Case Study #5 Exam – Hemophilia
advertisement

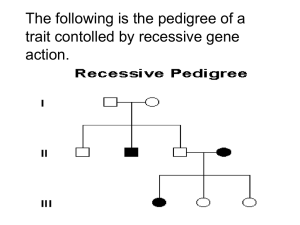
Case Study #5 Exam – Hemophilia 1. Hemostasis is best defined as: a. Coagulation b. The intrinsic clotting pathway c. Platelet plug d. Sequence of responses that stops bleeding e. Vascular spasm 2. Which of the following make up the three components of hemostasis? a. Adhesion, vasodilation, fibrin clot b. Adhesion, intrinsic clotting pathway, fibrin clot c. Platelet plug, clotting pathways, fibrin clot d. Vasodilation, platelet plug, coagulation e. Vascular spasm, platelet plug, coagulation 3. Which statement best explains the steps of forming a platelet plug? a. Adhesion, coagulation, fibrin clot b. Adhesion, platelet release reaction, platelet aggregation c. Platelet aggregation, coagulation, fibrin clot d. Vascular spasm, platelet plug, coagulation e. Vascular spasm, platelet release reaction, fibrin clot 4. The intrinsic pathway is activated by: a. Aggregation of platelets b. Calcium c. Damage within the vessel d. Platelet phospholipids e. Tissue damage 5. The extrinsic pathway is activated by: a. Aggregation of platelets b. Calcium c. Damage within the vessel d. Platelet phospholipids e. Tissue damage 6. Which clotting mechanism is affected in a patient with hemophilia? a. Common pathway b. Extrinsic pathway c. Intrinsic pathway d. Platelet plug e. Vasoconstriction 7. Which clotting factor is deficient in hemophilia? a. Factor II b. Factor V c. Factor VIII d. Factor X e. Factor XII 8. Which statement correctly defines a gene? a. Large molecule that carries genetic information b. Non-sex determining chromosome c. One of 23 paired structures that houses cellular DNA d. Subunit of DNA that codes for proteins e. Total genetic information in a cell or organism 9. Which statement correctly defines DNA? a. Large molecule that carries genetic information b. Non-sex determining chromosome c. Sex determining chromosome d. Subunit of genetic material consisting of a chemical base, a phosphate, and a sugar molecule e. Variant form of the same gene 10. Which statement correctly defines an autosome? a. Large molecule that carries genetic information b. Non-sex determining chromosome c. One of 23 paired structures that houses cellular DNA d. Subunit of DNA that codes for proteins e. Total genetic information in a cell or organism 11. All somatic cells of the human body contain how many pairs of chromosomes? a. 12 b. 22 c. 23 d. 24 e. 48 12. Which statement(s) are true of hereditary mutations? a. DNA changes exist in all of the body’s cells b. Genetic changes are acquired through life c. Mutation in the DNA are triggered by the environment d. Mutations are a result of errors that come from cell division e. All of the above 13. Which statement best defines a dominant allele? a. A gene that is expressed, regardless of the other allele in the pair b. An individual gen of a pair of genes that code for the same trait c. An allele that is not expressed unless the corresponding allele is not dominate d. A single strand of DNA e. On of a pair of homologous chromosomes 14. Which statement best defines a carrier? a. An individual that has a mutated recessive gene together with a normal allele b. An individual with two recessive genes that expresses the disease c. An individual with a dominant gene that expresses the disease d. A male who receive a mutated gene on the X chromosome e. A female who expresses a mutated gene passed on one X chromosome 15. Sally is a carrier of the hemophilia gene. Her husband is not affected. What percentage of their children will express the disease? a. 25% of males b. 50% of males c. 100% of males d. 50% of males and females e. None will be affected 16. If two parents with an autosomal recessive gene marry, statistically speaking, what percentage of their children express the disease? a. 25% b. 50% c. 75% d. 100% e. All males will express the disease 17. Tom has hemophilia. He marries Sally who is not affected. Genetic testing demonstrates she does not carry the gene. What percentage of their children will not be carriers or express the hemophilia gene? a. 50% of their daughters will not be affected b. 50% or their sons will not be affected c. 100% of their daughters will not be affected d. 100 % of their sons will not be affected e. None will carry the gene 18. Tom has hemophilia. He marries Sally who is not affected. Genetic testing demonstrates she does not carry the gene. What percentage of their children will express the disease? a. 25% b. 50% c. 75% d. 100% e. None will express the disease 23. Gene therapy refers to: a. Bacterial manufacture of Factor VIII b. Inactivation of viruses by biochemical methods c. Insertion of missing genes into patient cell by viral vectors d. Surgical replacement of missing chromosomes e. None of the above 19. A Protime (PT) measures: a. Amount of platelets b. Factor VIII levels c. Function of extrinsic pathway factors d. Function of intrinsic pathway factors e. Platelet function 24. A hematologist studies: a. Arthritic disease b. Disorders of the blood c. Endocrine disease d. Genetic family patterns e. Methods to purify replacement blood products 20. Factor assays detect: a. Platelet abnormalities b. Specific factor(s) that are deficient c. Defects in the extrinsic pathway d. Defects in the common pathway e. All of the above 21. Hemophilia can best be defined as a bleeding disorder caused by: a. A deficiency in the common pathway b. A deficiency of a necessary blood clotting factor c. A low number of platelets d. Abnormally functioning platelets e. All of the above 22. Hemophilia can lead to severe deformities caused from: a. Autoimmune proteins attacking the joints b. Bleeding into the joints c. Excessive falls from loss of blood d. Inheritance of a mutated autosomal dominant gene e. All of the above 25. Prevention methods for hemophilia include: a. Careful monitoring of infant sons at risk b. Gene therapy c. Genetic engineering d. Not passing the X-linked gene e. Recombinant Factor VIII