Pulley Systems & Mechanical Advantage Lab Worksheet
advertisement

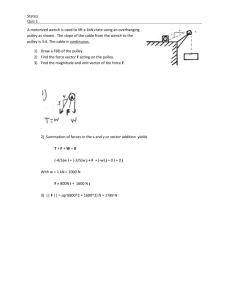
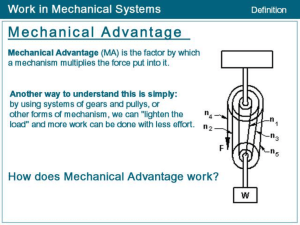
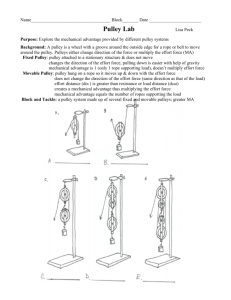
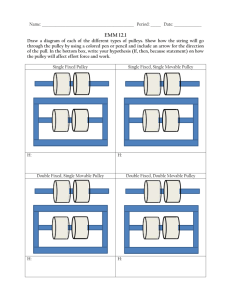
Simple Machines Pulley Up Problem: How does the type of pulley affect its mechanical advantage? What type of pulley system gives the greatest mechanical advantage? Description: A pulley is a wheel with a groove along its outer edge that holds a rope or, in this case, a string. Two or more pulleys are usually used together to reduce the amount of force needed to lift a load. However, as with all simple machines the same amount of work is necessary for the load to reach the same height as it would without the pulleys. The size of the force is reduced, but it must act through a longer distance. Background: Use the information above when writing the background. Variables: Identify the three variables in this experiment. Explain how the variables will be changed, measured or controlled. How will you change it? Independent Variable/s The one you change How will you measure it? Dependent Variable The measurable result you are looking for Constants/Controlled Variables List the factors you keep exactly the same in all parts of the lab How will you control it? Hypothesis: Write a hypothesis for this experiment. Materials: ring stand and ring pulleys string Newton-meter Digital Balance Mass MA = Resistance Effort Method: 1. Measure the resistance force of the mass using the spring balance. 2. Set up the system below. Find the effort force and record on the data table. 3. Set up this movable pulley system. Find the effort force and record on the data table. Figure 1 Pulley A Figure 2 Pulley B 3. Set up the systems below, find the effort force for each and record. Figure 3 Pulley C Figure 4 Pulley D Figure 5 Pulley E 4. Calculate the mechanical advantage for each pulley by dividing the resistance force (weight of the mass on the spring balance) by the effort force (how hard you pulled on the spring balance). Show a sample calculation. Processing of Data: A. Data Table Pulley System Resistance (weight of mass/load) in Newton Effort (pulling force in Newton (N) Trial 1 A single fixed B single movable C D E B. Summary of Observations Trial 2 Trial 3 Average Mechanical Advantage (MA= Resistance/Effort) Conclusion: 1. Answer your aim and support your answer with detailed evidence (your results). Provide an explanation of your results. 2. Write a paragraph explanation of the results and the “science” behind the results. Additional guide questions: a. Was there a difference in the mechanical advantage for the single fixed pulley (A) and the single movable pulley (B)? Explain your answer. b. As you add pulleys, what happened to the effort force you used to raise the mass? c. Why would anyone use a single fixed pulley if it does not give you a mechanical advantage? d. A machine never gives you something for nothing. Although the effort force is decreased, something else is increased. What must be increased? e. How does a pulley make the Work easier? How is this simple machine used in the real world? Evaluation: In the table provided below, identify errors and explain the effects these errors had on the results. Provide suggestions for improvement. State whether your experiment was a fair test. Weaknesses/Errors How it affected the results Improvement Overall, state whether these errors altered the final outcome of the experiment. (Was it a fair test?) CHECKLIST Part 1a: Design Plan Title and Date are provided; properly headed Background links to the topic on pulleys and mechanical advantage Aim is provided. Variables (independent, dependent, constant) are correctly identified Hypothesis: Qualitative/Quantitative predictions provided and follows If, then… because…. format 1b: Appropriate tools and techniques Materials are listed with necessary quantitative information (amount and size) Method - consists of easy to follow numbered steps (not written as a narrative). Uses active voice. Diagram of apparatus is neatly drawn and labeled appropriately; ruler and pencil drawn (labels down right hand side) 1c: Presentation of data Data table is properly headed, shows results for the variables and reflects average of the 3 trials Part 2a: Conclusion Aim is answered and supported by the data to prove hypothesis Provides an explanation of the results. Explained the science behind the experiment. Uses passive voice. 2b: Evaluation Identifies weaknesses in the method and provides suggestions for improvement Explains how the identified errors (if any) altered the final outcome Provides suggestions for future experiments. Organization Presentation-Typed, neatness; correct format; basic proofreading SELF PEER TEACHER