variables simplify
advertisement

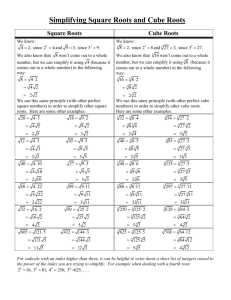
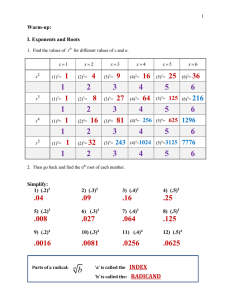
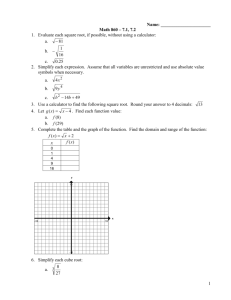
1 7.1 Roots and Radical Expressions Warm-up: I. Exponents and Roots 1. Find the values of x n for different values of x and n. x 1 x2 x2 (1)2= (2)2= x3 (1)3= (2)3= x4 (1)4= (2)4= x5 (1)5= (2)5= x3 (3)2= x4 (4)2= x5 (5)2= 2. Go back and find the nth root of each number (in the shaded rows)) Simplify: 3) (.2)2 4) (.3)2 5) (.4)2 6) (.5)2 7) (.2)3 8) (.3)3 9) (.4)3 10) (.5)3 11) (.2)4 12) (.3)4 13) (.4)4 14) (.5)4 Parts of a radical: a b ‘a’ is called the ___________________________ ‘b’ is called the: ___________________________ x6 (6)2= 2 If no index is written, this implies an index of : ______________ II. Finding Real Roots Find each real root. 8 15. 3 27 16 16. 4 81 17. 4 625 8x6 19. 5 243y 5 20. 1 81 21. 4 256x 4 y12 22. 0.01 23. 3 18. 24. 27. 3 4 0.0081 25. 3 27 26. 0.09 28. 5 32 29. 0.001 3 4 27 16 Summarizing: Even Roots Of a negative number Of a positive number Odd Roots 3 III. Practice with Roots and Variables. 30. 33. 36. 5 9x6 y12 31. 3 125x 6 y12 d 20 34. n 4n x 37. 32. 4 81a16b20 x 4 2 35. 3 x 2 6 6 3n 12n x IV. What happens when the exponents aren’t multiples of the index? (assume all variables are positive) 38. 27x5 y12 40. 4 27x5 y11 39. 3 32x 6 y8 41. 3 625x5 y11 4 Find the real-number solutions of each equation. 42. x2 = 4 43. x4 = 81 44. x2 = 0.16 45. x2 = 16 49 46. A cube has volume V = s3, where s is the length of a side. Find the side length for a cube with volume 8000 cm3. V. A twist? Simplify: 47) 50) 53) 56) 3 4 5 ( 2) 2 49) 3 ( 2)3 52) 3 ( x )3 54) 4 ( 2) 4 55) 4 ( x)4 57) 5 ( 2)5 58) 5 ( x )5 22 48) (2)3 51) (2) 4 (2)5 Summary: even variable = odd ( x)2 variable = Unless the instructions say: “do NOT assume all variables are positive,” you do not need to worry about absolute values. 5 VI. Practice: Find all the real cube roots of each number. 59. 343 60. 0.064 61. 1000 27 Find all the real fourth roots of each number. (The book says the answer can be plus and minus). It is wrong! 62. 81 63. 0.0001 6 7 7.2 Multiply and Divide Rational Functions 1) Simplifying Radicals (assume all variables are positive): 3 a) √50𝑥 5 b) √54𝑥 8 c) 2) Multiplying Radicals: 𝑛 𝑛 𝑛 𝑛 𝑛 Rule: If √𝑎 and √𝑏 are real numbers, then √𝑎 × √𝑏 = √𝑎𝑏. a) √3 ∙ √12 c) 3 e) g) 5 16 4 16 b) 4 d) 3 25 xy 8 3( 3 6) f) 3 2 5 3 4 4 x3 3 5 12 x5 5 6x 3 5x4 y3 3 16x 5 y 4 8 3) Dividing Radicals: 𝑛 𝑛 √𝑎 𝑛 𝑛 𝑎 Rule: If √𝑎 and √𝑏 are real numbers and 𝑏 ≠ 0, then 𝑛 = √𝑏. √𝑏 3 5 a) c) e) 1 5 d) x2 3 b) 5 4y 3 81 3 3 x5 3x 2 y 9 Mulitply: 1) 3 3) 5 4 x3 (2 x 4 x 3 4 6 x5 ) 6 y4 3 4 y5 Divide and Simplify: 4) 10 3 3 6) 5 4 4 xy 3 25 x 3 y 3 3 2 8 2) 3x 10 x 2 25x 5) 7) 4 4 3 3 2 25x 3 y xy 3 25 x 3 y 10 11 7.3 Binomial Radical Expressions Multiply each pair of conjugates. 3 1. 2 9 3 2 9 Add or subtract if possible. 2. 9 32 3 3. 5 22 3 4. 3 7 73 x 5. 143 xy 33 xy Simplify. Rationalize all denominators. Assume that all variables are positive. 6. 2 2 34 8. 6 45 y 2 4 20 y 2 10. 3 y 5 7. 2 y 5 5 9. 11. 2 12 5 12 4 3 81 2 3 72 3 3 24 3 10 5 2 12 13 Review 7.1-7.3 1) Simplify each radical expression. 2) Do NOT assume variables are positive. Simplify. a) 14 15 Notes for 7.4 Rational Exponents #1-8: Warm-up: 1) Recall: What is a rational number? (If you do not know this, look it up in your book) 2) On your calculator, find the value of each expression: 1 2 a) 1 2 1 2 b) 36 25 c) 49 3) What do you think it means to raise a number to the ½ power? 4) On your calculator, find the value of each expression: 1 a) 1 1 b) 125 3 8 3 c) 27 3 5) What do you think it means to raise a number to the 6) Write each expression as a radical expression: 1 1 2 a) 5 6 b) 4 5 c) x 3 7) Simplify: 3 274 8) Write each expression in exponential form: a) 5 x b) 4 x3 1 power? 3 16 This is because when you have a rational number as an exponent, the denominator is the index for the radical. Also, the numerator is the power it is raised to. Example 1: 4 3 27 is the same as 3 27 4 . This problem could be done two different ways. First Case 3 Solve. 4 3 3 (33 ) 4 4 3 9) Second Case (3 ) 4 4 4 3 3 3 3 3333 81 1 9 3 a) (27 x ) 3 3 4 3 34 81 b) 1 2 27 * 27 1 2 10) Now you try an example: (Can you add the fractions?) 1 2 3 4 x *x *x 1 5 (Remember, an exponent that is a fraction in the denominator is the same as having a radical sign in the denominator.) 11) Simplify: x 4 5 = Let’s think…. what can we multiply the top and bottom by to get the fraction exponent to disappear. 17 Simplify where possible. 12) 6 25x 4 13) 12 32 14) x 1 y3 16) 18) w 361.5 1 4 15) 3 81 4 2 10 5 243w 17) x-1.4 18 19 7.5: Solving Square Root and Other Radical Equations Warm-up: 1) Solve: x2 = 25 3) Simplify: 25 2) Simplify: 25 4) Simplify: 25 Big Idea: is looking for the PRINCIPLE Square root, Which means, the positive root. 5) Solve: x 5 6) Solve: 3 x 5 To UNDO a square root…. ___________________ both sides To UNDO a cube root… _______________________ both sides. 20 Examples: Solving Square Root and Other Radical Equations Solve. Check for extraneous solutions. 1. 1 ( x 2) 3 =5 2. 4 3x 3 + 5 = 53 21 Flow chart to help us solve: 3. x 1= x 1 4. 2x 1 =3 5. 1 x2 5=0 22 6. 9. x7 =x5 2x 5 = 7 7. 2 x 1 = 3 8. 2x 2 = 0 1 3 1 3 10. x +6=x 23 11. 4 x 2 3x 4 13. 2 x 1 26 x 12. 14. x 2 3 4 = 5 2 3 4 2x = 16