes among different types of proteins, carbohydrates, lipids or nucleic acids and their functions (e.g. hormone, heredity). ○ This is knowing all the little nitty gritty details of how these help our bodies functions, both in general and with specific functions. I may or may not test you on all of them, but you are responsible for them ● Matches the structural formulas of monomers to proteins, carbohydrates, lipids, or nucleic acids. ○ Make sure you know the way the monomers look chemically! It is on Remember, there are many versions of each monomer (i.e. there are 20 different amino acids) LS 1A: Macromolecules Level 2: ● Know the types of macromolecules in cells. Level 3: ● Explain the function of macromolecules in cells (lipids, protein, nucleic acid, carbohydrates) ○ Keep in mind that this is the function within a single cell, not in the organism. ○ These are generalized functions of the entire group ● Understand how macromolecules work to accomplish specific functions within a cell. ○ For this you need to know the different functions of different types of each macromolecules ○ Here you will be asked to explain HOW they function within the cell (as opposed to what the function is). Level 4 ● Explains the role of specific macromolecules in maintaining homeostasis in an organism. TOC#9 ○ Make sure you know them all. Each macromolecule has many versions. Some have more than one function. It may be helpful to make flashcards of these. Review Questions! These questions are for both proficiency scales. 1. What are the 6 elements you find in the 4 macromolecules of life? 2. Complete the following chart for the four types of macromolecules: Compound Elements Monomer Polymer What kind of food is it in? 3. Answer the following questions about why carbon is in all macromolecules a. What is the number of valence electrons in carbon? ____________ b. How many bonds can carbon makes? _________ c. What kinds of bonds does carbon make? 4. What is a monomer? What is a polymer? What is polymerization? 5. Explain dehydration synthesis and how it relates to polymerization. 6. Explain hydrolysis and how it relates to polymerization. 7. List the general functions of each macromolecule in the cell and in the body: Molecule Carbohydrates Function in cell Function in organisms Where is it found in organisms? Lipids Proteins Nucleic Acid Explain the function of the different types of these macromolecules 8. Explain the difference between glucose and glycogen: a. Type of Macromolecule: ________________________________________ Glucose Glycogen 9. Explain the difference between RNA and DNA: a. Type of Macromolecule:_________________________ DNA RNA 10. Name the 8 types of proteins, their functions, and name some examples: Type of Proteins Functions Examples 11. Name the 3 types of lipids you learned and their functions: Type of Lipids Functions 12. What are the differences between simple and complex carbohydrates? 13. For each monomer structure: write the kind of macromolecule it makes up Examples Homeostasis practice questions. Here are three examples. Make sure you could answer questions like this for all types of macromolecules in this study guide. 14. Hemoglobin is an important part of red blood cells. What type of macromolecule is Hemoglobin? How doe it help maintain homeostasis in an organism? 15. Diabetes is an illness where a person has excess sugar in their blood. Diabetes is due to either the pancreas not producing enough insulin, or the cells of the body not responding properly to the insulin produced. What type of macromolecule is insulin? What is the job of insulin? If this process isn’t working, recommend a diet for someone with this illness. 16. Lactase is a digestive enzyme. What type of macromolecule is lactase? How doe it help maintain homeostasis in an organism? Explain what may happen if this process isn’t working, recommend a diet for someone with this illness.