DEPARTMENT OF CHEMISTRY TEACHING LAB EXPERIMENT
advertisement

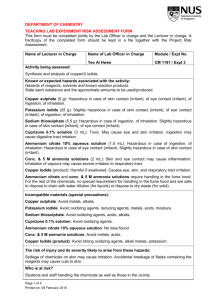
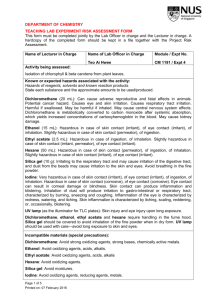
DEPARTMENT OF CHEMISTRY TEACHING LAB EXPERIMENT RISK ASSESSMENT FORM This form must be completed jointly by the Lab Officer in charge and the Lecturer in charge. A hardcopy of the completed form should be kept in a file together with the Project Risk Assessment. Name of Lecturer in Charge Name of Lab Officer in Charge Module / Expt No. Dr Hoang TG Activity being assessed: Mdm Irene Teo CM 1191/Expt 6 Separation of the components of an analgesic tablet Known or expected hazards associated with the activity: Hazards of reagents, solvents and known reaction products. State each substance and the approximate amounts to be used/produced. Aspirin: 500 mg Hazardous in case of skin or eye contact (irritant) Acetaminophen: 500 mg Slightly hazardous in case of skin and eye contact (irritant), of ingestion, of inhalation Caffeine 200 mg: Hazardous in case of skin or eye contact (irritant), of inhalation Starch 1g Slightly hazardous in case of skin contact (irritant), of eye contact (irritant), of ingestion, of inhalation. Methylene chloride: 20 mL Potential Acute Health Effects: Very hazardous in case of eye contact (irritant), of ingestion, of inhalation. Hazardous in case of skin contact (irritant, permeator). Inflammation of the eye is characterized by redness, watering, and itching. Potential Chronic Health Effects: CARCINOGENIC EFFECTS: Classified + (Proven.) by OSHA. Classified 2B (Possible for human.) by IARC. MUTAGENIC EFFECTS: Not available. TERATOGENIC EFFECTS: Not available. DEVELOPMENTAL TOXICITY: Not available. The substance is toxic to lungs, the nervous system, liver, mucous membranes, central nervous system (CNS). Repeated or prolonged exposure to the substance can produce target organs damage. Ethanol: 20 mL Eye: Causes severe eye irritation. May cause painful sensitization to light. May cause chemical conjunctivitis and corneal damage. Page 1 of 9 Printed on: 09 February 2016 Skin: Causes moderate skin irritation. May cause cyanosis of the extremities. Ingestion: May cause gastrointestinal irritation with nausea, vomiting and diarrhea. May cause systemic toxicity with acidosis. May cause central nervous system depression, characterized by excitement, followed by headache, dizziness, drowsiness, and nausea. Advanced stages may cause collapse, unconsciousness, coma and possible death due to respiratory failure. Inhalation: Inhalation of high concentrations may cause central nervous system effects characterized by nausea, headache, dizziness, unconsciousness and coma. Causes respiratory tract irritation. May cause narcotic effects in high concentration. Vapors may cause dizziness or suffocation. Hexane: 2 mL Hazardous in case of skin contact (permeator), of ingestion, of inhalation. Slightly hazardous in case of skin contact (irritant), of eye contact (irritant). Ethyl acetate: 4mL Hazardous in case of ingestion, of inhalation. Slightly hazardous in case of skin contact (irritant, permeator), of eye contact (irritant). Potential Chronic Health Effects: CARCINOGENIC EFFECTS: A4 (Not classifiable for human or animal.) by ACGIH. MUTAGENIC EFFECTS: Not available. TERATOGENIC EFFECTS: Not available. DEVELOPMENTAL TOXICITY: Not available. The substance is toxic to mucous membranes, upper respiratory tract. The substance may be toxic to blood, kidneys, liver, central nervous system (CNS). Repeated or prolonged exposure to the substance can produce target organs damage. Acetic acid: 0.5 mL Potential Acute Health Effects: Very hazardous in case of skin contact (irritant), of eye contact (irritant), of ingestion, of inhalation. Hazardous in case of skin contact (corrosive, permeator), of eye contact (corrosive). Liquid or spray mist may produce tissue damage particularly on mucous membranes of eyes, mouth and respiratory tract. Skin contact may produce burns. Inhalation of the spray mist may produce severe irritation of respiratory tract, characterized by coughing, choking, or shortness of breath. Inflammation of the eye is characterized by redness, watering, and itching. Skin inflammation is characterized by itching, scaling, reddening, or, occasionally, blistering. Page 2 of 9 Printed on: 09 February 2016 Potential Chronic Health Effects: Hazardous in case of skin contact (irritant), of ingestion, of inhalation. CARCINOGENIC EFFECTS: Not available. MUTAGENIC EFFECTS: Mutagenic for mammalian somatic cells. Mutagenic for bacteria and/or yeast. TERATOGENIC EFFECTS: Not available. DEVELOPMENTAL TOXICITY: Not available. The substance may be toxic to kidneys, mucous membranes, skin, teeth. Repeated or prolonged exposure to the substance can produce target organs damage. Repeated or prolonged contact with spray mist may produce chronic eye irritation and severe skin irritation. Repeated or prolonged exposure to spray mist may produce respiratory tract irritation leading to frequent attacks of bronchial infection. Sodium bicarbonate (5 g): Potential Acute Health Effects: Slightly hazardous in case of skin contact (irritant), of eye contact (irritant), of ingestion, of inhalation. Potential Chronic Health Effects: CARCINOGENIC EFFECTS: Not available. MUTAGENIC EFFECTS: Not available. TERATOGENIC EFFECTS: Not available. DEVELOPMENTAL TOXICITY: Not available. Repeated or prolonged exposure is not known to aggravate medical condition. Sodium sulphate: 1g Potential Acute Health Effects: Hazardous in case of eye contact (irritant). Slightly hazardous in case of skin contact (irritant), of ingestion, of inhalation. Potential Chronic Health Effects: CARCINOGENIC EFFECTS: Not available. MUTAGENIC EFFECTS: Not available. TERATOGENIC EFFECTS: Not available. DEVELOPMENTAL TOXICITY: Not available. Repeated or prolonged exposure is not known to aggravate medical condition. TLC plates NOTE: The hazard information listed is for the material bonded to the TLC plate. Inhalation: May cause dryness and irritation to mucous membranes, nose, and throat. Symptoms may include coughing, sore throat, dysphea, wheezing, and non-specific chest illnesses. Ingestion: No adverse effects expected. Skin Contact: May cause irritation with dryness and abrasion. Eye Contact: Causes irritation, redness, and pain. Chronic Exposure: Chronic inhalation of silica dust can produce silicosis, a disease of the lungs. Cardiopulmonary impairment may occur. Aggravation of Pre-existing Conditions: No information found. Page 3 of 9 Printed on: 09 February 2016 Iodine: Very hazardous in case of skin contact (irritant), of eye contact (irritant), of ingestion, of inhalation. Hazardous in case of skin contact (corrosive), of eye contact (corrosive). Eye contact can result in corneal damage or blindness. Skin contact can produce inflammation and blistering. Inhalation of dust will produce irritation to gastro-intestinal or respiratory tract, characterized by burning, sneezing and coughing. Inflammation of the eye is characterized by redness, watering, and itching. Skin inflammation is characterized by itching, scaling, reddening, or, occasionally, blistering. UV lamp (as the illuminator for TLC plates): Skin injury and eye injury upon prolonged exposure. Incompatible materials (special precautions): Dichloromethane: Avoid strong oxidizing agents, strong bases, chemically active metals. Ethanol: Avoid oxidizing agents, acids, alkalis. Ethyl acetate: Avoid oxidizing agents, acids, alkalis Hexane: Avoid oxidizing agents. Silica gel: Avoid moistures. Iodine: Avoid oxidizing agents, reducing agents, metals. Acetic acid: Avoid strong bases, chemically active metals The risk of injury and its severity likely to arise from these hazards: Accidental breakage of flasks may lead to cuts while spillage of the solvents/reagents may cause irritation to eyes, skin and respiratory tract. Who is at risk? Persons handling the chemicals as well as those in the vicinity. Measure to be taken to reduce the level of risk: Proper PPE must be worn. Refer to prepared risk assessment on Use of Glassware. Please refer to PSSO Safety Information Centre website on safety measures: http://www.chemistry.nus.edu.sg/PSSO/Safety.htm. Training prerequisites: Please refer to Completed Risk Assessment on http://www.chemistry.nus.edu.sg/PSSO/Safety/Risk/risk.htm#Common. Level of risk remaining: Low. Page 4 of 9 Printed on: 09 February 2016 Common Activities: Emergency action if : Spill: Methylene Chloride Small Spill: Dilute with water and mop up, or absorb with an inert dry material and place in an appropriate waste disposal container. Large Spill: Absorb with an inert material and put the spilled material in an appropriate waste disposal. Be careful that the product is not present at a concentration level above TLV. Check TLV on the MSDS and with local authorities. Spill: Ethanol Absorb spill with inert material (e.g. vermiculite, sand or earth), then place in suitable container. Remove all sources of ignition. Use a spark-proof tool. Provide ventilation. A vapor suppressing foam may be used to reduce vapors Spill: Hexane Small Spill: Absorb with an inert material and put the spilled material in an appropriate waste disposal. Large Spill: Flammable liquid, insoluble in water. Keep away from heat. Keep away from sources of ignition. Stop leak if without risk. Absorb with DRY earth, sand or other non-combustible material. Do not get water inside container. Do not touch spilled material. Prevent entry into sewers, basements or confined areas; dike if needed. Call for assistance on disposal. Be careful that the product is not present at a concentration level above TLV. Check TLV on the MSDS and with local authorities. Spill: Ethyl acetate Small Spill: Dilute with water and mop up, or absorb with an inert dry material and place in an appropriate waste disposal container. Large Spill: Flammable liquid. Keep away from heat. Keep away from sources of ignition. Stop leak if without risk. Absorb with DRY earth, sand or other non-combustible material. Do not touch spilled material. Prevent entry into sewers, basements or confined areas; dike if needed. Be careful that the product is not present at a concentration level above TLV. Check TLV on the MSDS and with local authorities. Spill: Acetic acid Page 5 of 9 Printed on: 09 February 2016 Small Spill: Dilute with water and mop up, or absorb with an inert dry material and place in an appropriate waste disposal container. If necessary: Neutralize the residue with a dilute solution of sodium carbonate. Large Spill: Flammable liquid. Corrosive liquid. Keep away from heat. Keep away from sources of ignition. Stop leak if without risk. If the product is in its solid form: Use a shovel to put the material into a convenient waste disposal container. If the product is in its liquid form: Absorb with DRY earth, sand or other non-combustible material. Do not get water inside container. Absorb with an inert material and put the spilled material in an appropriate waste disposal. Do not touch spilled material. Use water spray curtain to divert vapor drift. Prevent entry into sewers, basements or confined areas; dike if needed. Call for assistance on disposal. Neutralize the residue with a dilute solution of sodium carbonate. Be careful that the product is not present at a concentration level above TLV. Check TLV on the MSDS and with local authorities. Sodium bicarbonate: Small Spill: Use appropriate tools to put the spilled solid in a convenient waste disposal container. Finish cleaning by spreading water on the contaminated surface and dispose of according to local and regional authority requirements. Large Spill: Use a shovel to put the material into a convenient waste disposal container. Finish cleaning by spreading water on the contaminated surface and allow to evacuate through the sanitary system. Fire: Use ABC extinguishers available in the lab. Is the experiment suitable for out-of-hours operation? References if any: http://www.jtbaker.com/msds/englishhtml/b5380.htm http://www.sigmaaldrich.com/MSDS/MSDS/DisplayMSDSPage.do Page 6 of 9 Printed on: 09 February 2016 Yes No Signature of Lab Officer in charge:………………………..…………………….. Date:………………………… Signature of Lecturer in Charge:………… …………………………………….. Date:… ……………………... Prepared Risks Assessments for standard equipment and operation are with the kind permission of Dr. Ken MacNeil, School of Chemistry, University of Bristol. Page 7 of 9 Printed on: 09 February 2016 Activity being assessed: Note any activity to be used which entail risk (e.g. use of glass vacuum apparatus, high pressures, high voltage, radiation, high temperatures). Give reference to any special protocols to be followed, and if appropriate attach copies to the risk assessment form. State any additional precautions taken to minimise risk. Known or expected hazards associated with the activity: FOR EACH CHEMICAL, read the MSDS and note:a) Particular hazards (e.g. highly toxic, carcinogenic, corrosive, flammable, pyrophoric, explosive, volatile, dust hazard). Note any dangerous combinations of properties (e.g. volatile and toxic). b) Requirements for safe handling (e.g. fume cupboard, inert atmosphere, low temperature). c) How to dispose of residuals Dispose to drain, with water dilution Neutralise, then to drain with suitable dilution To flammable liquid waste receptacle To non-flammable liquid waste receptacle Keep for recovery/recycling Keep for special disposal later (e.g. heavy metals) Double bag and dispose to dry waste Special procedure (specify) Incompatible materials (special precautions) Note any dangerously incompatible materials and hazards arising from contact of any reagents and substances used with common materials such as paper, benches, hoses, etc. Measures to be taken to reduce the level of risk Include hazards of previously unknown products. Location of work – laboratory, open bench, fume cupboard Level of risk remaining: Likelihood and consequences of any accident or unforeseen events whilst carrying out the activity. When this has been done, choose the appropriate procedure:a) Close supervision and/or attendance of trained first-aider needed. b) Specific approval of supervisor needed. c) Training is needed prior-to or during the operations specified. d) Training is complete and only general laboratory competence required. e) No risk perceived. Emergency action: Page 8 of 9 Printed on: 09 February 2016 a) Any special requirements to deal with accidental spillage or leakage. b) What to do in the event of accidental exposure (skin contact, inhalation, etc.). Page 9 of 9 Printed on: 09 February 2016