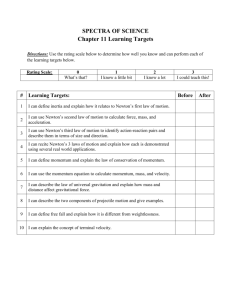
I can statements
advertisement

Mathematical Modeling 1. You will use mathematical tools to measure and predict. 2. You will apply accuracy and precision when measuring. 3. You will display and evaluate data graphically. Motion 1. You will represent motion through the use of words, motion diagrams, and graphs. 2. You will use the terms position, distance, displacement, and time interval in a scientific manner to describe motion. Accelerated Motion 1. You will develop descriptions of accelerated motion. 2. You will use graphs and equations to solve problem involving moving objects. 3. You describe the motion of objects in free fall. Newton’s Laws 1. You will use Newton’s laws to solve problems. 2. You will determine the magnitude and direction of the net force that causes a change in an object’s motion. 3. You will classify forces according to the agents that cause them. 1D and 2D Vectors 1. You will represent vector quantities both graphically and algebraically. 2. You will use Newton’s law to analyze motion when friction is involved. 3. You will use Newton’s laws and your knowledge of vectors to analyze motion in two dimensions. 2D Motion 1. You will use Newton’s laws and your knowledge of vectors to analyze motion in two dimensions. 2. You will solve problems dealing with projectile and circular motion. 3. You will solve relative –velocity problems. Gravitation 1. You will learn the nature of gravitational force. 2. You will relate Kepler’s law of planetary motion to Newton’s laws of motion. 3. You will describe the orbits of planets and satellites using the law of universal gravitation. Rotational Motion 1. You will learn how to describe and measure rotational motion. 2. You will learn how torque changes rotational velocity. 3. You will explore factors that determine the stability of an object. 4. You will learn the nature of centrifugal and Coriolis “force.” Momentum and Impulse 1. You will describe momentum and impulse and apply them to interactions between objects. 2. You will relate Newton’s third law of motion to conservation of momentum. 3. You will explorer the momentum of rotating objects. Work and Power 1. You will recognize that work and power describe how the external world changes the energy of a system. 2. You will relate force to work and explain how machines ease the load. Conservation of Energy 1. You will learn that energy is a property of an object that can change the object’s position, motion, or its environment. 2. You will learn that energy changes from one form to another, and that the total amount of energy in a closed system remains constant. Thermodynamics 1. You will learn how temperature relates to the potential and kinetic energies of atoms and molecules. 2. You will distinguish heat from work. 3. You will calculate heat transfer and absorption of thermal energy. States of Matter 1. You will explain the expansion and contraction of matter caused by changes in temperature. 2. You will apply Pascal’s, Archimedes; and Bernoulli’s principles in everyday situations. Wave Nature of Light 1. You will learn how interference and diffraction patterns demonstrate that light behaves like a wave. 2. You will learn how interference and diffraction patterns occur in nature and how they are used, Waves 1. You will examine vibrational motion and learn how it relates to waves. 2. You will determine how waves transfer energy. 3. You will describe wave behavior and discuss its practical significance. Electric Statics 1. You will observe the behavior of electric charges and analyze how these charges interact with matter. 2. You will examine the forces that act between electric charges. Sound 1. You will describe sound in terms of wave properties and behavior. 2. You will examine some of the sources of sound. 3. You will explain properties that differentiate between music and noise. Light 1. 2. You will understand sources of light and how light illuminates the universe around us. You will be able to describe the wave nature of light and some phenomena that reveal this nature. Mirrors 1. You will learn how light reflects off different surfaces. 2. You will learn about the different types of mirrors and their uses. 3. You will use ray tracing and mathematical models to describe images formed by mirrors. Refraction 1. You will learn how light changes direction and speed when it travels through different materials. 2. You will compare properties of lenses and the images that they form. 3. You will learn about different applications of lenses, including how lenses in your eyes enable you to see. Electric Fields and Potential 1. You will relate electric fields to electric forces and distinguish between them. 2. You will relate electric potential difference to work and energy. 3. You will describe how charges are distributed on conductors. 4. You will explain how capacitors store electric charges. Simple Circuits 1. You will explain energy transfer in circuits. 2. You will solve problems involving current, potential difference, and resistance. 3. You will diagrams simple electric circuits. Resistors and Circuits 1. You will distinguish among series circuits, parallel circuits, and seriesparallel combinations, and solve problems involving them. 2. You will explain the functions of fuses, circuit breakers, and ground-fault interrupters, and describe how ammeters and voltmeters are used in circuits Magnetism 1. You will assign forces of attraction or repulsion between magnetic poles. 2. You will relate magnetism to electric charge and electricity. 3. You will describe how electromagnetism can be harnessed for practical applications. Magnetic Fields 1. You will describe how changing magnetic fields can generate electric potential differences. 2. You will apply the phenomenon to construction of generators and transformers. Electro-Magnetism 1. You will learn how combined electric and magnetic fields can be used to determine the masses of electrons, atoms, and molecules. 2. You will explain how electromagnetic waves are created, travel through space, and are detected. Duality of Nature 1. You will understand that light behaves like particles having momentum and energy. 2. You will learn that small particles of matter behave like waves and are subject to diffraction and interference. Modern Physics 1. You will learn about the discovery of the atom’s composition. 2. You will determine energies of the hydrogen atom. 3. You will learn how quantum theory led to the modern atomic model. 4. You will learn how lasers work and what their applications are. Nuclear Physics 1. You will describe the components of a nucleus and how radioactive decay affects these components. 2. You will calculate the energy released in nuclear reaction. 3. You will examine how radioactive isotopes and nuclear energy are produced and used. 4. You will understand the building blocks of matter.