Hendra Gunawan, E061060161 2010 Habitat and Distribution of
advertisement

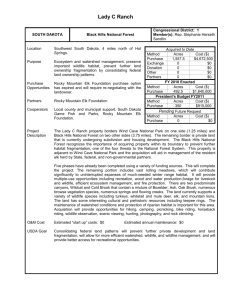
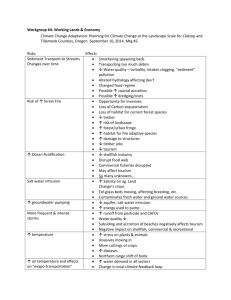
Hendra Gunawan, E061060161 2010 Habitat and Distribution of Javan Leopard (Panthera pardus melas Cuvier, 1809) on Fragmented Landscape in Centra Java Javan Leopard (Panthera pardus melas Cuvier, 1809) is limited distributed in Java Island. It’s population is continually decreasing so it listed in Red list by the IUCN as critically endangered species. The decrease was mainly caused by fragmentation and degradation of forest. The objectives of this research are to map the distribution, to identify the metapopulation types and habitat characteristics, to measure the fragmentation of natural forest and to build a spatial model of habitat suitability. The methods were include GPS mapping of population, metapopulation analyses, habitat analyses, fragmentation analyses using patch analyst and spatial modeling of habitat suitability using ArcView 3.2. The results found that there are 48 locations of javan leopards that distributed in five types of forest, i.e. pines plantation (43,8 %), teak plantation (27,1 %) natural mountain forest (14,5 %), mixed plantation forest (8,3 %) and natural lowland forest (6,3 %). Javan leopard have preference to certain type of forest (P≤0,05). Total population estimation of the javan leopard in Central Java was 234-383 individuals. There are eight components that crucial for habitat of javan leopard and relevant for spatial modeling of habitat suitability, i.e. patch extent, prey, forest vegetation, climate, water, topography, altitude and status of forest. Fragmentation in the last 16 years has reduced 88,0 % of total natural forest area in central java and fluctuate the number of patches, total edge and edge density. Javan leopards are distributed in non-equilibrium metapopulation (31,25 %), mainland-islands metapopulation (22,92 %), classic metapopulation (10,42 %) and patchy metapopulation (35,42 %). Spatial model of habitat suitability result 7,67 % patches of low suitability, 36,92 % patches of moderate suitability and 55,41 % patches of high suitability. The validity of the model is 95,83