Treatment-of-Uterine-Fibroids
advertisement

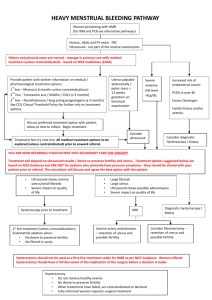
Treatment of Uterine Fibroids Uterine fibroids (leiomyoma) are benign (non-cancerous) tumors of the uterus. Many women have fibroids and are not aware of them. The uterus could contain a single fibroid of almost any size, or multiple fibroids could enlarge the uterus as much as a pregnancy does. Fibroids of the uterus are very common. Up to 50% of women will develop a fibroid in their life. There is a genetic connection, so this condition tends to run in families. The problems caused by fibroids depend on the size and location of the fibroid(s). Fibroids affecting the lining of the inside of the uterus are most likely to cause symptoms. But, even fibroids within the wall or on the outside of the uterus can be problematic. Fibroids can arise from any part of the uterus MRI showing one large fibroid filling the pelvis up to the umbilicus Worsening menstrual bleeding and more painful menses are the most common symptoms of women with uterine fibroids. Excessive blood loss can result in significant anemia. Infertility and miscarriage are related to uterine fibroids as well. Other symptoms may include frequent urination or waking at night to urinate. Large fibroids can place pressure on the bowel causing pain and constipation. Partial obstruction of the urinary system can result. Large fibroids may cause pain and pressure anywhere within the abdominal cavity. Treatment of Uterine Fibroids About half a million hysterectomies are completed every year. One third of these procedures are done for uterine fibroids. For those women with symptoms who have completed their families, hysterectomy is often recommended. This is the only treatment option that eliminates the possibility of new fibroid formation. For those women desirous of pregnancy or those who just wish to preserve their uterus, other options are available. Myomectomy refers to the removal of uterine fibroids with preservation of the uterus. With this surgical treatment, symptoms resolve and fertility is preserved and enhanced. Abdominal or open myomectomy requires an incision of several inches across the lower abdomen. The fibroids are separated form the uterus and the uterus is repaired. After surgery, a hospital stay of 2-4 days is typical and recovery at home can last from 3-6 weeks. The uterus will need to heal for several months before pregnancy is attempted. This Open Myomectomy I technique has been available for over 50 years and is still considered the “gold standard”. A single fibroid in the wall of the uterus is projecting from the top posterior portion of the uterus. The fibroid is removed. The uterus has a normal shape after removal of the fibroid and repair of the uterine wall Open Myomectomy II Uterus with multiple fibroids Fibroids removed from uterus Uterus after repair from fibroid removal Open Myomectomy III Uterus enlarged with many fibroids Fibroids removed from uterus Uterus after repair from fibroid removal Hysteroscopy refers to the inspection of the inside of the uterus with a thin telescope that is passed through the vagina and through the uterine cervix. Intracavitary fibroids occupy the inside of the uterus. Some fibroids (submucosal) grow from the uterine wall and push into the uterine cavity. Instruments attached to the hysteroscope allow the surgeon to remove fibroids from inside the uterus. One of those instruments is called a resectoscope; one of the newest instruments is called MyoSure. A balloon catheter may be placed in the uterus after surgery to prevent scarring. This catheter is removed in the office 1-2 weeks after the procedure. Hysteroscopy is an outpatient procedure and recovery is only a few days. Sometimes hysteroscopy may be used in combination with other surgical treatments for fibroids. Picture from hysteroscopy of a fibroid inside the uterine cavity. JJHscope1.WMV Laparoscopy refers to the inspection of the abdominal cavity. A small incision is made in the abdomen (usually at the umbilicus). Up to four additional incisions, all less than an inch, allow for the introduction of instruments for operative repair. Abnormalities of the pelvis can be evaluated, confirmed and often treated with this technique including the removal of uterine fibroids. Problems such as pelvic adhesions and endometriosis can be diagnosed and treated at the same time. Patients can return home the same day or after an overnight stay in the hospital. Recovery at home lasts for 1-2 weeks; much less than with the open myomectomy technique. Some studies show that pelvic scarring after surgery is reduced with this technique compared to open myomectomy. The da Vinci robotic assistant is often used for the laparoscopic removal of fibroids. This instrument allows for the removal of larger and more numerous fibroids, situations that formerly required open surgery. Laparoscopic view of uterus with large fibroid Removing fibroid from Uterus with da Vinci robotic assistant Fibroid separated from uterus Defect in uterus after fibroid removal Uterus after repair with da Vinci robotic assistant Other treatment options include uterine artery embolization (UAE) and MRI guided high focused ultrasound. These techniques improve symptoms and allow for preservation of the uterus. However, some studies demonstrate a higher incidence of complications in future pregnancies after UAE. The MRI guided treatment is so new, we don’t know how it would affect a future pregnancy. These treatments are generally not recommended for women who would like to become pregnant. Physicians at NFC were among a small group of physicians performing laparoscopic myomectomy in place of open myomectomy since the early 1990’s. They were the first physicians in Tennessee and the surrounding area to use the da Vinci system for the removal of uterine fibroids. Their years of experience in the surgical treatment of infertility means that your NFC physician has expertise in the repair and preservation of female pelvic anatomy. A consultation with an NFC physician may include a physical exam, pelvic ultrasound and other studies. Your NFC physician will discuss with you the treatment options that are most appropriate for you.