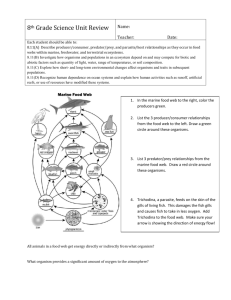
Marine Biology 2014 Cumulative Final Exam Review Sheet NOTE
advertisement

Marine Biology 2014 Cumulative Final Exam Review Sheet NOTE- IF YOU KEPT ALL OF YOUR PREVIOUS REVIEW SHEETS YOU CAN USE THOSE INSTEAD OF REWRITING EVERYTHING. I WILL NOT BE COLECTING THIS REVIEW SHEET AS A GRADE. IT IS SIMPLY TO GUIDE YOU AND PREPARE YOU FOR THE FINAL EXAM. History of Marine Science and Scientific Method 1. What are the steps of the scientific method in order? 2. How much of the Earth’s surface is covered with seawater? 3. Know the following scientists and their contributions to marine biology: a. Edward Forbes b. Alexander Agassiz c. Charles Darwin d. Charles Wyville Thomas 4. Define oceanography. 5. Define the scientific method. 6. What is the difference between induction and deduction? 7. What is the very first step in the scientific method? 8. Know the contributions of the HMS Beagle and the HMS Challenger. 9. What was the first US Marine Laboratory? 10. What is a scientific theory and in order for it to be accepted what must it show? 11. Define Marine Biology. 12. What is the difference between an independent, dependent, and controlled variable? 13. The earliest recorded direct studies of marine biology came from which people? 14. Why are oceans important? 15. Where does our knowledge of the ocean come from? 16. What contributed to our current knowledge of Marine Science the most? 17. What are the important marine laboratories around the nation and what coast are they on? Marine Ecology 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. Define ecosystem, biosphere, population, biotic, abiotic, and species. What is the difference between anaerobic and aerobic respiration? Define habitat and understand what makes up an organisms habitat. What do nutrients do when they are limited? How do they affect the bay? Where do the products of metabolism accumulate and what are metabolic wastes? What is the difference between zones of stress, optimal zones, and zones of intolerance? What must organisms that live in the intertidal deal with on a daily basis? What were the first living organisms considered to be? When is an environment considered harsh? 10. Define symbiosis and know the three types of symbiosis. Be able to provide examples. 11. What is the difference between an ectotherm and an endotherm? 12. What is the difference between a community and a population? 13. What are keystone species? 14. What is the difference between Type 1, Type 2 and Type 3 survival curves? 15. How do nutrients reach the upper levels of the ocean? 16. How much energy is transferred from trophic level to trophic level? 17. What are the important nutrients for photosynthesis both organic and inorganic? 18. What is the difference between abiotic and biotic factors? Give examples. 19. What fundamental role do animals play in the carbon cycle? 20. What is eutrophication and what can it lead to? 21. What is the most important marine photosynthetic organism? 22. Where do chemosynthetic organisms get their energy? 23. What is an important inorganic nutrient found in photosynthesis? 24. What is the difference between intraspecific competition and interspecific competition? 25. Why are estuaries important? 26. Define salinity. 27. What is a niche? 28. What was oxygen like early on? 29. Define competitive exclusion. 30. Know all of the ocean zones, where they are located, and how they are defined. 31. Where does all of our energy come from? 32. What is the proper order of a predator- prey relationship? Tampa Bay Unit 1. Define the following: watershed, food chain, estuary, food web, brackish, and nursery. 2. What counties make up the Tampa Bay watershed area? 3. What are the four major rivers that make up the Tampa Bay watershed? 4. Why is Tampa Bay considered to be an estuary and why is it so important to the ecosystem? 5. Where are contaminated soils most abundant in Tampa Bay? Why do you think so? 6. Are there any endangered or threatened species in Tampa Bay? Why so and list at least five? 7. What has happened to the bay since 1950 til present day? Lead me through the decades. 8. How many creeks drain into the bay? Major rivers? 9. How many people move to the Tampa Bay area weekly? 10 How many species of fish are found in the bay? List three. 11. What is the relationship between Tampa Bay and its watershed? 12. Why is mixing of freshwater and salt water in the bay important? 13. Why is the word nursery used to describe the bay? 14.Be able to label the map of the bay. 15. What is phytoplankton and why is it important? 16. How much money does the Port of Tampa contribute to the economy each year? 17. Who were the first people to inhabit the Tampa Bay area? 18. What are seagrasses? 19. Create a food web using worms, bull shark, manatee, pelican, seagrass, phytoplankton, red drum, shrimp, sand, and a blue crab. 20. What does turbidity mean? 21. Why did fishing in Tampa Bay become less productive after 1950? 22. Explain why the following affect the bay: storm water run-off, power plants, vehicle emissions, bioaccumulation, increased population growth, and industry. 23. Where is the most abundant bird sanctuary located in all of Florida? 24. What is a sanctuary and why is it important that we have places like these? 25. How many pairs of birds come to the local sanctuary every spring? 26. List at least five bird species that live at the sanctuary? 27. What is land acquisition and why is it so important? 28. What is a Florida friendly yard and how does it affect the bay if you don’t have one? 29. What type of hands on activities can students like you get involved in? 30. Define restoration. 31. How do oyster habitats stabilize the shoreline? 32. What are prop scars and what can they do to the seagrass beds? 33. What are the three types of mangroves found in Tampa Bay? Why are they important? Describe each one. 34. Define epiphytes. 35. What are the three types of sea grasses? Why are they important? 36. Define hydrophytes. 37. What is Spartina alterniflora? Why is it important? 38. What are rhizomes and why are they important? 39. What is the function of specialized lacunae? Geology of the Ocean Floor and Hydrothermal Vent / Deep Sea Communities 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Be able to label the map of the major lithospheric plates. List the plates. What makes rift communities unique? Explain how the ocean formed. Explain what the first cells had to be like. What is the oldest marine fossil, how old, and where was it found? What is another name for our oceans? How many are there? List them from largest to smallest. 7. What is the difference between a sea and a gulf? Provide two examples for each 8. What is the difference between lithosphere and asthenosphere? 9. Describe the three differences between the oceanic crust and the continental crust. 10. What was the source of the water that gave rise to the oceans? 11. Why was Earth’s early atmosphere devoid of oxygen? 12. Describe the processes that account for the drifting of continents away from one another or toward one another. 13. Describe nine lines of evidence that support the theory of seafloor spreading and continental drift. 14. Describe in detail the theory of seafloor spreading. 15. Describe the three types of plate boundaries, draw a picture of each one, and provide one location for each. 16. Describe the formation of the Ocean. 17. Who is the man of Pangaea? What were the two land masses called before they separated into continents? 18. What are convection currents? Who names them? 19. Explain what the Mid Oceanic Ridge is and why it’s important. 20. Describe rift valleys, fracture zones, rift zones, seamounts, hydrothermal vents, turbidity currents, submarine canyons, abyssal hills and plains. 21. What is the deepest trench? 22. What two opposing roles do turbidity currents play in shaping the continental shelf? 23. Why are continents much older than oceanic crust? Explain in terms of continental drift. 24. What are the five types of sediment and describe each one. 25. Explain continental margins, continental shelf, rise, and slope. 26. Define chemosynthesis. 27. Where does the deep sea begin? 28. Describe the oceans conveyor belt in detail. Include upwelling and why gyres are involved. 29. How long do vent communities live? 30. What main chemical compound do the vents rely on? 31. How hot are these vents? 32. Who discovered these vents? 33. Where are these vents located? 34. How does a vent form? 35. What single celled organism is the basis of the food web? 36. What is the function of the red plumes on the tubeworms? 37. Why are vents important? 38. List six deep sea adaptations. 39. Why are most organisms in the deep sea small? 40. List six deep sea animals. 41. Where can we find deep sea isopods? 42. What colors of the spectrum are absorbed first? What colors penetrate the deepest? 43. What is the chemical equation for bioluminescence? 44. What is a photophore? 45. How do they get the bacteria inside them? 46. How is bioluminescence controlled? 47. Define bioluminescence? 48. What are the functions of bioluminescence? Explain three of them. Salinity, Currents, and Tides 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. Why is water able to mix with other substances such as salt or sugar? List the properties of water that make it unique. What types of bonds hold water together? Why is this a weak bond? What colors of the spectrum get absorbed first and which ones the deepest? Give examples of polar and non-polar substances. Why is pH important to ocean organisms? What is the pH of the ocean? 8. How do we express salinity as a measurement? 9. What is the average salinity of the ocean? 10. How is the salinity at the poles different from the salinity at the equator? 11. What main gases are regulated in the ocean? 12. Where is the oxygen minimum zone found? 13. What role do bicarbonate ions play in the ocean? 14. What two main factors control the density of the water? 15. What is a zone of rapid temperature change called? 16. Explain the Coriolis Effect in great detail. 17. What force is mainly responsible for creating waves? 18. What are Tsunamis? 19. Describe the three types of tides. 20. Explain the difference between spring and neap tides. How do they correlate with the phases of the moon? 21. List five ways in which tides affect the ocean. 22. How much later do tides occur each day? 23. What is the difference between osmoconformers and osmoregulators? 24. What are the three main gases in the ocean? 25. What holds more gas cold or warm water? 26. The amount of gas depends on what three factors? 27. What percentage of sunlight is actually absorbed by the Earth? 28. Why are surface currents important? 29. What produces gyres? How many are there? List them. 30. Which current is the strongest? How fast does it move? 31. What two currents directly affect Florida? 32. What are the main driving forces of surface currents? 33. What four things control surface currents? 34. What organism relies on the Gulf Stream for survival? 35. A current can move fast or slow explain its oxygen and nutrient content. 36. What is another name for the Global Conveyor Belt? 37. What is the difference between upwelling and downwelling? 38. Why is upwelling important? 39. How much of the commercial fishery relies on upwelling areas? 40. Why is downwelling critical to deep sea creatures? 41. Where in the world has the most drastic tide? 42. Why do tides occur? 43. How often does the moon orbit the Earth? 44. When the moons gravity pulls the ocean towards the moon it causes a what? What happens on the other side of the earth? Plankton, Sea Grasses, and Mangroves: 1. Define photosynthesis. 2. Why is Cyanobacteria so unique? 3. Know the difference between all of the different types of plankton. 4. Why is plankton important? 5. What is the difference between diatoms and dinoflagellates? Be specific! 6. Define chemosynthesis. 7. Why are chemosynthetic bacteria unique? 8. What is the difference between aerobic and anaerobic organisms? 9. What is a stromatolite? 10. What group are zoozanthellae members of? 11. What causes HAB’s? 12. Diatoms belong to which Domain? 13. What is the frustule of diatoms made up of? 14. How are diatoms used commercially? 15. What is symbiosis? 16. Why are flowering plants salt tolerant? 17. Define hydrophyte and give an example. 18. What are rhizomes? 19. How do seagrasses add nutrients to the marine food web? 20. What is the purpose of specialized lacunae? 21. How are saltmarsh plants different from seagrasses? 22. Why are sea grasses, saltmarsh plants, and mangrove important? 23. What is the function of salt glands in cordgrass? 24. Mangroves have specialized roots that do what? 25. What is the function of pneumatophores? 26. How do marine plants help control algal blooms? 27. What are the three types of sea grasses? Scientific names? 28. What are epiphytes? Marine Invertebrates (Seniors do not complete) 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. What phylum do sponges belong to? Are sponges sessile or motile and what does that mean? What type of symmetry do sponges have? What is the function of the osculum? What is the function of the ostia? What is the function of the choanocyte? What is the function of the archaeocytes or amebocytes? How do sponges feed? What is the function of the spicules? 10. What are the skeletons of sponges made up of? 11. How do sponges reproduce mostly? 12. What do sponges compete with other organisms for? 13. How do sponges avoid predators? 14. Describe the class Demospongia. 15. What phylum do jellies and any organism with stinging cells belong to? 16. What are Cnidarians called that only exhibit the polyp stage in their life cycle? 17. What type of symmetry do Cnidarians have? 18. Where are nematocysts produced? 19. What is special about hydrozoans? 20. Jellyfish and box jellies belong to which class? 21. The Portuguese Man-o-war belongs to which class? 22. Give an example of an Anthozoan. 23. What is special about Cassiopeia? 24. What is the gut of Cnidarians called? 25. Clownfish forms a symbiotic relationship with which Anthozoan? 26. What animal has eight rows of comb plates? 27. What phylum do comb jellies belong? 28. What do comb jellies eat? 29. Most species of comb jellies are which: sexual, asexual, or hermaphroditic? 30. List the characteristics of molluscs. 31. Give examples of organisms that belong to phylum Mollusca. 32. Give an example of each: gastropod, cephalopod, and a bivalve. 33. What is contained in the visceral mass? 34. What structure secretes the shell of a mollusc? 35. What is the function of the radula? 36. Explain the three layers of a mollusc shell. 37. What is unique about Scaphopods? 38. What animals are covered by eight dorsal plates? 39. What class do nudibranchs belong to? 40. What organelle do nudibranchs have that allow them for adequate gas exchange? 41. What protects the shells insides? Hint – it’s hard! 42. Molluscs that have two jointed valves and shells belong to which class? 43. How do bivalves feed? 44. What muscle closes the valves of the clam? 45. What is the siphuncle (siphon) of nautiloids used for? 46. What is the function of a chromatophore? 47. List all of the things that have attributed to the success of Arthropods? 48. What is the exoskeleton of an arthropod made up of? 49. What is the function of the chelicerae? 50. What is the purpose of the molting process? 51. What animals belong to the order Decapoda? 52. What is an important food source for baleen whales? 53. What organisms dominate the zooplankton community of temperate waters? 54. Are barnacles sessile or motile? 55. Spiny skinned organisms belong to which phylum? 56. What type of symmetry do Echinoderms have? 57. What is the function of the pedicellarie? 58. What is the function of the madreporite? 59. What class do brittle stars belong to? 60. What sea star has greatly affected the coral reef ecosystem? 61. What is Aristotle’s lantern? 62. What class does a sea cucumber belong to? 63. What is the process in which sea cucumbers protect themselves from predators by releasing their internal organs?