Flood-Information-Sheet
advertisement

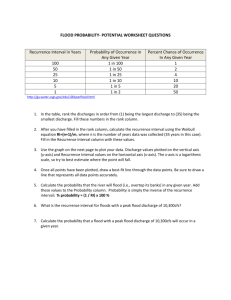
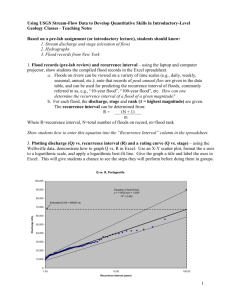
Flood Information- University of Iowa Intro to Environmental Science Lab Discharge The volume of water passing through a channel cross section in a given interval of time is a measure of the stream’s discharge. The common unit for recording discharge is cubic feet per second (ft.3 /s or cfs). Discharge is determined using the following equation, which is also known as Darcy’s law: Discharge=cross-sectional area of the channel x flow velocity Q=A x V Flood A flood is defined as the temporary overflow of a river onto adjacent lands not normally covered by water. The stage (or water level) of a river or stream is measured and recorded at a gaging station. Stage is recorded in feet or meters above a known base height. A flood recurrence level (or RI) is the average interval between floods of a particular size. The Weibull method calculates the recurrence interval by using the average time between two floods of equal or greater magnitude. This method uses the formula: RI= (n+1)/m RI equals the recurrence interval in years, n is the number of years of record, and m is the magnitude (or rank) of the annual flood discharges from the largest (ranked 1) to the smallest on record. We can better understand the frequency of flood events by creating a flood-frequency curve. A stream’s peak flood discharge values (in cfs) are plotted on the y-axis against the recurrence interval on the x-axis. Next, a best-fit line is drawn through the data points. The flood-frequency curve provides an estimate for how often a flood of a particular magnitude will occur. For example, if Creek X has a discharge of 1,000 cfs every 2 years, then in 10 years there should be 5 occurrences of a 1,0000 cfs discharge. Probability The probability that a flood will occur during any given year is the reciprocal of the recurrence interval multiplied by 100. The formula to use is: P= (1/RI) x 100% P is the percent probability of a certain-sized flood occurring in any given year, and RI is the recurrence interval. Example: What is the percent probability of a 50-year flood occurring in a given year? P= (1/50) x 100= 0.02 x 100= 2% Frequency Analysis A statistical technique (called frequency analysis) is used to estimate the probability of the occurrence of a given event. In this case, the event is a flood of a given size. Because it’s a statistical calculation, you can’t calculate a Recurrence Interval for one flood. You need a set of data that’s been collected over several years. Ten or more years of data are required to perform a frequency analysis for the determination of recurrence intervals. More confidence can be placed in the results of a frequency analysis based on, for example, 30 years of record than on an analysis based on 10 years of record. A recurrence interval of 100 means that there is a 1 in 100 chance that a flood of this size will occur in any given year. Notice that the bigger the recurrence interval (i.e., the bigger the flood), the lower the probability of it occurring.