Art History | Medieval + Italian and Northern Renaissance
advertisement

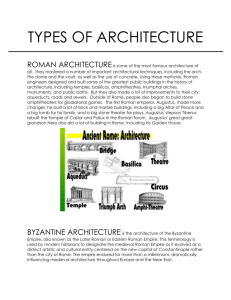
Art History | Medieval + Italian and Northern Renaissance Resources Khan Academy → http://smarthistory.khanacademy.org/ Metropolitan Museum of Art → Heilbrunn Timeline of Art History http://www.metmuseum.org/toah/ Medieval Period (Middle Ages) Roughly 500 – 1500 – Fall of Rome until Renaissance Terms reflect early historical view of an age of decline between two golden eras. Actually an age of complexity, richness and innovation that gave rise to modern Europe. Shaped by relationships developed in demise of Roman authority – especially Northern (Germanic) leaders and the Catholic Church. Periods within this era: 527 – 867 Early Byzantine, rule of Justinian 750 – 900 Carolingian period, Rule of Charlemagne 900 – 1000 Ottonian period, Otto I creates Holy Roman Empire 11th and 12th centuries, Romanesque style, Crusades and pilgrimages mid-12th – 15th centuries, Gothic style, monarchy, growth of cities Byzantine Term derives from Greek colony, Byzantium, which was the eastern part of Roman Empire from 330 CE, when Constantine declared Constantinople the capital, until the Ottoman invasion in 1453. Justinian I (527 – 565): Extensive building program (Hagia Sophia), codified and reformed Roman law Ecclesiastical works of art, San Vitale mosaic program, portraiture and propaganda Flat surfaces, heavy outlines, almond eyes, gold inlay Romanesque “In the Roman style” Use of arches, barrel vaults, thick masonry walls Pilgrimages to see relics and icons Bayeux Tapestry Gothic Abbot Suger (St. Denis) Soaring height – towers and spires Rib vaults Rose window (stained glass) Flying buttresses Early Renaissance in Italy (C. 1400-1500) Flat space, Byzantine influence Religious scenes with Madonna and Child or Saints as major focus Egg tempera on wood Extensive use of gold backgrounds (to be seen in candlelit churches) Masters Cimabue Giotto di Bondone (Arena Chapel) Masaccio Filippo Brunelleschi (Dome of Florence Cathedral – Duomo) High Renaissance in Italy (C. 1500-1520) Rebirth of classical art and literature Measured proportions Balance Ideal beauty Religious and mythological scenes Heroic male nudes Formal portraits Underlying anatomical structure: great period of scientific discovery Use of perspective Masters Donatello Michelangelo Buonarroti Leonardo de Vinci Raphael Titian Mannerism (1520-1600) Elongation and distortion of forms Emotion over reason Imagination superior to reality Artificial Masters Parmigianino Bronzino Pontormo The Renaissance in the North Develop use of oil paints Extreme detail Emotional Folding, polyptychs and altarpieces Elements of realism Masters Limbourg Brothers Robert Campin Jan van Eyck Rogier van der Weyden Albrecht Dürer Hans Holbein Heironymous Bosch Peter Bruegel El Greco (Domenikos Theotokopoulos) – Greek working in Spain