Supplemental Content - JACC: Clinical Electrophysiology
advertisement
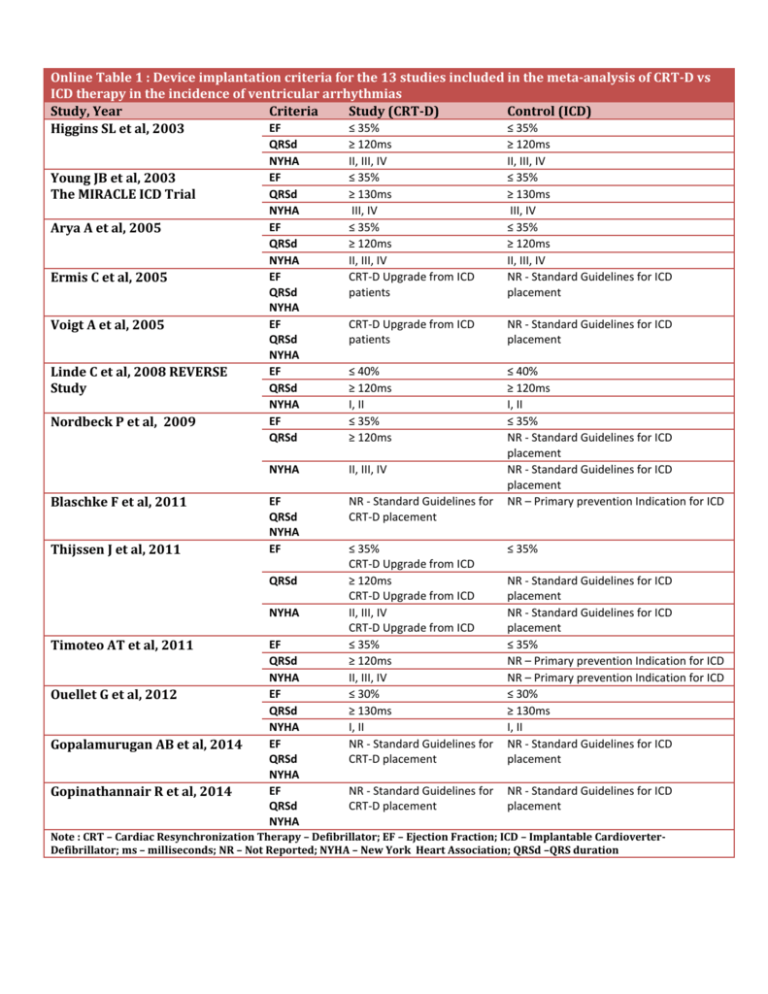
Online Table 1 : Device implantation criteria for the 13 studies included in the meta-analysis of CRT-D vs ICD therapy in the incidence of ventricular arrhythmias Study, Year Criteria Study (CRT-D) Control (ICD) EF ≤ 35% ≤ 35% Higgins SL et al, 2003 Young JB et al, 2003 The MIRACLE ICD Trial Arya A et al, 2005 Ermis C et al, 2005 Voigt A et al, 2005 Linde C et al, 2008 REVERSE Study Nordbeck P et al, 2009 Blaschke F et al, 2011 Thijssen J et al, 2011 QRSd NYHA EF QRSd NYHA EF QRSd NYHA EF QRSd NYHA EF QRSd NYHA EF QRSd NYHA EF QRSd ≥ 120ms II, III, IV ≤ 35% ≥ 130ms III, IV ≤ 35% ≥ 120ms II, III, IV CRT-D Upgrade from ICD patients ≥ 120ms II, III, IV ≤ 35% ≥ 130ms III, IV ≤ 35% ≥ 120ms II, III, IV NR - Standard Guidelines for ICD placement CRT-D Upgrade from ICD patients NR - Standard Guidelines for ICD placement ≤ 40% ≥ 120ms I, II ≤ 35% ≥ 120ms NYHA II, III, IV EF QRSd NYHA EF NR - Standard Guidelines for CRT-D placement ≤ 40% ≥ 120ms I, II ≤ 35% NR - Standard Guidelines for ICD placement NR - Standard Guidelines for ICD placement NR – Primary prevention Indication for ICD QRSd NYHA Timoteo AT et al, 2011 Ouellet G et al, 2012 Gopalamurugan AB et al, 2014 Gopinathannair R et al, 2014 EF QRSd NYHA EF QRSd NYHA EF QRSd NYHA EF QRSd NYHA ≤ 35% CRT-D Upgrade from ICD ≥ 120ms CRT-D Upgrade from ICD II, III, IV CRT-D Upgrade from ICD ≤ 35% ≥ 120ms II, III, IV ≤ 30% ≥ 130ms I, II NR - Standard Guidelines for CRT-D placement ≤ 35% NR - Standard Guidelines for CRT-D placement NR - Standard Guidelines for ICD placement NR - Standard Guidelines for ICD placement NR - Standard Guidelines for ICD placement ≤ 35% NR – Primary prevention Indication for ICD NR – Primary prevention Indication for ICD ≤ 30% ≥ 130ms I, II NR - Standard Guidelines for ICD placement Note : CRT – Cardiac Resynchronization Therapy – Defibrillator; EF – Ejection Fraction; ICD – Implantable CardioverterDefibrillator; ms – milliseconds; NR – Not Reported; NYHA – New York Heart Association; QRSd –QRS duration Online Table 2: Ventricular arrhythmia definition and device settings for the 13 studies included in the meta-analysis of CRT-D vs ICD therapy in the incidence of ventricular arrhythmias Study, year Higgins SL et al, 2003 Young JB et al, 2003 The MIRACLE ICD Trial Arya A et al, 2005 Ermis C et al, 2005 Voigt A et al, 2005 Linde C et al, 2008 REVERSE Study Nordbeck P et al, 2009 Blaschke F et al, 2011 Thijssen J et al, 2011 Timoteo AT et al, 2011 Ouellet G et al, 2012 VA Definition VT/VF episodes requiring appropriate ATP or shock therapy VT/VF episodes requiring appropriate ATP or shock therapy VT/VF episodes requiring appropriate ATP or shock therapy VT/VF episodes requiring appropriate ATP or shock therapy VT/VF episodes requiring appropriate ATP or shock therapy Sustained VT/VF episodes irrespective of device therapies - All episodes adjudicated by events committee (only 10% of all sustained VA not treated) VT/VF episodes requiring appropriate ATP or shock therapy VT/VF episodes requiring appropriate ATP or shock therapy VT/VF episodes requiring appropriate ATP or shock therapy Device Settings Not reported Not reported Zones not clearly specified. Proportion and cycle length of VA were comparable and not significantly different between two groups VT:<400 ms but ≥320 ms VF:<320 ms Not reported Zones & therapies: left to the discretion of the implanting physician. Zones & therapies: left to the discretion of the implanting physician. .Mean VT detection: 350+/- 24 ms . Mean VF detection: 310+/- 16 ms. VT :>170–180 bpm VF :>200 bpm. VT monitor zone: 150 to 188 beats/min. VT :>188-210 beats/min. VF>210 beats/min with different therapy settings Not reported VT/VF episodes requiring appropriate ATP or shock therapy VT/VF episodes requiring appropriate VT zone>180 beats/min.VF zone >250 beats/min ATP or shock therapy VT/VF episodes requiring appropriate Zones & therapies: left to the discretion of the Gopalamurugan AB ATP or shock therapy implanting physician. et al, 2014 Gopinathannair R et Sustained VA lasting >30 sec or requiring Not reported ICD therapy al, 2014 Note : ATP – Anti-Tachycardia Pacing; bpm – beats per minute; ms – milliseconds; VF – Ventricular Fibrillation; VT – Ventricular Tachycardia Online Table 3 : Ventricular arrhythmia definition and device settings for the 13 studies included in the meta-analysis of CRT responders vs non-responders in the incidence of ventricular arrhythmias Study, year VA Definition Device Settings Di Biase L et al, 2008 VT/VF episodes requiring appropriate ATP or shock therapy Mean VT detection = 395 +/- 29 ms (atleast 16 consecutive beats) Mean VF detection = 313 +/- 14 ms (sustained for 12 of 16 beats) Markowitz SM et al, 2008 Schaer BA et al, 2010 Gold MR et al, 2011 Device settings at discretion of implanting physician ThijssenJ et al, 2011 Eickholt C et al, 2012 Shahrzad S et al, 2012 VT/VF episodes requiring appropriate ATP or shock therapy VT/VF episodesrequiring appropriate ATP or shock therapy Sustained VT/VF episodes irrespective of device therapies All episodes adjudicated by events committee (only 10% of all sustained VA not treated). VT/VF episodes requiring appropriate ATP or shock therapy VT/VF episodes requiring appropriate ATP or shock therapy VT/VF episodes requiring appropriate ATP or shock therapy Itoh M et al, 2013 VT/VF episodes requiring appropriate ATP or shock therapy VT: <350 ms(>171 beats/min) Primary prevention:VT:175–180 beats/min. Secondary prevention: VT: 20 beats/minlower than the clinically observed VT. VF :210 beats/min. Device settings at discretion of implanting physician VT monitor: 150 to 188 beats/min. VT 188 -210 beats/min. VF>210 beats/min VT: 450 msto 300 ms, VF: < 300 ms VT :>168/min.VF: >187/min Manfredi JA et VT/VF episodes requiring Device settings at discretion of implanting physician al, 2013 appropriate ATP or shock therapy Friedman DJ VT/VF episodes requiring Device settings at discretion of implanting physicianbut generally VT et al, 2014 appropriate ATP or shock therapy zones in range of 160–190 beats/min. Garcia-Lunar I VT/VF episodes requiring Device settings at discretion of implanting physician et al, 2014 appropriate ATP or shock therapy Ruwald MH et VT/VF episodes requiring VT :180 to 250 bpm. VF: ≥250 bpm. al, 2014 appropriate ATP or shock therapy van der VT/VF episodes requiring VT Monitor: 150 to 188-190 beats/min, VT: 188-190 to 220Heijden AC et appropriate ATP or shock therapy 231beats/min. al, 2014 VF> 220-231beats/min Note : ATP – Anti-Tachycardia Pacing; bpm – beats per minute; ms – milliseconds; VF – Ventricular Fibrillation; VT – Ventricular Tachycardia Funnel Plot of Standard Error by Log odds ratio 0.0 0.2 Standard Error 0.4 0.6 0.8 1.0 -4 -3 -2 -1 0 1 2 3 Log odds ratio e-Figure 5: Funnel plot of studies included in the Meta-analysis of CRT-D vs ICD in the incidence of Ventricular Arrhythmias assuming Random Effect Model 4 Funnel Plot of Standard Error by Log odds ratio 0.0 Standard Error 0.5 1.0 1.5 2.0 -3 -2 -1 0 1 2 Log odds ratio e-Figure 6: Funnel plot of studies included in the Meta-analysis of CRT responders vs non-responders in the incidence of Ventricular Arrhythmias assuming Random Effect Model 3