UbD Template ChCh

UbD Template 2.0
Plan for Improving Student Learning Through Communities of Shared Teaching and Learning Practice
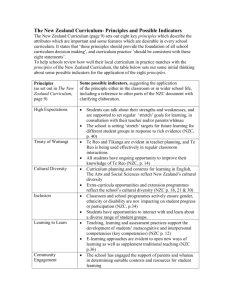
ESTABLISHED GOALS
o
○
,G
Stage 1 Desired Results
Transfer
Staff will be able to independently use their learning to…
○
,T
Identify and apply the essential elements of the NZC to create a relevant, authentic 21 st C curriculum relevant to their school community.
Meaning
ESSENTIAL QUESTIONS
UNDERSTANDINGS
○
,U
Staff will understand that…
o The NZC is a national framework for curriculum design that tailors learning to each learning community o Curriculum is developed from big ideas that connect and underpin essential learning areas o Big ideas in curriculum develop and deepen student understanding and their transfer of learning o Curriculum is defined by the identified “end in mind’ for learners o The ‘end in mind’ for learners is defined by the alignment of the vision of learning community with the NZC o Key competencies guide and frame expected learning behaviours and dispositions and therefore essential to a relevant year 7/8 curriculum o Effective planning includes Key Competencies and that require deliberate and conscious teaching o Effective curriculum is connected across learning areas and levels and helps students important ideas and transfer learning o An established curriculum review and development process gives everyone a voice and the opportunity to lead and model the creation of cutting edge, current curriculum o Curriculum that is inquiry/problem based leads to authentic relevant project based opportunities that excite and engage middle years learners o Tikanga and Te Reo Maori in a year 7/8 curriculum underpins and connects learning and learners
○
,Q
o What is effective 21 st C curriculum? o How are big ideas defined and identified? o Why include big ideas in curriculum design? o How does curriculum design impact the development of global citizens? o Why use big ideas to frame curriculum design? o How does the curriculum design process lead effective and purposeful change? o How do Key Competencies impact learning and learners in the middle years? o What makes teaching and learning engaging and effective for year 7 and 8? o How do we create and sustain effective curriculum design? o Why frame the middle years curriculum through inquiry, problem solving and project based learning? o What is literacy in a 21 st C curriculum? o How do the literacies and numeracy underpin an effective 21 st C curriculum?
Acquisition
Staff will know…
○
,K
o The NZ curriculum is the essential map that drives the development of school based curriculum o The NZC consists of key components that fall under three main sections: Directions for Learning, Guidance, The
School Curriculum o Each of the key components of the NZC provides essential information and guidance when designing school based curriculum o Big ideas are over arching ideas identified within and across curriculum areas o A responsive curriculum for middle years learners must recognize and provide opportunity for social awareness, complex authentic contexts o Authentic effective learning contexts must include positive relationships with adults and community involvement. o Effective curriculum design can only be sustained when a system of review and renewal is regularly built into the term school calendar o Curriculum mapping is a system wide process that involves all members of a learning community in regular review, revision and renewal o Effective engaging Year 7 and 8 curriculum is a result of backward design that clearly identifies the expected end in mind in the form of a transfer goal, understandings, essential questions, knowledge, skills and Authentic assessment o An inquiry/problem based curriculum includes clearly scaffolded stages of learning that starts in the known o There are specific strategies necessary to scaffold
Inquiry/problem based learning o Inquiry/problem based learning requires critical and creative thinking strategies
Staff will be skilled at…
○
,S
Align school vision with expectations for year 7
& 8 learners
Identify big ideas within curriculum areas
Compare and connect big ideas across curriculum areas
Examine the NZC for essential elements to inform school curriculum design
Analyse 21 st C skills, literacies and fluencies to inform relevant curriculum design
Evaluate current curriculum design against
NZC and 21 st C expectations
Adapt and renew curriculum based on the outcomes of the evaluation
Analyse various curriculum models and strategies and identify possible frameworks and processes
Examine strategies for creating a culture of inquiry in learning?
Create a viable process for curriculum design that includes the voices of all members of the learning community
Compare and contrast the strengths and barriers for effective curriculum in secondary schools
Apply new learning to collaboratively create an effective relevant curriculum for todays learners
Summarise outcomes and identify next steps in learning
Evaluative Criteria
o Design process embedded within the school systems and calendared accordingly o Curriculum design formats and frameworks selected and applied using backward design o Self directed, self managing learners identify next steps in learning o Students applying the learning dispositions and habits of mind required to be an independent contributor to the global community o Teachers know the individual learner and clearly identify their next steps in developing the knowledge, skills and dispositions required to achieve o
Stage 2 - Evidence
Assessment Evidence
PERFORMANCE TASK(S):
o A 21 c century year 7/8 curriculum design process in place. o Year 7 and 8 Curriculum mapped to identify big ideas and curriculum connections o Year 7/8 Students engaged in a range of relevant inquiry/problem based learning opportunities that challenge them to apply the skills and knowledge of a global citizen
○,TT
OTHER EVIDENCE:
o An articulated vision for a year 7 to 13 school o NZC in evidence in curriculum maps and unit plans. o Teams work collaboratively to develop big ideas that require critical and creative thinking to build deep knowledge and understanding o Environment that has rich authentic tasks and performance based assessment o Collaborative learning environment that includes the world beyond the classroom o Self directed inquiring learners collaborating with teacher and other members of the class o Teachers lead a personalized learning environment where knowledge skills and dispositions of individual learners are the focus
○
,OE
Stage 3 – Learning Plan
Summary of Key Learning Events and Instruction
o Establish the learning Roles for the day – Who Owns the Learning (Alan November) o Review requirements of NZC and how this reflects the requirements for effective 21 st C learning. Compare and contrast the two and form conclusions about the impact on school based curriculum design o Examine the school vision and identify the story behind this vision. What are the expectations for students leaving the schools? What does this mean for Year 7 and 8.
What are our indicators? How does this shape curriculum design?
o Review the concept of big ideas in curriculum design
Review examples
Brainstorm possible big ideas/concepts
Examine an essential learning area page for big ideas and review across strands
Select possible big ideas to frame the year 7/8 curriculum and begin an initial draft of a relevant map o Review essential elements of backwards design process
Goals
Transfer
Understandings
Essential Questions
Knowledge
Skills
Authentic assessment
Evidence of Learning o Problem Based Learning – A Task
Share a GRASPS task for each group to complete a draft of their curriculum design process, requirements for effective classroom implementation and indicators of successful implementation o Summarise next steps and plan of action