GRADE GRID - SI worksheet-2-3-15
advertisement
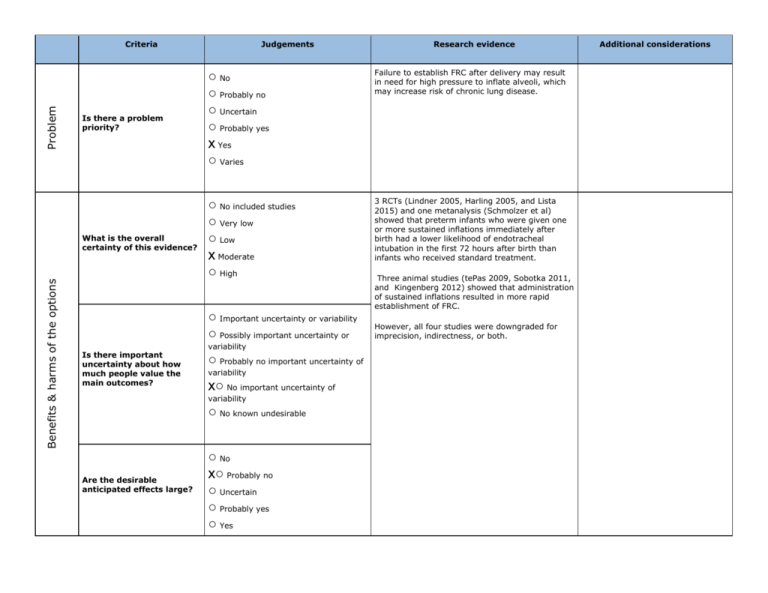
Problem Criteria Is there a problem priority? Benefits & harms of the options What is the overall certainty of this evidence? Judgements ○ No ○ Probably no ○ Uncertain ○ Probably yes x Yes ○ Varies Failure to establish FRC after delivery may result in need for high pressure to inflate alveoli, which may increase risk of chronic lung disease. ○ No included studies ○ Very low ○ Low x Moderate ○ High 3 RCTs (Lindner 2005, Harling 2005, and Lista 2015) and one metanalysis (Schmolzer et al) showed that preterm infants who were given one or more sustained inflations immediately after birth had a lower likelihood of endotracheal intubation in the first 72 hours after birth than infants who received standard treatment. ○ Important uncertainty or variability ○ Possibly important uncertainty or Is there important uncertainty about how much people value the main outcomes? variability ○ Probably no important uncertainty of variability x○ No important uncertainty of variability ○ No known undesirable Are the desirable anticipated effects large? Research evidence ○ No x○ Probably no ○ Uncertain ○ Probably yes ○ Yes Three animal studies (tePas 2009, Sobotka 2011, and Kingenberg 2012) showed that administration of sustained inflations resulted in more rapid establishment of FRC. However, all four studies were downgraded for imprecision, indirectness, or both. Additional considerations Criteria Judgements ○ Varies Are the undesirable anticipated effects small? Resour ce use Are the desirable effects large relative to undesirable effects? Are the resources required small? ○ No ○ Probably no x○ Uncertain ○ Probably yes ○ Yes ○ Varies ○ No x○ Probably no ○ Uncertain ○ Probably yes ○ Yes ○ Varies ○ No ○ Probably no ○ Uncertain Research evidence Additional considerations Criteria Judgements Research evidence Additional considerations ○ Probably yes x○ Yes ○ Varies Equity Is the incremental cost small relative to the net benefits? What would be the impact on health inequities? ○ No ○ Probably no ○ Uncertain x○ Probably yes ○ Yes ○ Varies The equipment required is routinely available ○ Increased ○ Probably increased ○ Uncertain ○ Probably reduced ○ Reduced x○ Varies Healthcare systems that could utilize sustained inflations would very likely have also have other available methods for providing ventilatory support. In low resource situations, it is equally unlikely that sustained inflations or other types of respiratory support would be available. Feasibility Acceptability Criteria Is the option acceptable to key stakeholders? Is the option feasible to implement? Judgements Research evidence Additional considerations Some institutions report using sustained inflations as standard of care. (eg, Lindner 1999 961) Application of a sustained inflation will briefly delay initiation of positive pressure ventilation should the baby not respond to the initial SI. Four studies that used SI as part of the experimental protocol did not report any problems with implementation. (te Pas 2007 322, Lindner 1999 961, Lista 2011 45, Lista 2015 in press) Some institutions report using SI routinely in preterm infants immediately after birth to establish FRC (eg, Lindner 1999 961) ○ No ○ Probably no ○ Uncertain x○ Probably yes ○ Yes ○ Varies ○ No ○ Probably no ○ Uncertain ○ Probably yes x○ Yes ○ Varies Recommendation Balance of consequences Undesirable consequences clearly outweigh desirable consequences in most settings Undesirable consequences probably outweigh desirable consequences in most settings The balance between desirable and undesirable consequences is closely balanced or uncertain Desirable consequences probably outweigh undesirable consequences in most settings Desirable consequences clearly outweigh undesirable consequences in most settings ○ ○ ○ ○ ○ Type of recommendation We recommend against offering this option routinely We suggest not offering this option We suggest offering this option We recommend offering this option x○ ○ ○ ○ Recommendation We suggest against routine use of sustained inflation to establish functional residual capacity in preterm infants who do not breathe spontaneously immediately after birth Justification Although use of SI reduced the need for intubation in the first 72 hr, there is no evidence of long-term benefit, and there was considerable variability among the studies reviewed. In addition, available data suggest that use of SI may increased the incidence of air leak. Subgroup considerations Use of sustained inflations in extremely low birth weight/extremely immature newborns might result in pneumothorax Implementation considerations There is no standardized method at present for delivering sustained inflations Would not be able to be implemented in low-resource settings. Monitoring and evaluation Babies who receive sustained inflations should be monitored for evidence of pneumothorax as well as for other complications of prematurity Research possibilities Studies to determine the optimal duration and pressure to use during sustained inflation; comparison of single vs multiple applications of sustained inflations immediately after birth