H3A-HighSchool-5-18-15 - Workshops+SJCOE Workshop
advertisement
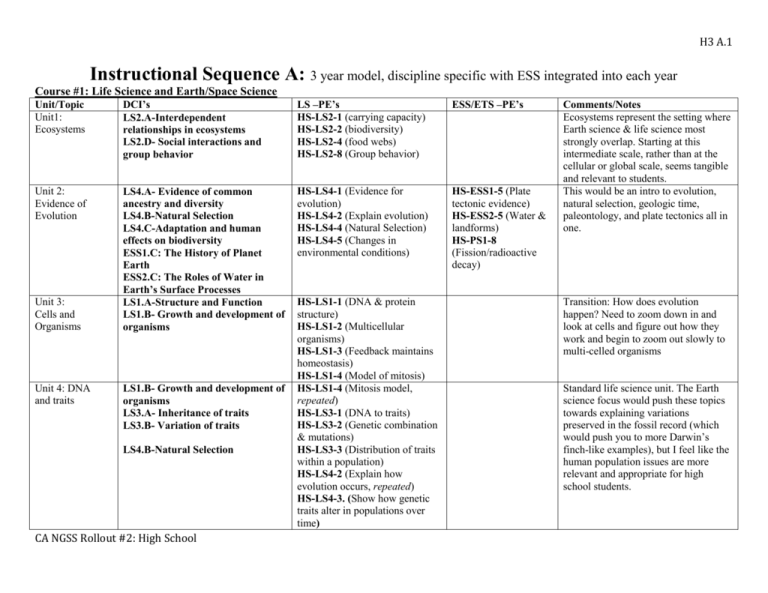
H3 A.1 Instructional Sequence A: 3 year model, discipline specific with ESS integrated into each year Course #1: Life Science and Earth/Space Science Unit/Topic Unit1: Ecosystems DCI’s LS2.A-Interdependent relationships in ecosystems LS2.D- Social interactions and group behavior LS –PE’s HS-LS2-1 (carrying capacity) HS-LS2-2 (biodiversity) HS-LS2-4 (food webs) HS-LS2-8 (Group behavior) ESS/ETS –PE’s Unit 2: Evidence of Evolution LS4.A- Evidence of common ancestry and diversity LS4.B-Natural Selection LS4.C-Adaptation and human effects on biodiversity ESS1.C: The History of Planet Earth ESS2.C: The Roles of Water in Earth’s Surface Processes LS1.A-Structure and Function LS1.B- Growth and development of organisms HS-LS4-1 (Evidence for evolution) HS-LS4-2 (Explain evolution) HS-LS4-4 (Natural Selection) HS-LS4-5 (Changes in environmental conditions) HS-ESS1-5 (Plate tectonic evidence) HS-ESS2-5 (Water & landforms) HS-PS1-8 (Fission/radioactive decay) Unit 3: Cells and Organisms Unit 4: DNA and traits LS1.B- Growth and development of organisms LS3.A- Inheritance of traits LS3.B- Variation of traits LS4.B-Natural Selection CA NGSS Rollout #2: High School HS-LS1-1 (DNA & protein structure) HS-LS1-2 (Multicellular organisms) HS-LS1-3 (Feedback maintains homeostasis) HS-LS1-4 (Model of mitosis) HS-LS1-4 (Mitosis model, repeated) HS-LS3-1 (DNA to traits) HS-LS3-2 (Genetic combination & mutations) HS-LS3-3 (Distribution of traits within a population) HS-LS4-2 (Explain how evolution occurs, repeated) HS-LS4-3. (Show how genetic traits alter in populations over time) Comments/Notes Ecosystems represent the setting where Earth science & life science most strongly overlap. Starting at this intermediate scale, rather than at the cellular or global scale, seems tangible and relevant to students. This would be an intro to evolution, natural selection, geologic time, paleontology, and plate tectonics all in one. Transition: How does evolution happen? Need to zoom down in and look at cells and figure out how they work and begin to zoom out slowly to multi-celled organisms Standard life science unit. The Earth science focus would push these topics towards explaining variations preserved in the fossil record (which would push you to more Darwin’s finch-like examples), but I feel like the human population issues are more relevant and appropriate for high school students. H3 A.2 Unit/Topic Unit 5: History of Earth’s Atmosphere: Photosynthesis & Respiration DCI’s LS1.C- Organization for matter and energy flow in organisms LS2.B- Cycles of matter and energy transfer in ecosystems ESS1.C: The History of Planet Earth ESS2.D: Weather and Climate ESS2.E: Biogeology Unit 6: Ecosystem Stability & the Response to climate change LS2.C- Ecosystem dynamics, functioning, and resilience LS4.C-Adaptation and human effects on biodiversity ESS3.D: Global Climate Change CA NGSS Rollout #2: High School LS –PE’s ESS/ETS –PE’s HS-LS1-5 (Photosynthesis) HS-ESS1-6 (Earth’s HS-LS1-6 (Sugars to amino early history) acids) HS-ESS2-6 (Carbon HS-LS1-7 (Respiration) cycle) HS-LS2-3 (Aerobic & Anaerobic HS-ESS2-7 (Corespiration) evolution of life & HS-LS2-5 (Photosynthesis, atmosphere) respiration, & carbon cycle) HS-LS2-6 (Ecosystems stability) HS-LS2-6 (Ecosystems stability, HS-ESS3-5 (Climate repeated) forecasts) HS-LS2-7 (Human impacts on HS-ESS3-6 biodiversity) (Simulations of HS-LS4-5 (Extinctions & human-natural Growth from changes in interactions) environment) HS-ETS1-4 HS-LS4-6 (Mitigating human (Simulation of impacts on biodiversity) proposed solutions) Comments/Notes This is a very strong Earth/Life science connection with a lot of overlap of the standards. This is a good way to put life science standards in the context of an Earth science problem. Saved until last because it includes the most sophisticated applications and serves as a bridge to the physical science courses. H3 A.3 Course #2: Chemistry and Earth/Space Science Unit DCI Chem PEs ESS/ETS PE’s Crosscutting concepts Summary Unit 1 Structures and Properties of Matter PS1.A – structures & properties of matter HS-PS1-1 HS-PS1-2 HS-PS1-3 HS-PS1-4 Patterns Cause and effect Energy and matter Structure and function The properties of matter are a function of atomic and molecular structure. Atomic and molecular structure can be inferred from the properties of bulk matter. Unit 2 Chemical Reactions PS1.B Chemical Reactions HS-PS1-5 HS-PS1-6 HS-PS1-7 Chemical processes can be predicted and explained knowing the properties of the reactants, conditions, and the Law of the conservation of mass Unit 3 Conservation of Energy and Energy Transfer PS3.B Conservation of Energy & Energy Transfer PS3.D Energy & Chemical Processes in Everyday Life ESS1.C, History of Planet Earth ESS2.A Earth Materials & Systems ESS2.A Earth Materials & Systems ESS2.C Roles of Water in Earth’s Surface Processes ESS2.D Weather & Climate ESS3.A Natural Resources ESS3.D Global Climate Change ETS1.B HS-PS3-1 HS-PS3-4 HS-PS3-3 HS-ESS1-5 HS-ESS2-3 Patterns Energy and matter Stability and change Cause and effect Energy and matter Scale, proportion, and quantity Unit 4 Chemistry of Climate Change CA NGSS Rollout #2: High School HS-ESS2-1 HS-ESS2-2 HS-ESS2-4 HS-ESS2-5 HS-ESS2-6 HS-ESS3-1 HS-ESS3-2 HS-ESS3-4 HS-ESS3-6 HS-ETS1-3 HS-ETS1-4 Energy cannot be created nor destroyed, but may change form. The entropy of an isolated system increases over time. Students apply their models of chemical reactions and energy flows in systems to the problem of climate change. H3 A.4 Course #3: Physics and Earth/Space Science Unit DCI PE ESS/ETS PE’s Crosscutting concepts Summary Unit 1 Forces and Motion PS2.A Forces & Motion HS-PS2-1 HS-PS2-2 HS-PS2-3 Cause and effect Systems, and system models Force is equal to the product of mass and acceleration. In a closed system, the total momentum is constant. Unit 2 Types of Interactions PS2.B Types of Interactions HS-PS2-4 HS-PS2-5 HS-PS2-6 Unit 3 Energy PS1.C Nuclear Processes PS3.A Definitions of Energy PS3.B Conservation of Energy & Entry Transfer PS3.C Relationship between Energy & Forces ESS1.C History of Planet Earth ESS2.A Earth Materials and Systems PS4.AWave Properties PS4.B Electromagnetic Radiation PS4.CInformation Technologies & Instrumentation PS3.DEnergy & Chemical Processes in Everyday Life HS-PS1-8 HS-PS3-2 HS-PS3-5 HS-PS3-3 HS-ETS1-2 HS-ESS1-5 HS-ESS2-3 Cause and effect Structure and function Energy and matter: Flows, cycles, and conservatio n The inverse-square law applies to gravity and electromagnetic interactions. Flowing electrons produce a magnetic field, and spinning magnets cause electric currents to flow. Energy is the capacity for doing work and may exist in potential, kinetic, thermal, electrical, chemical, nuclear, or other various forms. ESS1.C, ESS2.A Energy & matter Cause & effect Systems & system models Stability and change Electromagnetic radiation has many applications, and can be modeled as a wave of changing electric and magnetic fields or as particles called photons. Unit 4 Waves and Electromagnetic Radiation CA NGSS Rollout #2: High School HS-PS4-1 HS-PS4-3 HS-PS4-4 HS-PS4-5 HS-PS4-2