Unit 3: Expressions
advertisement
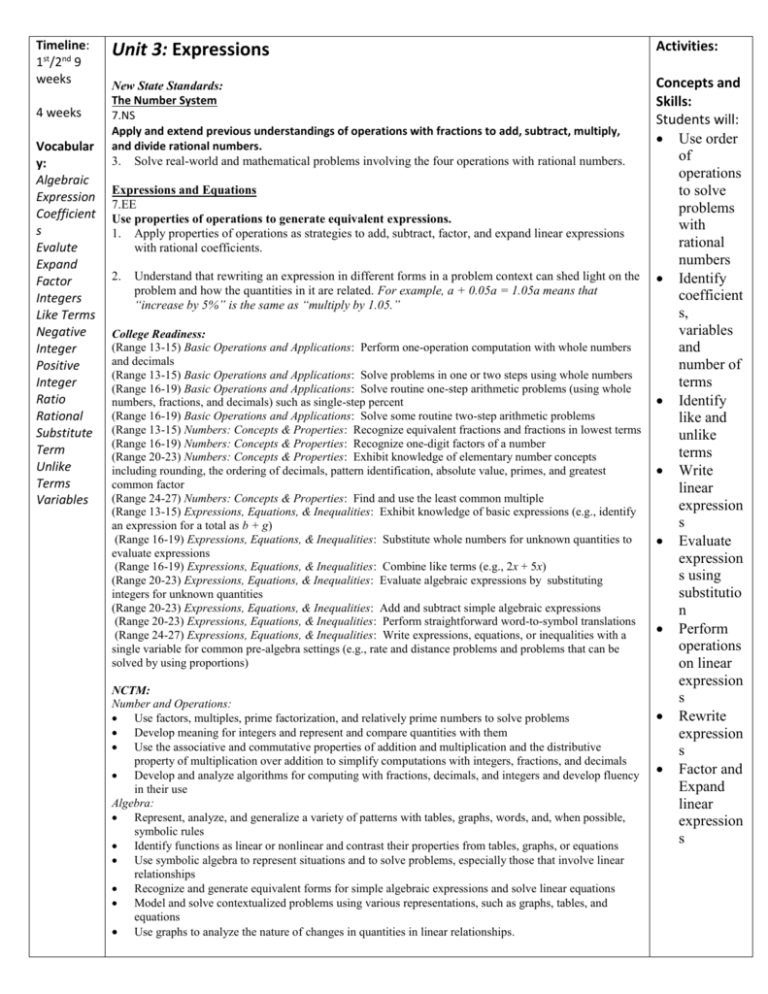
Timeline: 1st/2nd 9 weeks 4 weeks Vocabular y: Algebraic Expression Coefficient s Evalute Expand Factor Integers Like Terms Negative Integer Positive Integer Ratio Rational Substitute Term Unlike Terms Variables Unit 3: Expressions Activities: New State Standards: The Number System 7.NS Apply and extend previous understandings of operations with fractions to add, subtract, multiply, and divide rational numbers. 3. Solve real-world and mathematical problems involving the four operations with rational numbers. Concepts and Skills: Students will: Use order of operations to solve problems with rational numbers Identify coefficient s, variables and number of terms Identify like and unlike terms Write linear expression s Evaluate expression s using substitutio n Perform operations on linear expression s Rewrite expression s Factor and Expand linear expression s Expressions and Equations 7.EE Use properties of operations to generate equivalent expressions. 1. Apply properties of operations as strategies to add, subtract, factor, and expand linear expressions with rational coefficients. 2. Understand that rewriting an expression in different forms in a problem context can shed light on the problem and how the quantities in it are related. For example, a + 0.05a = 1.05a means that “increase by 5%” is the same as “multiply by 1.05.” College Readiness: (Range 13-15) Basic Operations and Applications: Perform one-operation computation with whole numbers and decimals (Range 13-15) Basic Operations and Applications: Solve problems in one or two steps using whole numbers (Range 16-19) Basic Operations and Applications: Solve routine one-step arithmetic problems (using whole numbers, fractions, and decimals) such as single-step percent (Range 16-19) Basic Operations and Applications: Solve some routine two-step arithmetic problems (Range 13-15) Numbers: Concepts & Properties: Recognize equivalent fractions and fractions in lowest terms (Range 16-19) Numbers: Concepts & Properties: Recognize one-digit factors of a number (Range 20-23) Numbers: Concepts & Properties: Exhibit knowledge of elementary number concepts including rounding, the ordering of decimals, pattern identification, absolute value, primes, and greatest common factor (Range 24-27) Numbers: Concepts & Properties: Find and use the least common multiple (Range 13-15) Expressions, Equations, & Inequalities: Exhibit knowledge of basic expressions (e.g., identify an expression for a total as b + g) (Range 16-19) Expressions, Equations, & Inequalities: Substitute whole numbers for unknown quantities to evaluate expressions (Range 16-19) Expressions, Equations, & Inequalities: Combine like terms (e.g., 2x + 5x) (Range 20-23) Expressions, Equations, & Inequalities: Evaluate algebraic expressions by substituting integers for unknown quantities (Range 20-23) Expressions, Equations, & Inequalities: Add and subtract simple algebraic expressions (Range 20-23) Expressions, Equations, & Inequalities: Perform straightforward word-to-symbol translations (Range 24-27) Expressions, Equations, & Inequalities: Write expressions, equations, or inequalities with a single variable for common pre-algebra settings (e.g., rate and distance problems and problems that can be solved by using proportions) NCTM: Number and Operations: Use factors, multiples, prime factorization, and relatively prime numbers to solve problems Develop meaning for integers and represent and compare quantities with them Use the associative and commutative properties of addition and multiplication and the distributive property of multiplication over addition to simplify computations with integers, fractions, and decimals Develop and analyze algorithms for computing with fractions, decimals, and integers and develop fluency in their use Algebra: Represent, analyze, and generalize a variety of patterns with tables, graphs, words, and, when possible, symbolic rules Identify functions as linear or nonlinear and contrast their properties from tables, graphs, or equations Use symbolic algebra to represent situations and to solve problems, especially those that involve linear relationships Recognize and generate equivalent forms for simple algebraic expressions and solve linear equations Model and solve contextualized problems using various representations, such as graphs, tables, and equations Use graphs to analyze the nature of changes in quantities in linear relationships.